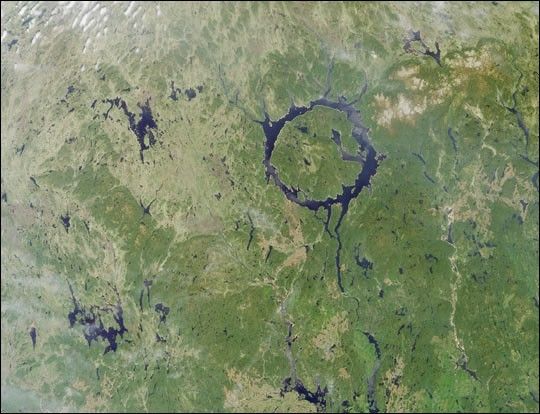
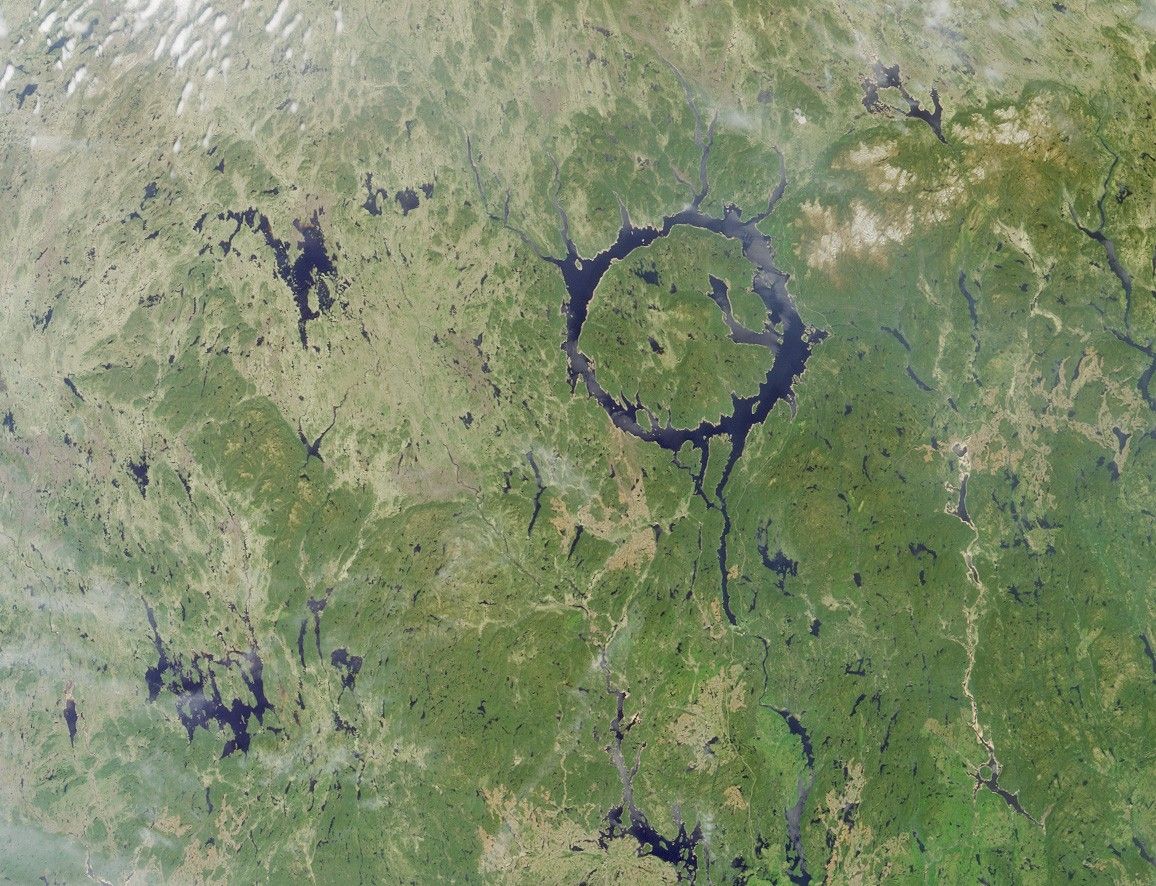
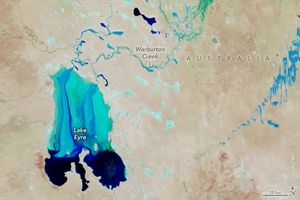
The large annular lake in this image represents the remnants of oneof the largest impact craters still preserved on the surface of theEarth. Lake Manicouagan in northern Quebec, Canada, surrounds thecentral uplift of the impact structure, which is about 70 kilometers indiameter and is composed of impact-brecciated (relatively large pieces of rock embeddedin finer grained material) rock. Glaciation and othererosional processes have reduced the extent of the crater, with theoriginal diameter estimated at about 100 kilometers (60 miles). This natural-colorimage of the region was acquired by the Multi-angle Imaging Spectroradiometer’s(MISR’s) nadir (vertical-viewing) camera on June 1, 2001.
The impact that formed Manicouagan is thought to have occurred about212 million years ago, toward the end of the Triassic period. Somescientists believe that this impact may have been responsible for a massextinction associated with the loss of roughly 60 percent of all species. Ithas been proposed that the impact was created by an asteroid with adiameter of about 5 kilometers. The lake is bounded by erosion-resistantmetamorphic and igneous rocks, and shock metamorphic effects areabundant in the target rocks of the crater floor. Today Lake Manicouaganserves as a reservoir and is one of Quebec’s most important regions forAtlantic salmon fishing.
References & Resources
NASA image courtesy NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL, MISR Team.