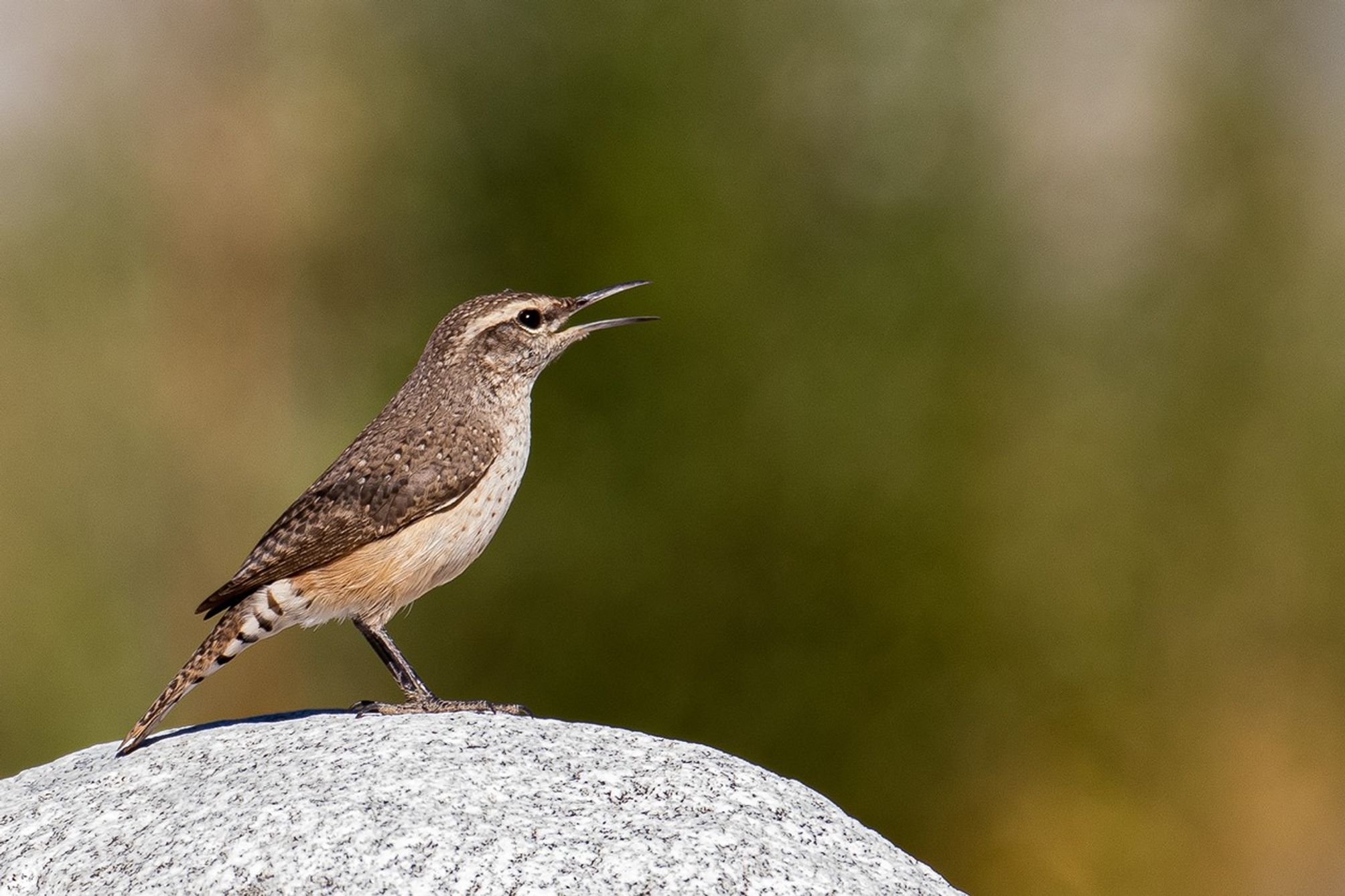
Through the eBird citizen scientist program, millions of birders have recorded their observations of different species and submitted checklists to the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Through a partnership with NASA, the lab has now used this data to model and map bird population trends for nearly 500 North American species.
Led by Alison Johnston of the University of St. Andrews in Scotland, the researchers reported that 75% of bird species in the study are declining at wide-range scales. And yet this study has some good news for birds. The results, published in Science in May, offer insights and projections that could shape the future conservation of the places where birds make their homes.
“This project demonstrates the power of merging in situ data with NASA remote sensing to model biological phenomena that were previously impossible to document,” said Keith Gaddis, NASA’s Biological Diversity and Ecological Forecasting program manager at the agency’s headquarters in Washington, who was not involved in the study. “This data provides not just insight into the Earth system but also provides actionable guidance to land managers to mitigate biodiversity loss.”
A team from Cornell, the University of St. Andrews, and the American Bird Conservancy used land imaging data from NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instruments to distinguish among such specific bird habitats as open forests, dense shrublands, herbaceous croplands, and forest/cropland mosaics. They also drew on NASA weather information and water data that matched the dates and times when birders made their reports.
When combined with a 14-year set of eBird checklists — 36 million sets of species observations and counts, keyed directly to habitats — the satellite data gave researchers almost a strong foundation to produce a clear picture of the health of bird populations. But there was one missing piece.
Wrestling with Wren Data
While some eBird checklists come from expert birders who’ve hiked deep into wildlife preserves, others are sent in by novices watching bird feeders and doing the dishes. This creates what Cornell statistician Daniel Fink described as “an unstructured, very noisy data set,” complete with gaps in the landscape that birders did not reach and, ultimately, some missing birds.
