Names-to-Mars Chip for InSight Spacecraft
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/Lockheed Martin |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
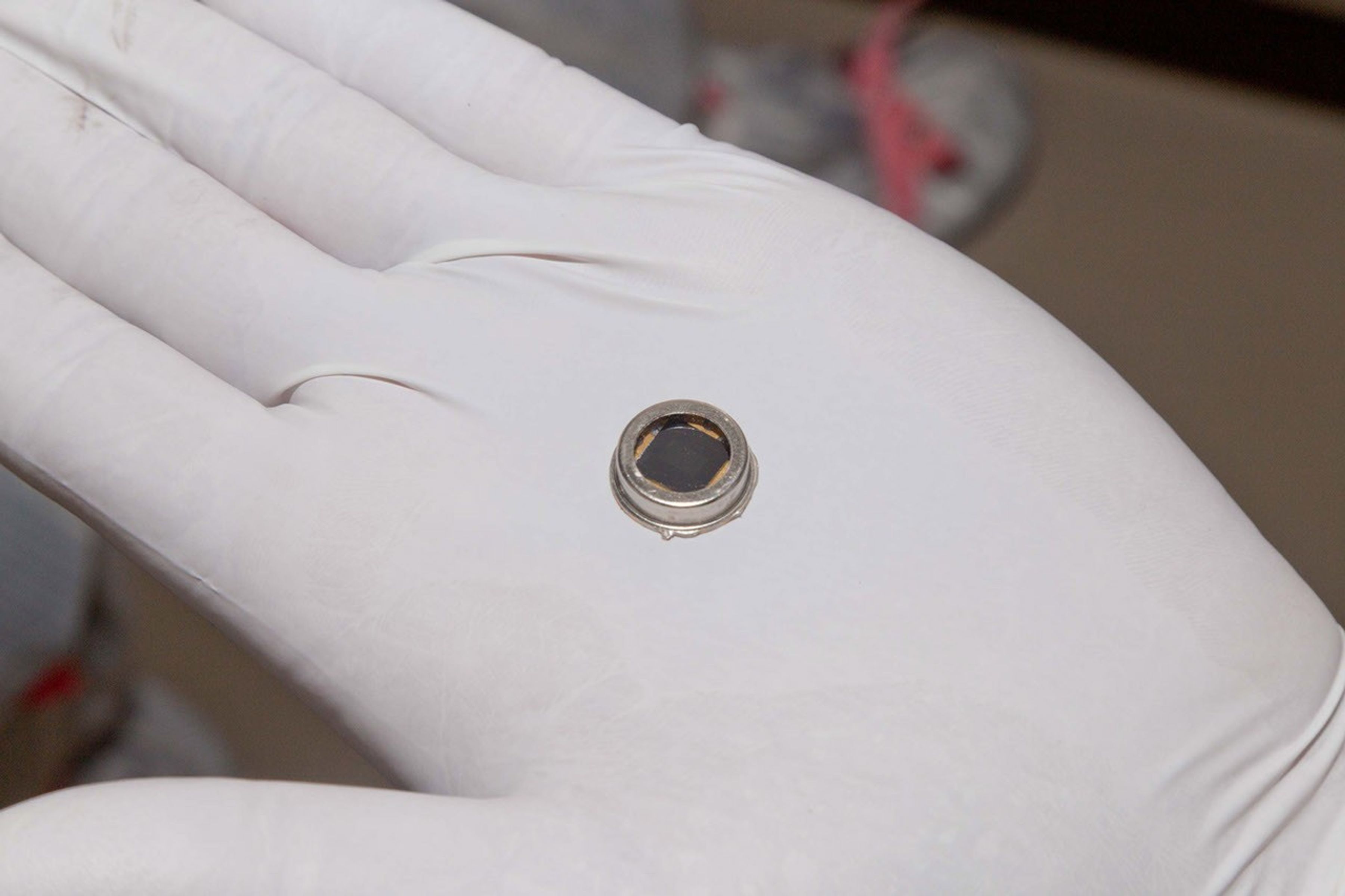
The dime-size microchip in this close-up image carries 826,923 names that will go to Mars on NASA's InSight lander. The image was taken in November 2015 inside a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, where the lander was built.
InSight, for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, will launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, in March 2016 and land on Mars on Sept. 28, 2016. This is the first Mars mission dedicated to study the deep interior of Mars. Its findings will advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth.
The chip is affixed to the InSight lander deck and will remain on Mars forever.
Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, etched the names onto a silicon wafer or microchip. They used an electron beam machine at JPL that specializes in etching very tiny features (less than 1 micron, or less than one one-thousandth the width of a human hair). They use this machine to make high-precision microdevices in JPL's Microdevices Laboratory.
This technique was also used to write millions of names that were transported on Mars rovers and Orion’s first test flight.
The InSight Project is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. InSight is part of NASA's Discovery Program, which is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.