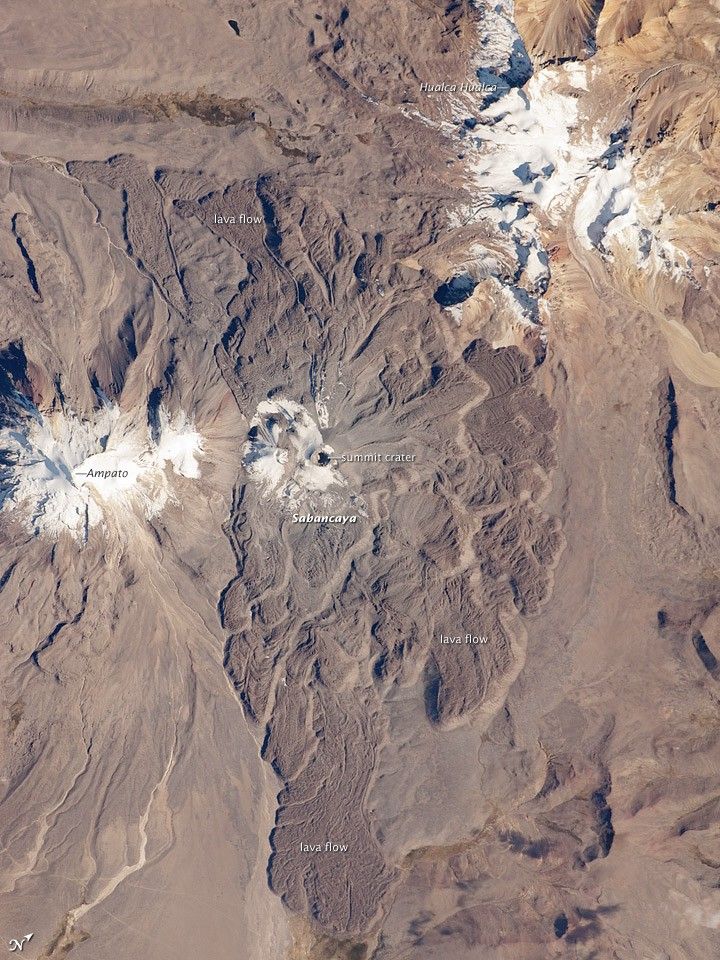
The 5,967-meter- (19,577-foot-) high Sabancaya stratovolcano (Nevado Sabancaya in the local language) is located in southern Perú, approximately 70 kilometers (40 miles) northwest of the city of Arequipa. The name Sabancaya means “tongue of fire” in the Quechua Indian language.
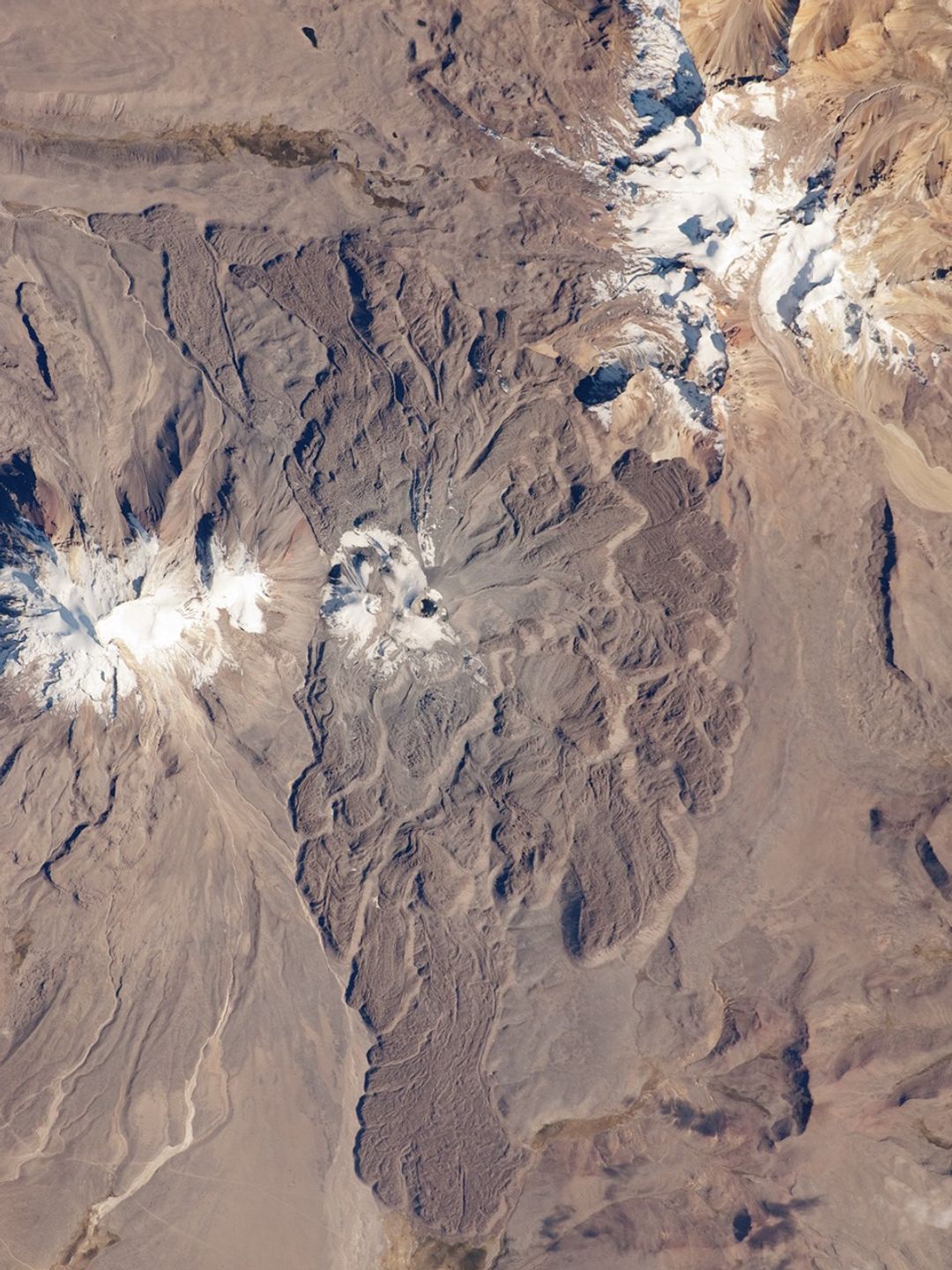
Sabancaya is part of a volcanic complex that includes two other nearby (and older) volcanoes, neither of which has been active historically. In this detailed astronaut photograph, Nevado Ampato is visible to the south (image left), and the lower flanks of Nevado Hualca Hualca are visible to the north (image top right). The snowy peaks of the three volcanoes provide a stark contrast to the surrounding desert of the Puna Plateau.
Sabancaya’s first historical record of an eruption dates to 1750. The most recent eruptive activity at the volcano occurred in July 2003, and it deposited ash on the volcano’s summit and northeastern flank. Volcanism at Sabancaya is fueled by magma generated at the subduction zone between the Nazca and South American tectonic plates.
Magma can erupt to the surface and form lava flows through the volcano’s summit (frequently forming a crater), but it can also erupt from lava domes and flank vents along the volcano’s sides. Lava has issued from all of these points at Sabancaya, forming numerous gray to dark brown scalloped lobes that extend in all directions except southwards (image center).
References & Resources
Astronaut photograph ISS024-E-8396 was acquired on July 15, 2010, with a Nikon D2Xs digital camera using a 400 mm lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by the Expedition 24 crew. The image in this article has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast. Lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by William L. Stefanov, NASA-JSC.