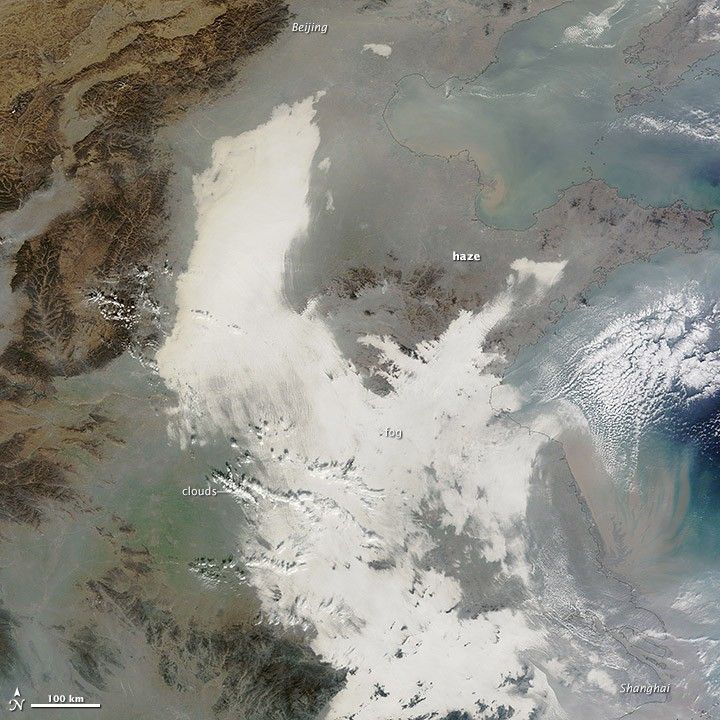
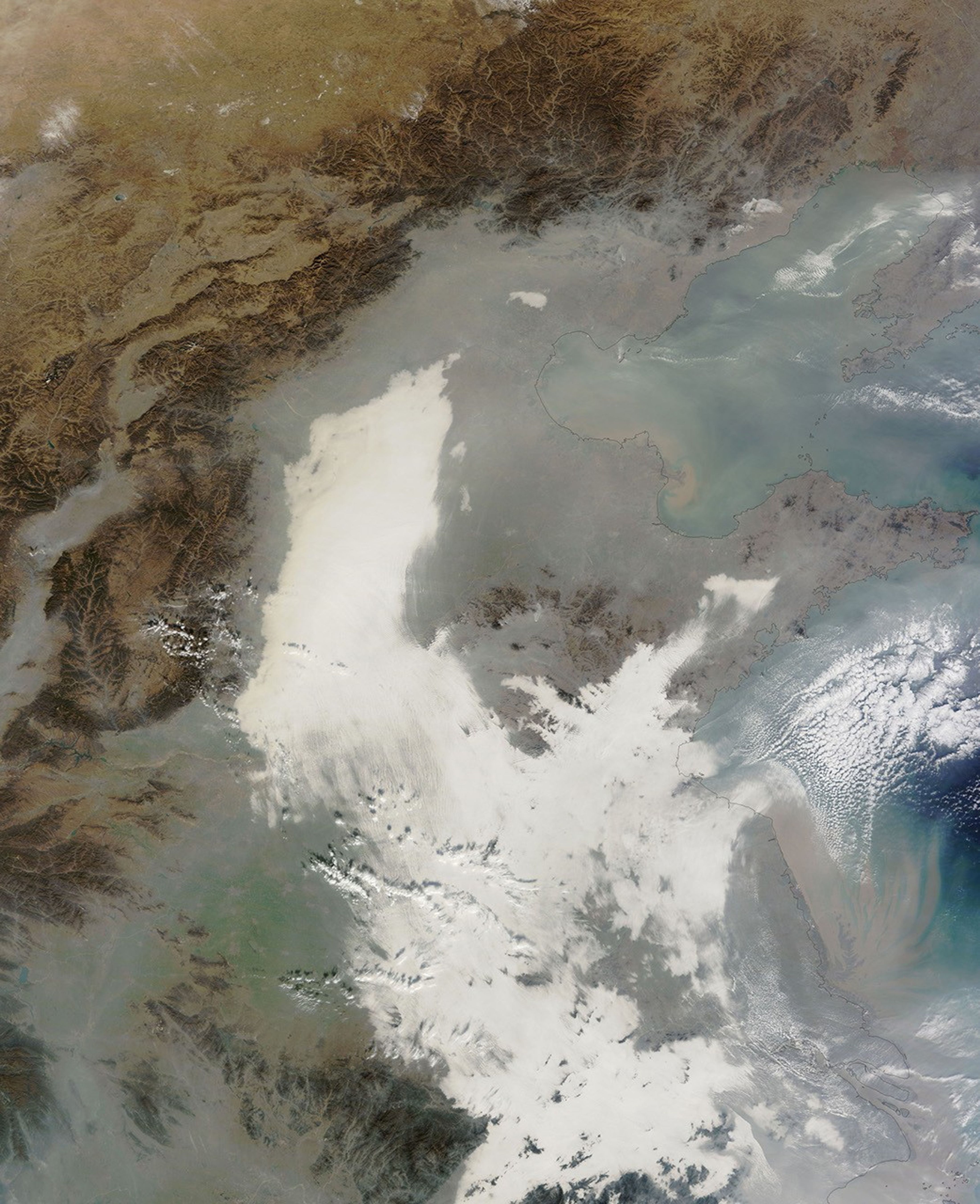
China suffered another severe bout of air pollution in December 2013. When the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this image on December 7, 2013, thick haze stretched from Beijing to Shanghai, a distance of about 1,200 kilometers (750 miles). For comparison, that is about the distance between Boston, Massachusetts, and Raleigh, North Carolina. The brightest areas are clouds or fog. Polluted air appears gray. While northeastern China often faces outbreaks of extreme smog, it is less common for pollution to spread so far south.
“The fog has a smooth surface on the top, which distinguishes it from mid- and high-level clouds that are more textured and have distinct shadows on their edge,” explained Rudolf Husar, director of the Center for Air Pollution Impact and Trend Analysis at Washington University. “If there is a significant haze layer on top of the fog, it appears brownish. In this case, most of the fog over eastern China is free of elevated haze, and most of the pollution is trapped in the shallow winter boundary layer of a few hundred meters.”
On the day this natural-color image was acquired by Terra, ground-based sensors at U.S. embassies in Beijing and Shanghai reported PM2.5 measurements as high as 480 and 355 micrograms per cubic meter of air respectively. The World Health Organization considers PM2.5 levels to be safe when they are below 25.
