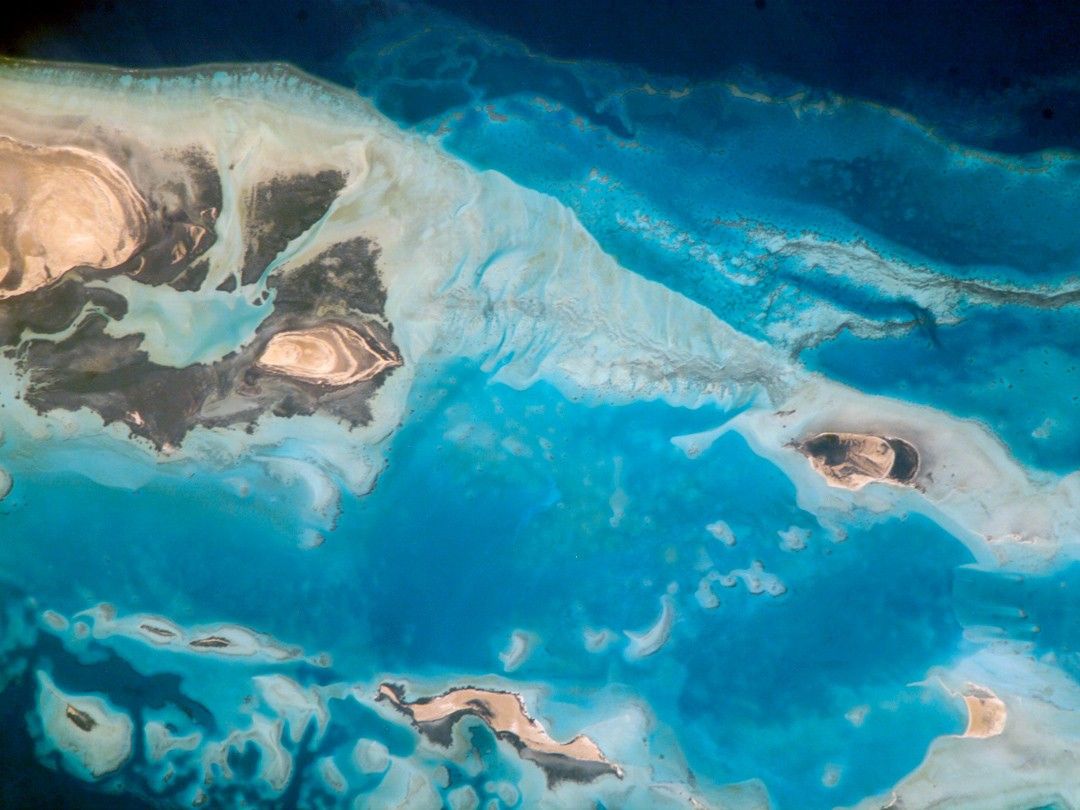
Saudi Arabia boasts the most coral reefs of any Middle Eastern country, as it includes coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf. This high-resolution astronaut photograph shows part of the Al Wadj Bank, located along the northern Red Sea coast. Despite the relatively high salinity of Red Sea water (compared to other oceans), approximately 260 species of coral have been documented in the region. Large tracts of the Saudi Arabian coastline are undeveloped, and reefs in these areas are in generally good ecological health. However, reefs located near large urban centers such as Jeddeh have suffered degradation due to land reclamation (dredging and filling), pollution, and increased sediment runoff from land.
The Al Wadj Bank (a bank is an underwater hill) includes a healthy and diverse reef system, extensive seagrass beds, and perhaps the largest population of dugong—a marine mammal similar to the North American manatee—in the eastern Red Sea. The portion of the Bank in this image illustrates the complex form and topography of the reef system. Several emergent islands (tan) are visible, surrounded primarily by dark green seagrass; the largest is at top left. Only the islands are above the waterline; over the reefs, the water color ranges from light teal (shallow) to turquoise (increasing depth). The southern edge of the reef is well defined by the deep, dark blue water of the Red Sea (top).
In recent years, countries that border the Red Sea have cooperated to form a regional conservation plan for reef ecosystems. The plan includes the designation of several Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), integrated coastal management plans, improved pollution controls, reef health monitoring, and public education efforts. The Al Wadj Bank is one of the areas designated as a MPA.
References & Resources
Astronaut photograph ISS016-E-19394 was acquired on December 30, 2007, with a Kodak 760C digital camera fitted with an 800 mm lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment. The image was taken by the Expedition 16 crew, and is provided by the Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center. The image in this article has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast. Lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by William L. Stefanov, NASA-JSC.