CP-11 Science
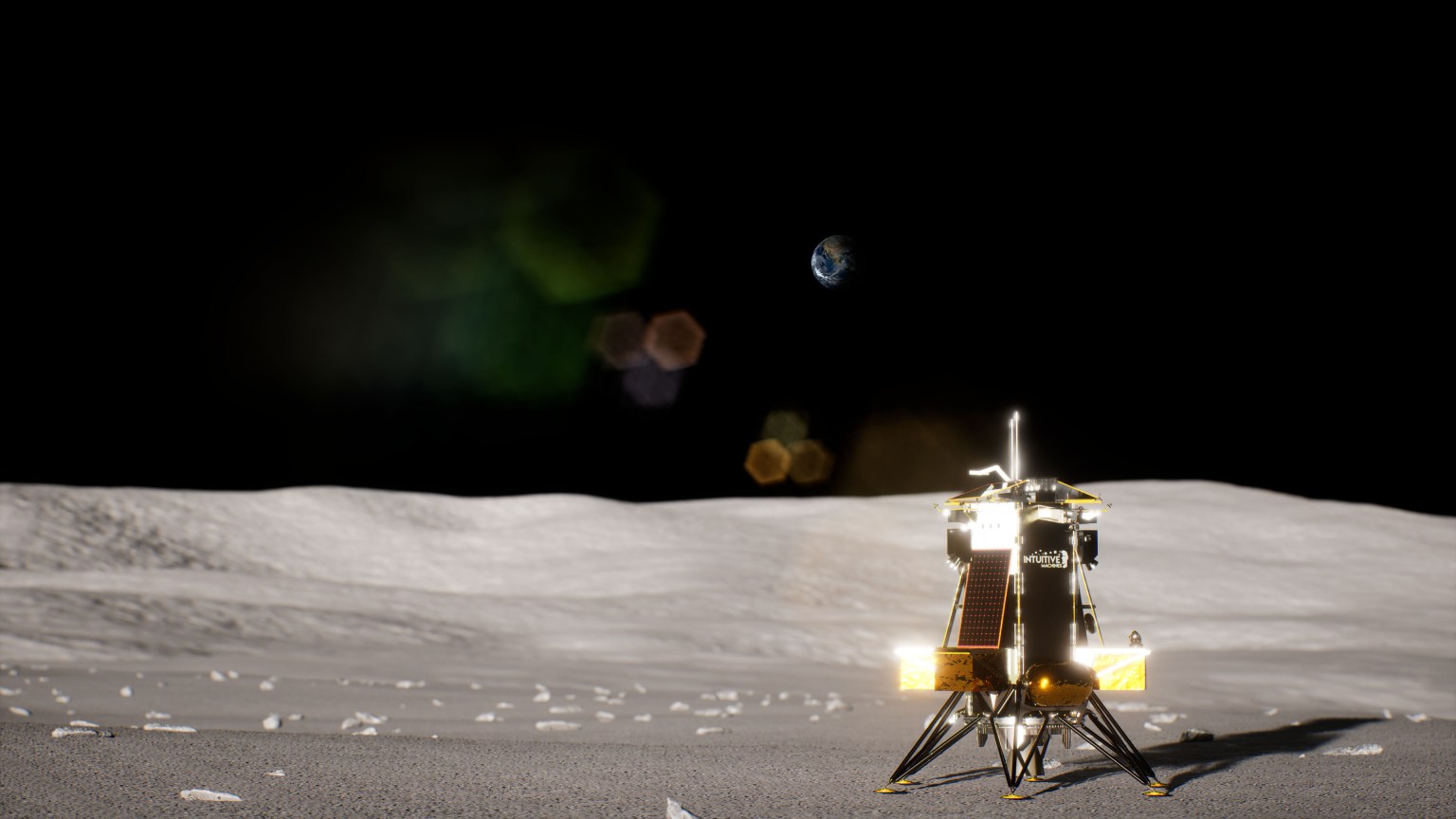
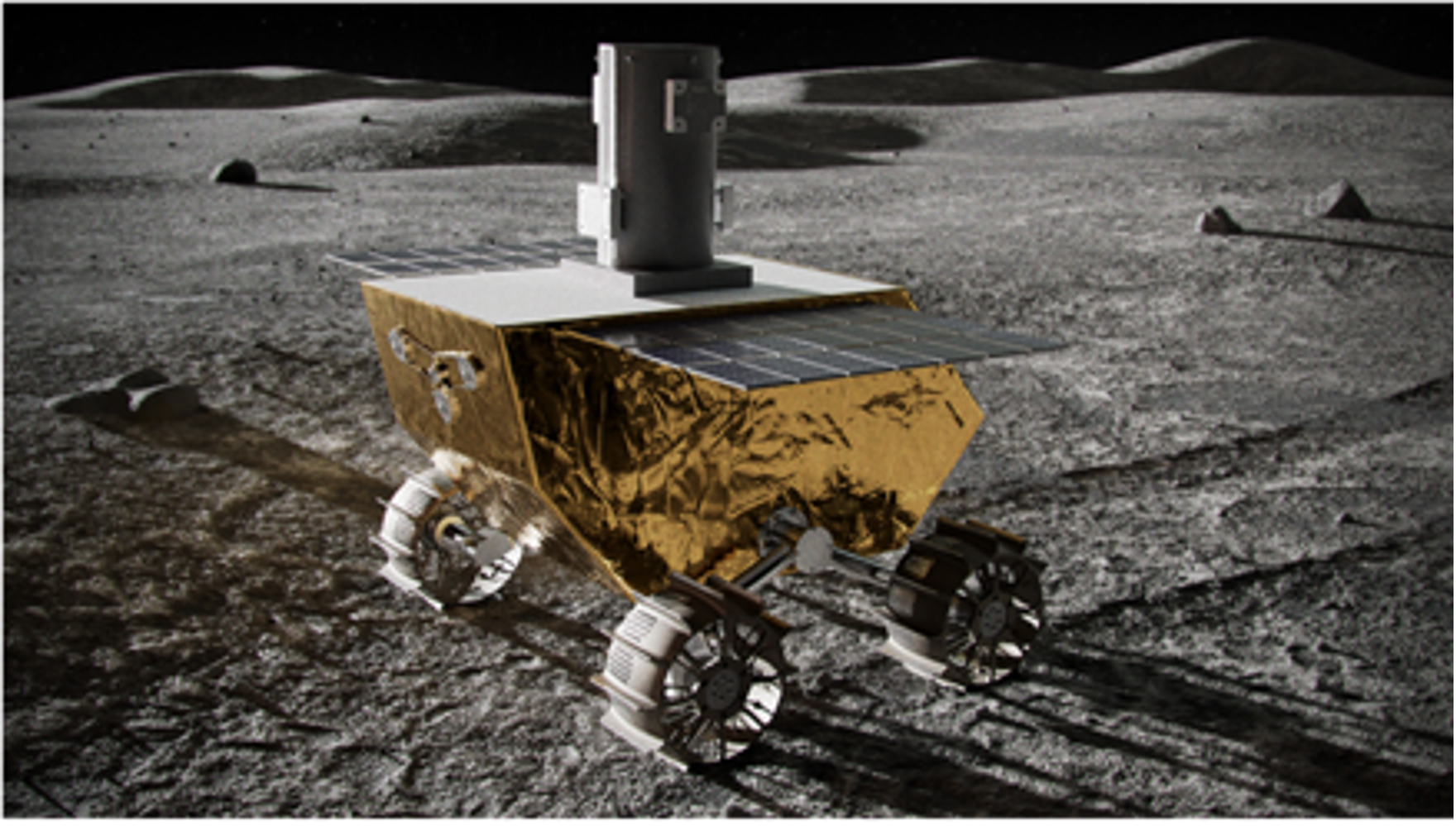
Intuitive Machines' Nova-C lander will deliver four NASA CLPS science payloads to Reiner Gamma on the lunar nearside.
Lunar Vertex (LVx)
- Summary: Lunar Vertex (LVx) is a joint lander and rover payload suite that will land at Reiner Gamma on the lunar nearside, which is also known as a lunar swirl. Scientists know that lunar swirls exist, but we do not know exactly what they are or how they form. We do know they are related to the Moon’s magnetic field. Lunar Vertex will take on some persistent lunar mysteries: the origins of these magnetic anomalies and any relation they might have to the visible swirls. The investigation will look closely at how these areas interact with the solar wind, the high-speed stream of energetic particles from the Sun.
- Type of Instrument: magnetometers on both the lander and rover, ion-electron plasma spectrometer, cameras on the lander, and a multispectral microscope on the rover.
- Key Measurement: The origin of lunar magnetic fields and their relation to surface swirls features.
