NASA Satellite Eyes Atmosphere to Improve Pollution and Climate Forecasting
Thanks to the latest sophisticated, satellite-based instruments, local and regional air pollution and their sources can now be observed closely from space. Researchers using nearly up-to-the-hour data from NASA's Aura satellite are now tracking important pollutants such as ozone and nitrogen oxide. What's more, the satellite's first global observations of ice in clouds will provide climatologists, weather forecasters and public officials around the world the ability to make better predictions of future climate change.
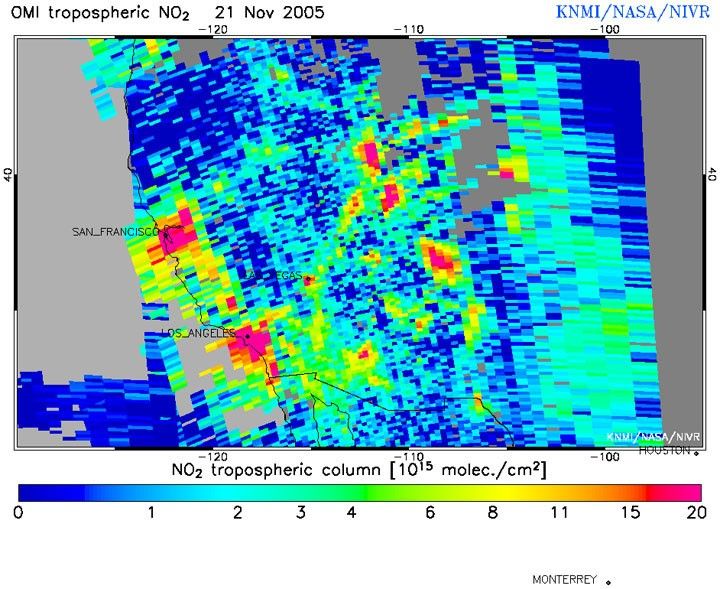
Tropospheric Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) measurements of the November 21, 2005 of Aura's Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) above California, USA, showing San Francisco, Las Vegas and Los Angeles. In the future this product will be available a few hours from measurement and could be used to improve air pollution forecasts.
12.08.2005
OMI
Aura’s Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) instrument can distinguish between aerosol types, such as smoke, dust, and sulfates, and measures cloud pressure and coverage, which provides data to derive tropospheric ozone.…
Learn More