Fine, airborne particulate matter (PM) smaller than 2.5 microns (about one thirtieth the width of a human hair) is considered dangerous because it is small enough to enter the passages of the human lungs. Most PM2.5 aerosol particles come from the burning of fossil fuels and of biomass (wood fires and agricultural burning).
At the time of the satellite image, the air quality index (AQI) reached 487 in Beijing and 404 in Shanghai. An AQI above 300 is considered hazardous to all humans, not just those with heart or lung ailments. AQI below 50 is considered good.
In some cities, authorities ordered school children to stay indoors, pulled government vehicles off the road, and halted construction in an attempt to reduce the smog, according to news reports.
References & Resources
- Associated Press, via The Washington Post (2013, December 6) Smog at Extremely Hazardous levels in Shanghai. Accessed December 9, 2013.
- Bloomberg News (2013, December 9) Shanghai Tells Children to Stay Inside for Seventh Day on Smog. Accessed December 9, 2013.
- The New York Times (2013, December 5) Air Pollution Shrouds Eastern China. Accessed Accessed December 9, 2013.
- U.S. Department of State (2013, December 9) U.S. Consulate Shanghai Air Quality Monitor. Accessed December 9, 2013.
- U.S. Department of State (2013, December 9) U.S Embassy Beijing Air Quality Monitor. Accessed December 9, 2013.
- Voice of America (2013, December 6) Flights Delayed as Air Pollution Hits Record in Shanghai. Accessed December 9, 2013.
- Xinhua (2013, December 9) Cities hit hard by smog. Accessed December 9, 2013.
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE MODIS Rapid Response. Caption by Adam Voiland.