- Task Order: CP-11
- Lead Development Organization: Johns Hopkins University/Applied Physics Laboratory
- Payload PI: Dr. David Blewett
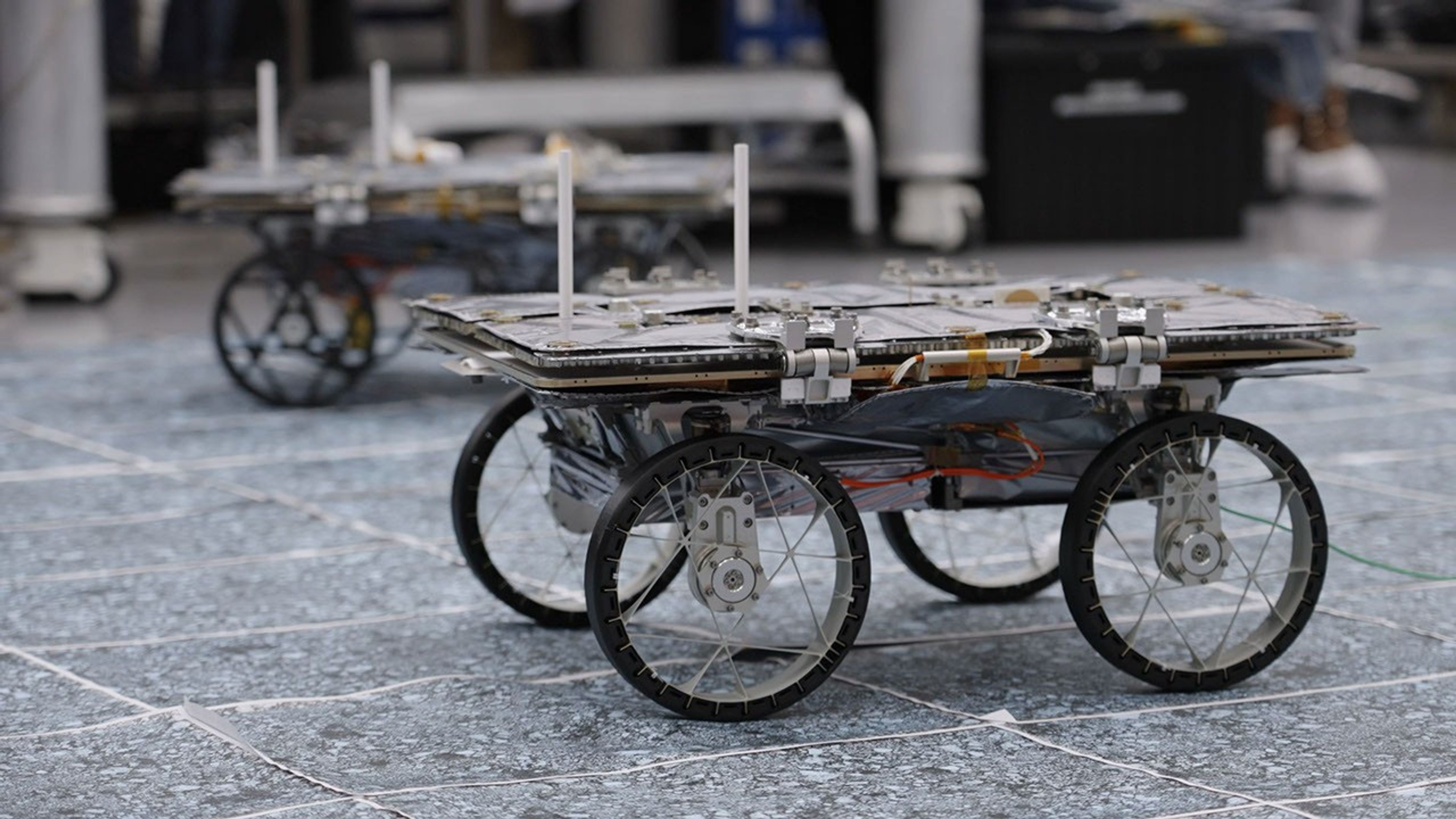
Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration (CADRE)
- Summary: The CADRE robots are a set of suitcase-sized mobile robots that will test autonomous robotic exploration capabilities on the lunar surface. Each robot contains an onboard computer with a wireless radio for communication and a stereo camera – which has multiple lenses and image sensors – for sensing the environment in front of it and capturing 3D imagery. In addition, the rovers will each carry a Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) payload to make distributed science measurements.
