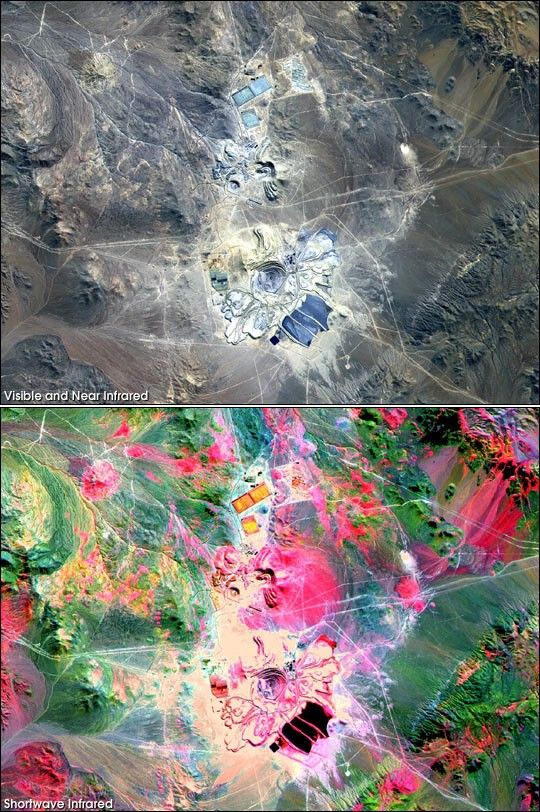
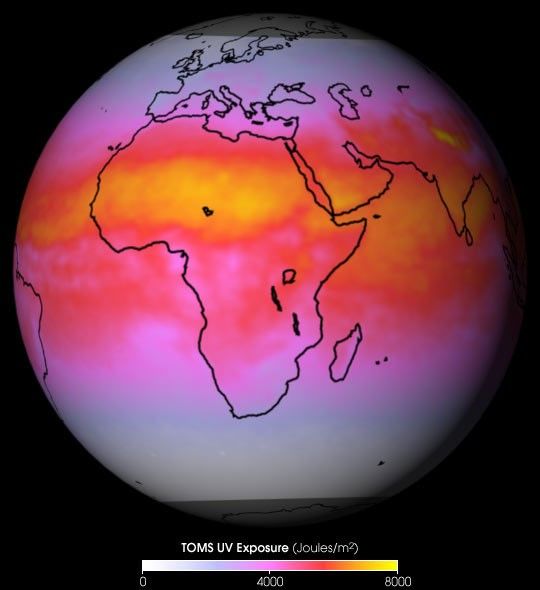
NASA’s Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer(TOMS) provides measurements that enable scientists to accuratelyestimate how much of the sun’s UV-B (290 to 320 nm) radiation reaches the Earth'ssurface. Too much exposure to these wavelengths causes sunburn inhuman skin.
The false-color image above is a global map, averaged from TOMSsnapshots collected every day over a one-month period, showing wheremore or less UV radiation reaches the surface. Yellow pixels show thehighest levels of radiation at the surface, red and pink hues areintermediate values, and white indicates little or no UV exposure.
The TOMS sensor flies in a polar orbit, crossing the equator every dayat 12 noon local time, allowing it to measure the total amount of ozonein a column of atmosphere as well as cloud cover over the entire globe.Ozone and clouds absorb most of the ultraviolet light passing throughthe atmosphere. TOMS also measures the amount of solar radiationescaping from the top of the atmosphere. It is the combination of thosethree measurements that enables scientists to accurately estimate theamount of UV radiation that reaches the Earth's surface.
Ultraviolet radiation exposure data and images.
References & Resources
Data courtesy TOMS science team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
None