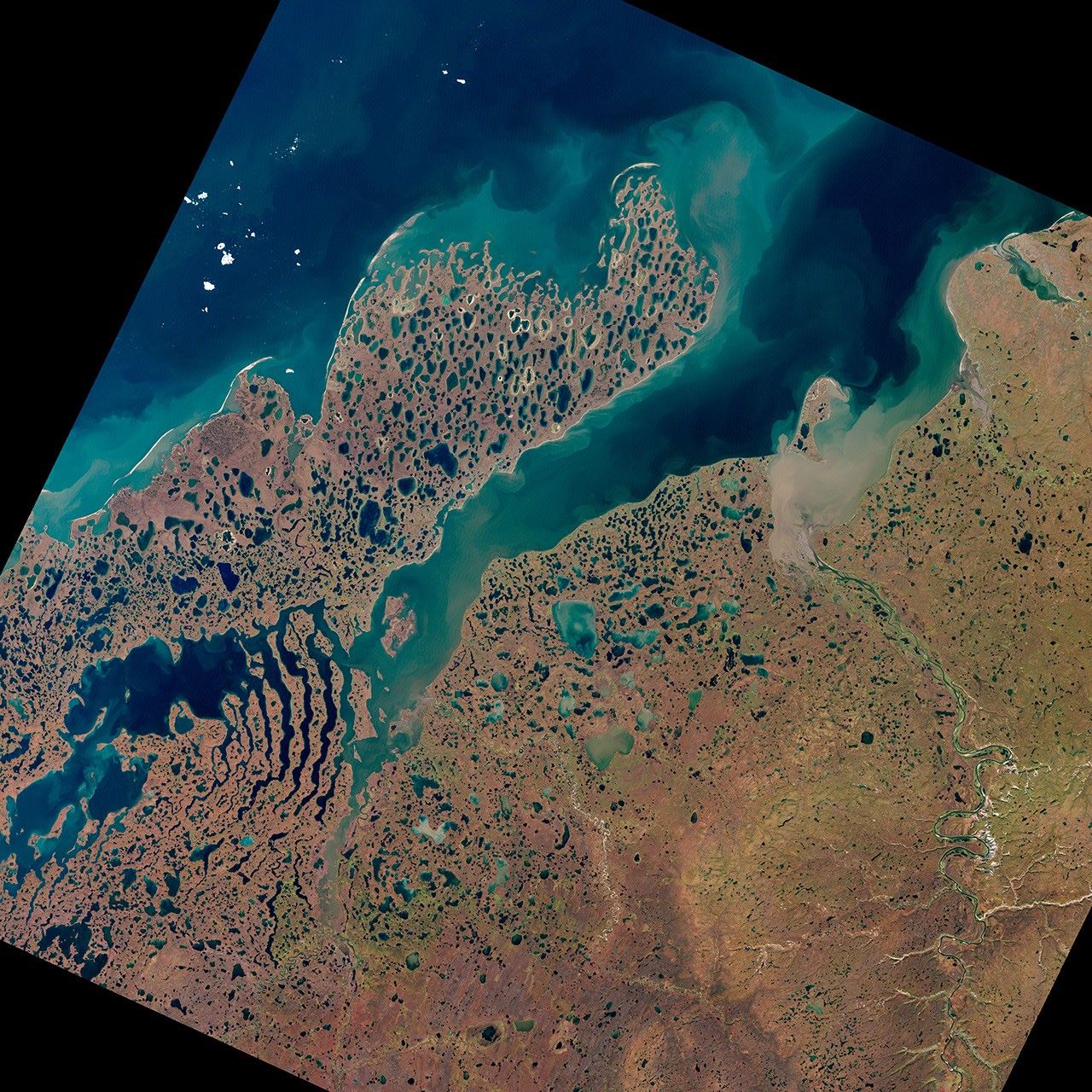
The land around Liverpool Bay in Canada’s Northwest Territories owes its otherworldly appearance to ice, both past and present. Thousands of years ago, this area was buried under a massive ice sheet that sprawled over much of North America. During that time, glacial activity carved out parallel lakes separated by strips of land that look like giant skeletal fingers. After the glaciers retreated, pockets of ice lingered underground. As those pockets have melted and the frozen ground has thawed, lakes have formed.
The Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus on the Landsat 7 satellite captured this natural-color image on September 2, 2000, in a region east of Alaska, along the Beaufort Sea. The area includes part of Liverpool Bay, the Eskimo Lakes, and the Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula. Tundra overlies permafrost around Liverpool Bay, but at this time of year, the nearby ocean is free of sea ice, and little if any snow is on the ground. This image has been rotated so that north is on the right.
Geologists have offered different explanations for the formation of the finger-shaped ridges around Eskimo Lakes, but all relate to glacial action. The ridges may be moraines created by the movement of ice, or they might be sediment ridges that formed between channels of subglacial melt water.
Smaller lakes pepper the landscape around Liverpool Bay. Unlike the fingers, these thermokarst lakes have formed from processes that continue today, namely ice and permafrost melt. Once a thermokarst lake forms, its relatively warm water erodes the surrounding permafrost, causing the lake to expand. But these lakes also can drain quickly, funneling water to lower elevations. Landsat observations of the Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula from 1978 to 2001 showed substantial changes in lake area due to alternating lake expansion and drainage.
Just as melt water can enlarge a thermokarst lake, seawater can breach one. Storms and strong waves enhance the ocean’s ability to eat through coastal permafrost. The extremely uneven coastline of Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula testifies to the interaction between ocean, permafrost, and melt water.
References & Resources
- Hill, P.R., Hequette, A., Ruz, M.H., Jenner, K.A. (1991). Geological Survey of Canada Open File Report 2387.
- Murton, J.B., Waller, R.I., Hart, J.K., Whiteman, C.A., Pollard, W.H., Clark, I.D. (2004). Stratigraphy and glaciotectonic structures of permafrost deformed beneath the northwest margin of the Laurentide ice sheet, Tuktoyaktuk Coastlands, Canada. Journal of Glaciology, 50(170), 399–412.
- Murton, J.B., Whiteman, C.A., Waller, R.I., Pollard, W.H., Clark, I.D., Dallimore, S.R. (2005). Basal ice facies and supraglacial melt-out till of the Laurentide Ice Sheet, Tuktoyaktuk Coastlands, western Arctic Canada. Quaternary Science Reviews, 24(5–6), 681–708.
- NOAA Paleoclimatology. (2003, January 28). What is Glaciation? Accessed August 18, 2011.
- Penn State University. (n.d.). Spatial and Temporal Influences of Thermokarst Failures on Surface Processes in Arctic Landscapes. Accessed August 18, 2011.
- Plug, L.J., Walls, C., Scott, B.M. (2008). Tundra lake changes from 1978 to 2001 on the Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula, western Canadian Arctic. Geophysical Research Letters, 35, L03502.
- State of the Cryosphere. (2008, October 31). Permafrost and Frozen Ground. National Snow and Ice Data Center. Accessed August 18, 2011.
NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using Landsat data provided by the United States Geological Survey. Caption by Michon Scott.