- Type of Instrument: Mini-rovers and Ground Penetrating Radar
- Key Measurement: Testing autonomous roving capabilities
- Task Order: CLPS CP-11
- Lead Development Organization: JPL
- Payload PI: Jean-Pierre de la Croix
- Project Manager: Subha Comandur
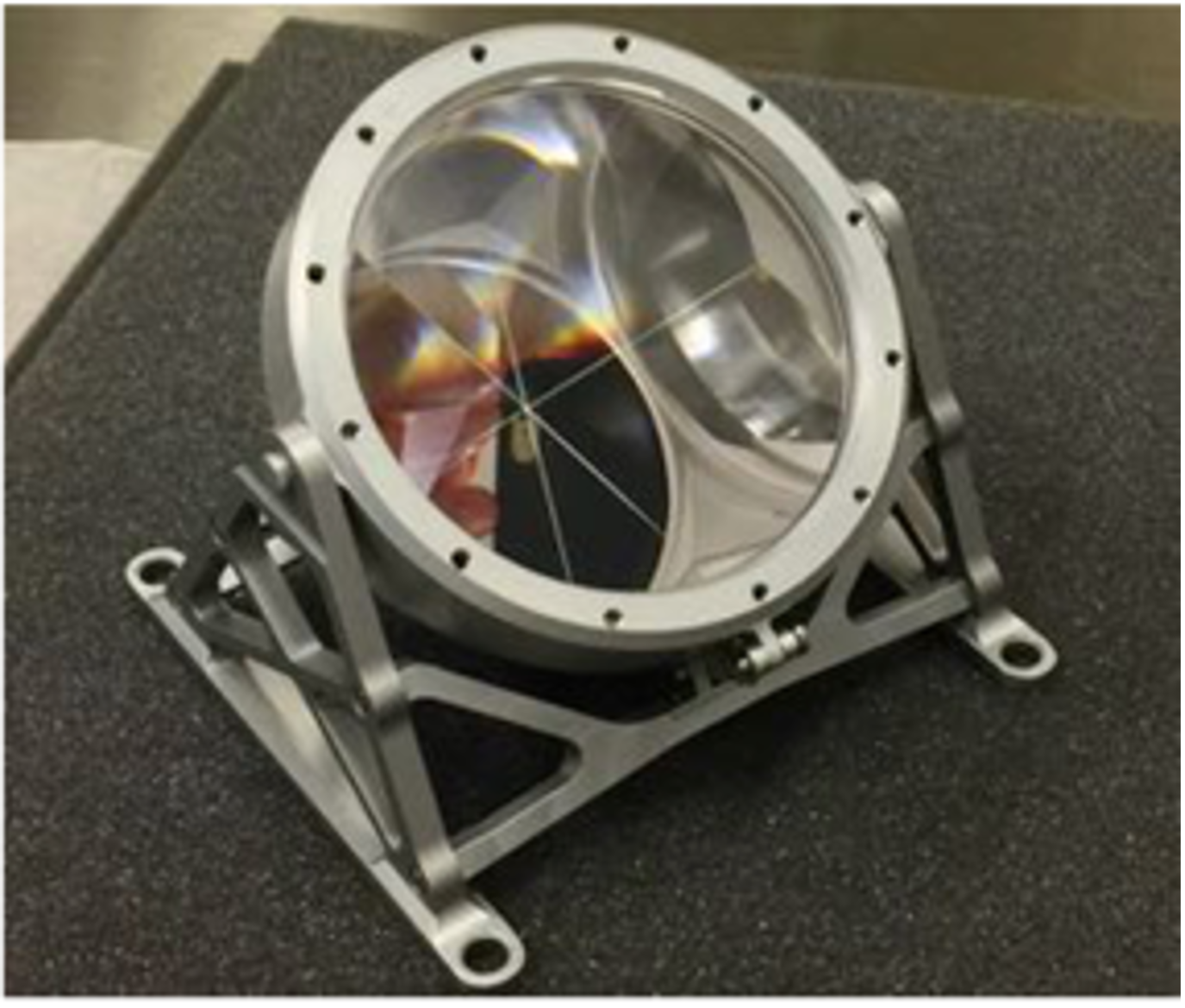
ESA's MoonLIGHT Pointing Actuator (MPAc)
- Summary: Moon Laser Instrumentation for General relativity High accuracy Test (MoonLIGHT) (INFN-LNF) shares its design with the Next Generation Laser Retroreflector NGLR from UMD flying on TO19D. These are 100 mm single, solid, large reflectors and are intended for direct lunar laser ranging from stations in USA, Italy (ASI-CGS) and France (Grasse). Its main applications are geophysics, precision tests of general relativity, and new theories of fundamental relativistic gravity. This array is also currently baselined for the Lunar Geophysical Network (LGN).
- Type of Instrument: Large reflector
- Key Measurement: Measure the size, shape, and liquid core of the Moon. Also, a target to measure Earth-Moon distance.
