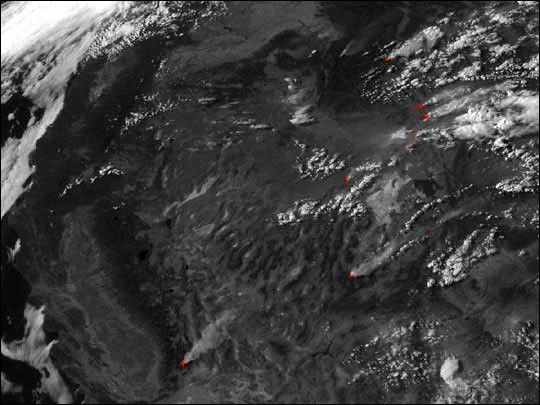
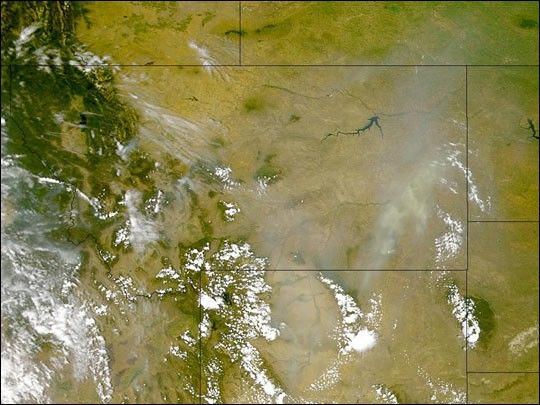
Continued hot, dry weather in the American west contributed tothe spread of numerous fires over the weekend of July 29–30,2000. This is the most active fire season in the UnitedStates since 1988, when large portions of YellowstoneNational Park burned.
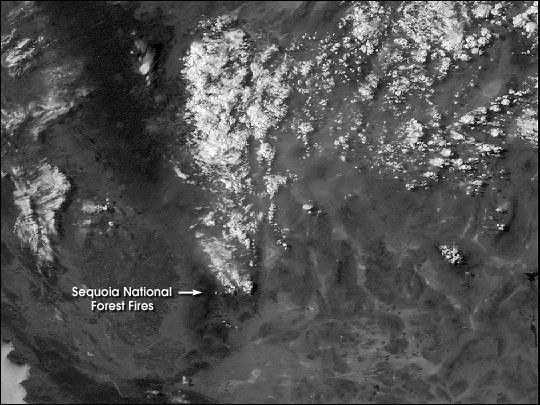
One of the largest fires currently burning has consumedmore than 63,000 acres in Sequoia National Forest. This NOAAGeostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)image shows the fire on the afternoon of July 30, 2000. Notethe clouds above the smoke plume. These often form during largefires because updrafts lift warm air near the ground highinto the atmosphere, cooling the air and causing the water vaporit contains to condense into droplets. The soot particles in the smokealso act as condensation nuclei for the droplets. View theanimation of GOES data to see the smoke forming clouds.
References & Resources
Image and Animation by Robert Simmon and Marit-Jentoft Nilsen, NASA GSFC, based on data from NOAA.