The steady crash of waves pounding the shore draws vacationers to beaches across the world when temperatures climb. Driven by the wind and tides, these familiar waves ride across the top of the ocean. But deeper waves also move through ocean waters, visible only from their influence on ocean currents. These waves are internal waves, and they run through lowest layers of ocean water, never swelling the surface.
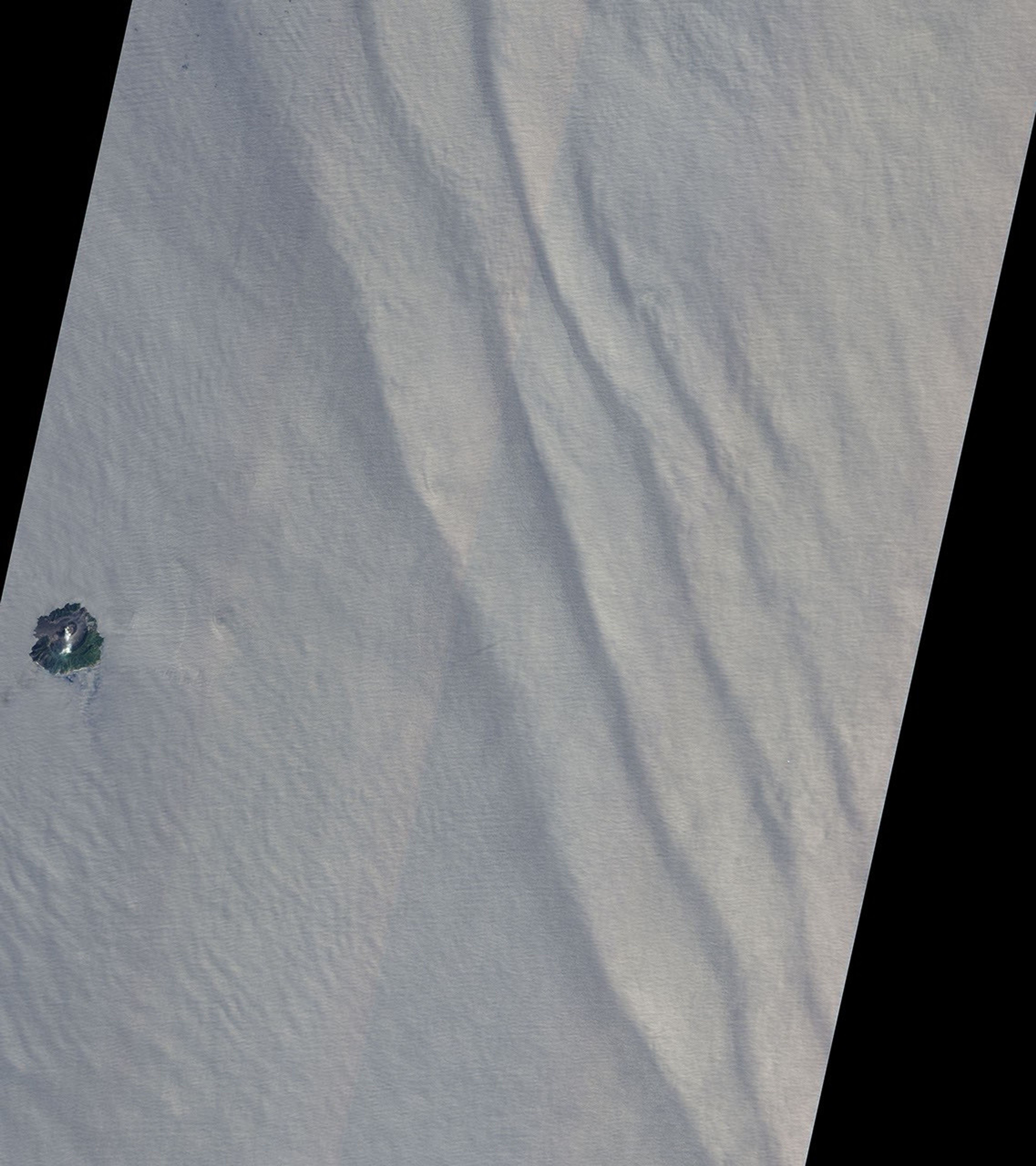
This image shows both internal waves and surface waves on the Indian Ocean near the Andaman Islands. The active Barren Island Volcano, part of the Andaman Islands, is shown emitting puffs of steam on the left side of the image. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on the Earth Observing 1 satellite acquired the image on March 6, 2007. Sunlight reflecting off the water’s surface gives it a pale, silvery blue color. The tiny wrinkles running roughly horizontally across the ocean are surface waves. Internal waves paint long diagonal lines across the ocean on the right side of the image.
Internal waves happen because the ocean is layered. Deep water is cold, dense, and salty, while shallower water is warmer, lighter, and fresher. The differences in density and salinity cause the various layers of the ocean to behave like different fluids. When tides drag the ocean over a shallow barrier such as a ridge on the ocean floor, it creates waves in the lower, denser layer of water. These waves, internal waves, can be tens of kilometers long and can last several hours.
As internal waves move through the lower layer of the ocean, the lighter water above flows down the crests and sinks into the troughs. This motion bunches surface water over the troughs and stretches it over the crests, creating alternating lines of calm water at the crests and rough water at the troughs.
It is the pattern of calm and rough water that makes the internal wave visible in satellite images. Calm, smooth waters reflect more light directly back to the satellite, resulting in a bright, pale stripe along the length of the internal wave. The rough waters in the trough scatter light in all directions, forming a dark line.
References & Resources
- Earth Observatory. (2003, July 1). Internal Waves, Sulu Sea. NASA. Accessed July 7, 2010.
- Earth Observatory. (2006, December 21). Internal waves in the Tsushima Strait. NASA. Accessed July 7, 2010.
- Earth Observatory. (2002, May 26). San Francisco Bay. NASA> Accessed July 7, 2010.
NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team. Caption by Holli Riebeek.