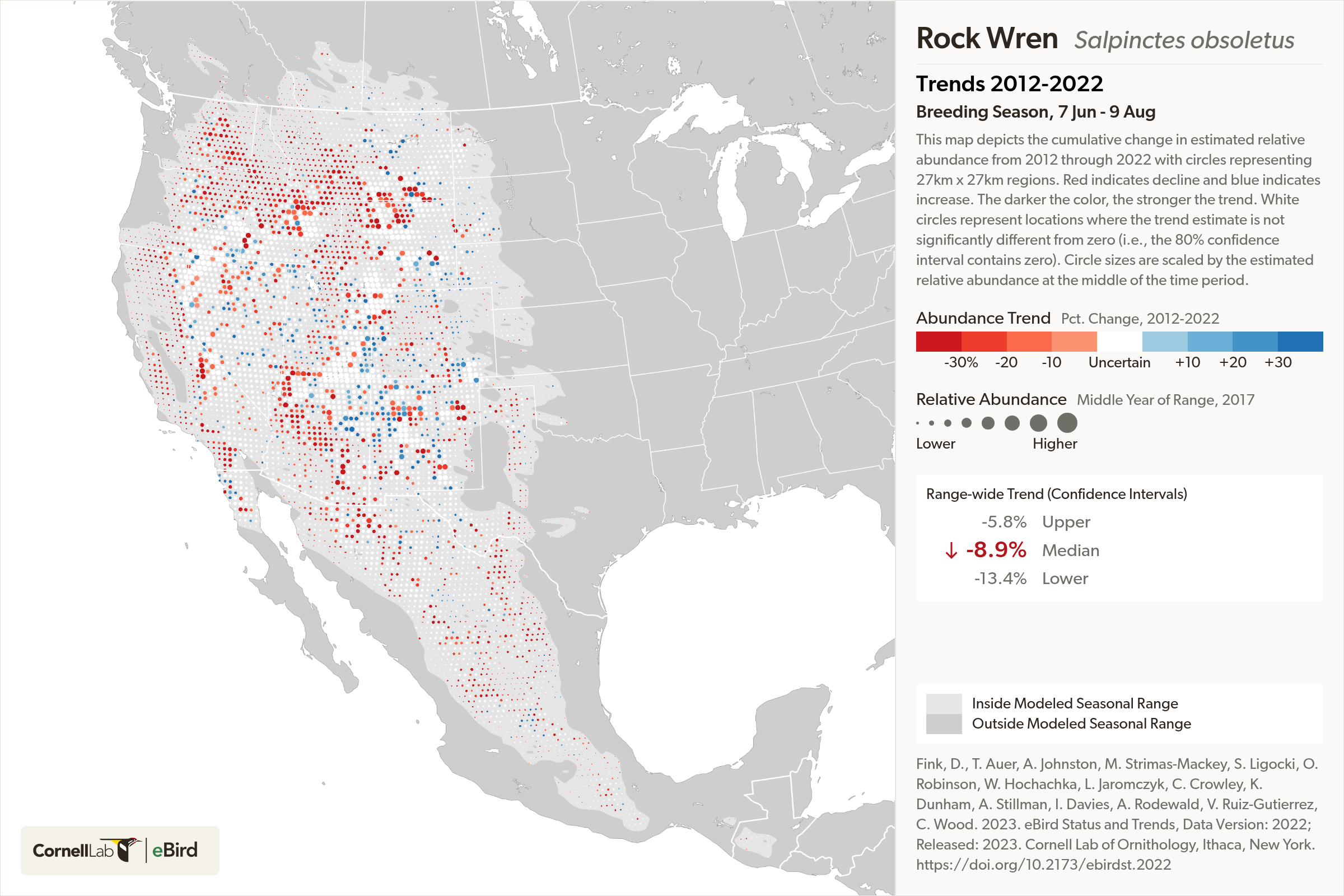
To account for gaps where birds weren’t counted, the researchers trained machine learning models to fill in the maps based on the remote sensing data. “For every single species — say the rock wren — we’ve created a simulation that mimics the species and a variety of ways that it could respond to changes in the environment,” Johnston said. “Thousands of simulations underlie the results we showed.”
The researchers achieved unprecedented resolution, zeroing in on areas 12 miles by 12 miles (27 km by 27 km), the same area as Portland, Oregon. This new population counting method can also be applied to eBird data from other locations, Fink said. “Now we’re using modeling to track bird populations — not seasonally through the year, but acrossthe years — a major milestone,” he added.
“We’ve been able to take citizen science data and, through machine learning methodology, put it on the same footing as traditionally structured surveys, in terms of the type of signal we can find,” said Cornell science product manager Tom Auer. “It will increase the credibility and confidence of people who use this information for precise conservation all over the globe.”
The Up Side
Since 1970, North America has lost one-quarter of its breeding birds, following a global trend of declines across species. The causes range from increased pollution and land development to changing climate and decreased food resources. Efforts to reverse this loss depend on identifying the areas where birds live at highest risk, assessing their populations, and pinpointing locations where conservation could help most.
For 83% of the reported species in the new study, the decline was greatest in spots where populations had previously been most abundant — indicating problems with the habitat.
“Even in species where populations are declining a lot, there are still places of hope, where the populations are going up,” Johnston said. The team found population increases in the maps of 97% of the reported species. “That demonstrates that there’s opportunity for those species.”
“Birds face so many challenges,” said Cornell conservationist Amanda Rodewald. “This research will help us make strategic decisions about making changes that are precise, effective, and less costly. This is transformative. Now we can really drill in and know where specifically we’re going to be able to have the most positive impact in trying to stem bird declines.”
NASA Headquarters, Washington