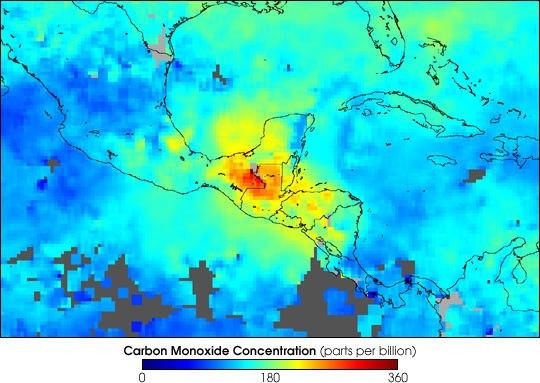
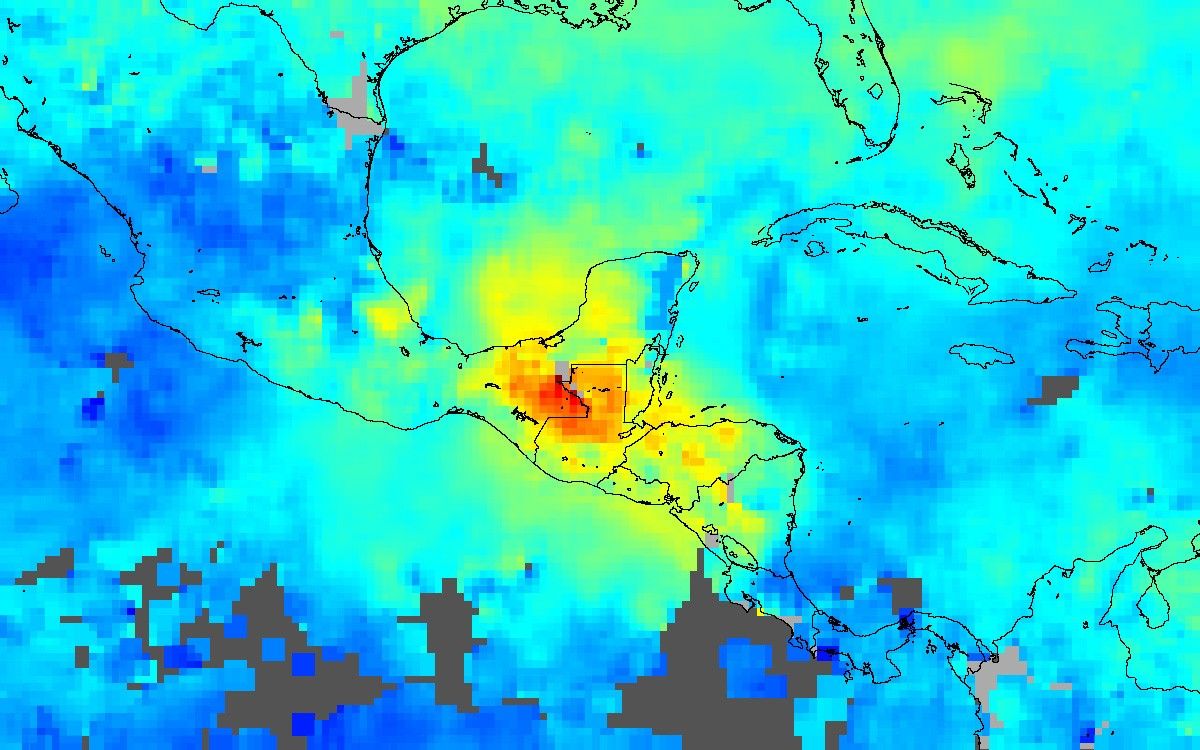
The widespread and intense biomass burning ocurring on the Yucatan Peninsula and other parts of Central America is producing high concentrations of carbon monoxide(CO) in the lower atmosphere, as shown in this image of observations by the Measurements of Pollution in The Troposphere (MOPITT) instrument aboard NASA’s Terrasatellite. This false-color image shows the mixing ratios of CO at an altitude of about 3 km (700 hPa) averaged from April 25 to May 1, 2003. Grayareas indicate where no data are available.
The highest mixing ratios are seen over the Yucatan Peninsula and over the border between Mexico and Guatemala. Carbon monoxide levels as high as 360 parts per billion by volume of air (red pixels) were measured. The orange and yellow pixels indicate high levels of CO over the countries south of Guatemala—Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua. The pollution is also being carried northeastward over the Gulf of Mexico toward the U.S. gulf coast states and the western parts of the Caribbean.
Images from the MODIS instruments aboard the Terra and Aqua satellites show the locations of the numerous fires across the region during this same time period as well as the thick, widespread pall of smoke they produced.
References & Resources
Image courtesy the NCAR and University of Toronto MOPITT Teams