- Task Order: CLPS CP-11
- Lead Development Organization: ESA
- Payload PI: Marco Muccino
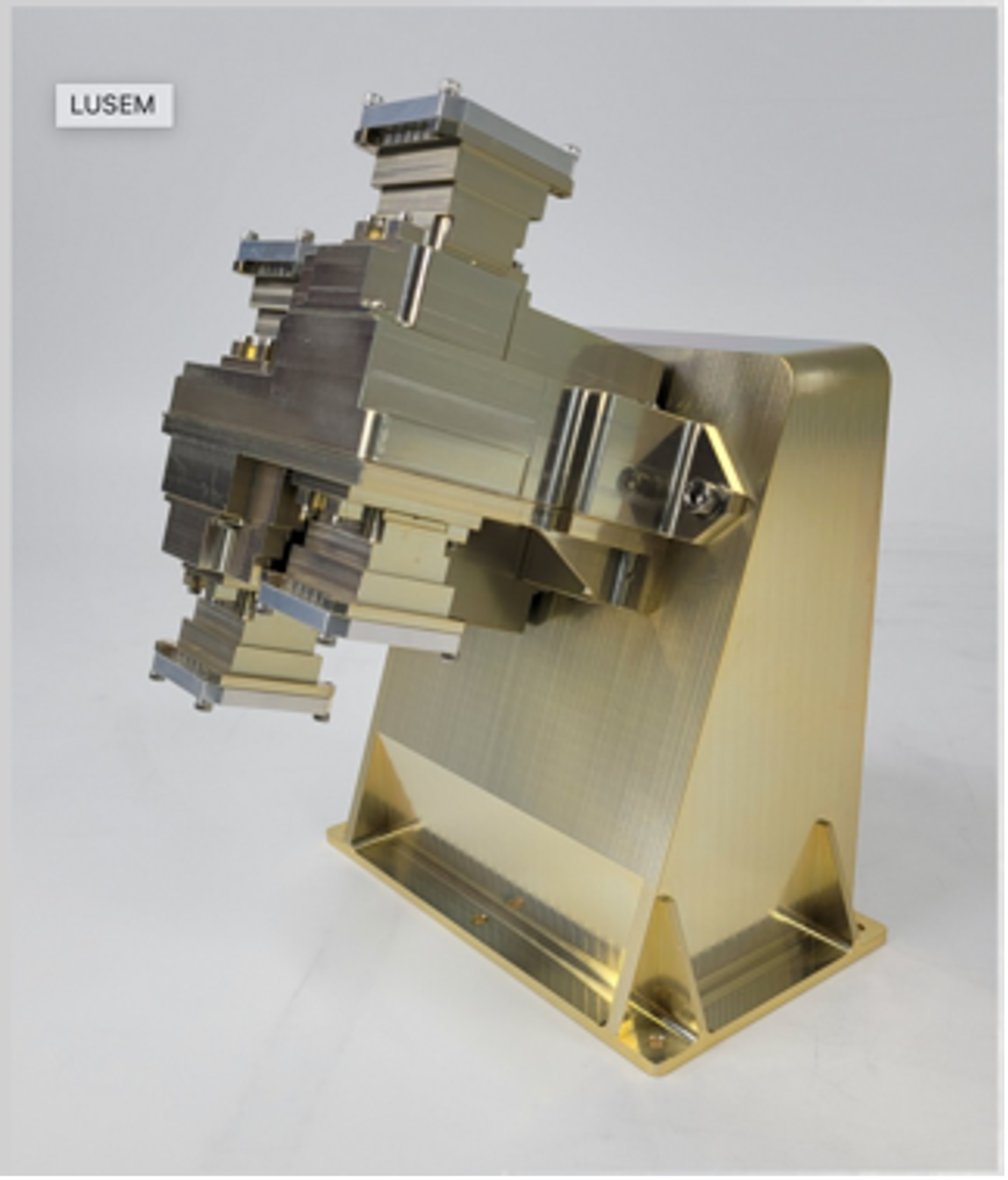
KASI's Lunar Space Environment Monitor (LUSEM)
- Summary: LUSEM will detect high energy particles and monitor variations in the near-surface space environment when the Moon is inside and outside the Earth's magnetotail - the trailing end of the magnetic fields surrounding our planet, which can serve as a buffer for incoming radiation.
- Type of Instrument: A pair of Solid-State Telescopes (SST)
- Key Measurement: Charged particles of ≥ 50 keV, separating ions and electrons
- Task Order: CP-11
- Lead Development Organization: Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI)
- Payload PI: Young-Jun Choi