CGRO
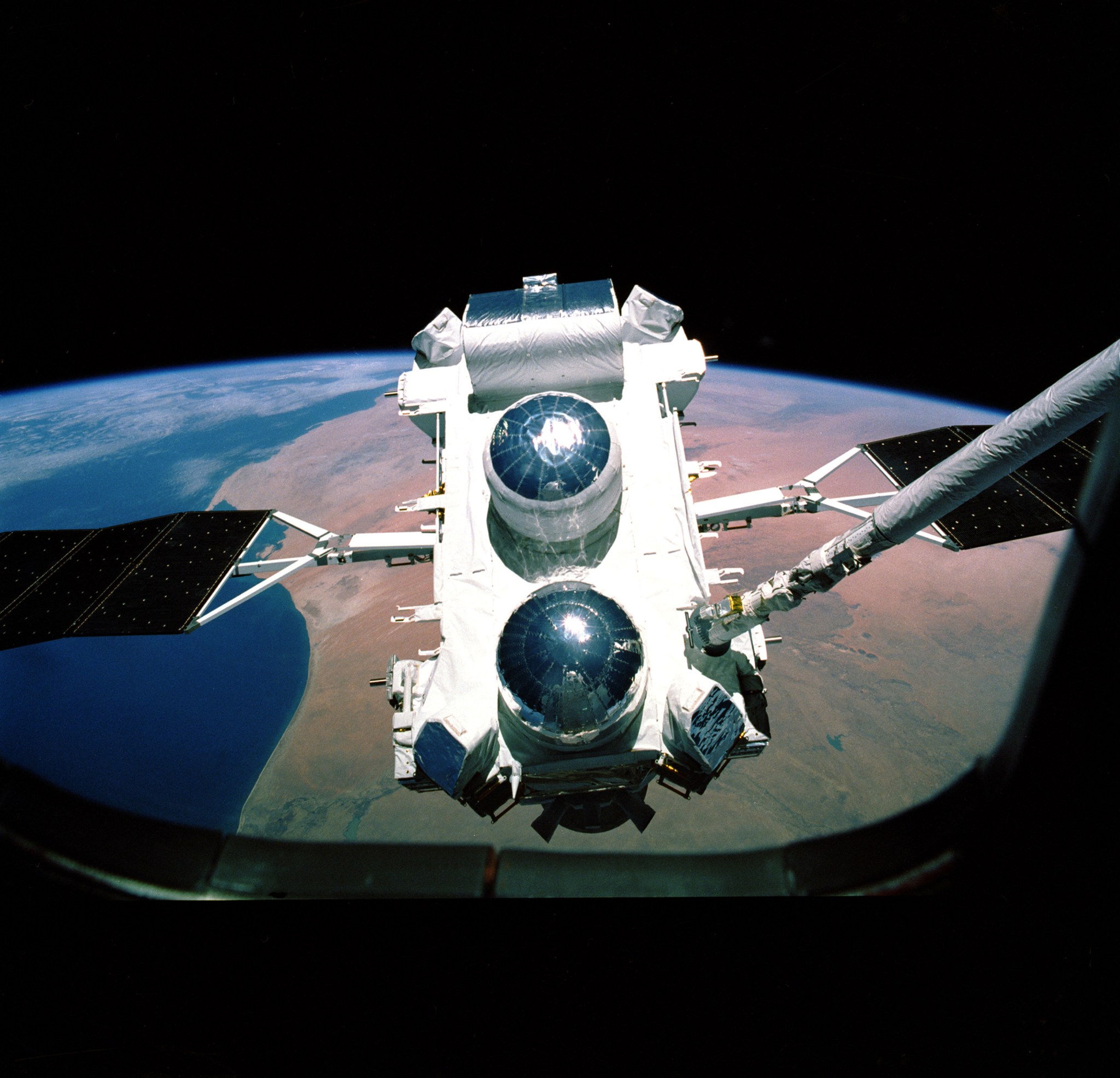
CGRO (Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory), one of NASA's Great Observatories, studied the gamma-ray sky using four telescopes that detected different energies. The mission found a class of active galaxies called blazars, mapped the Milky Way’s distribution of a radioactive isotope of aluminum, and hinted at gamma-ray bursts’ cosmological origins, among other discoveries.
Type
Space observatory
Launch
April 5, 1991
Wavelength
Gamma rays
Decommissioned
June 4, 2000
Featured Story
NASA Celebrates 25 Years of Breakthrough Gamma-ray Science
Twenty-five years ago this week, NASA launched the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, an astronomical satellite that transformed our knowledge of…
Read the Story