Cassini Targets a Propeller in Saturn’s A Ring
| PIA Number | PIA21433 |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
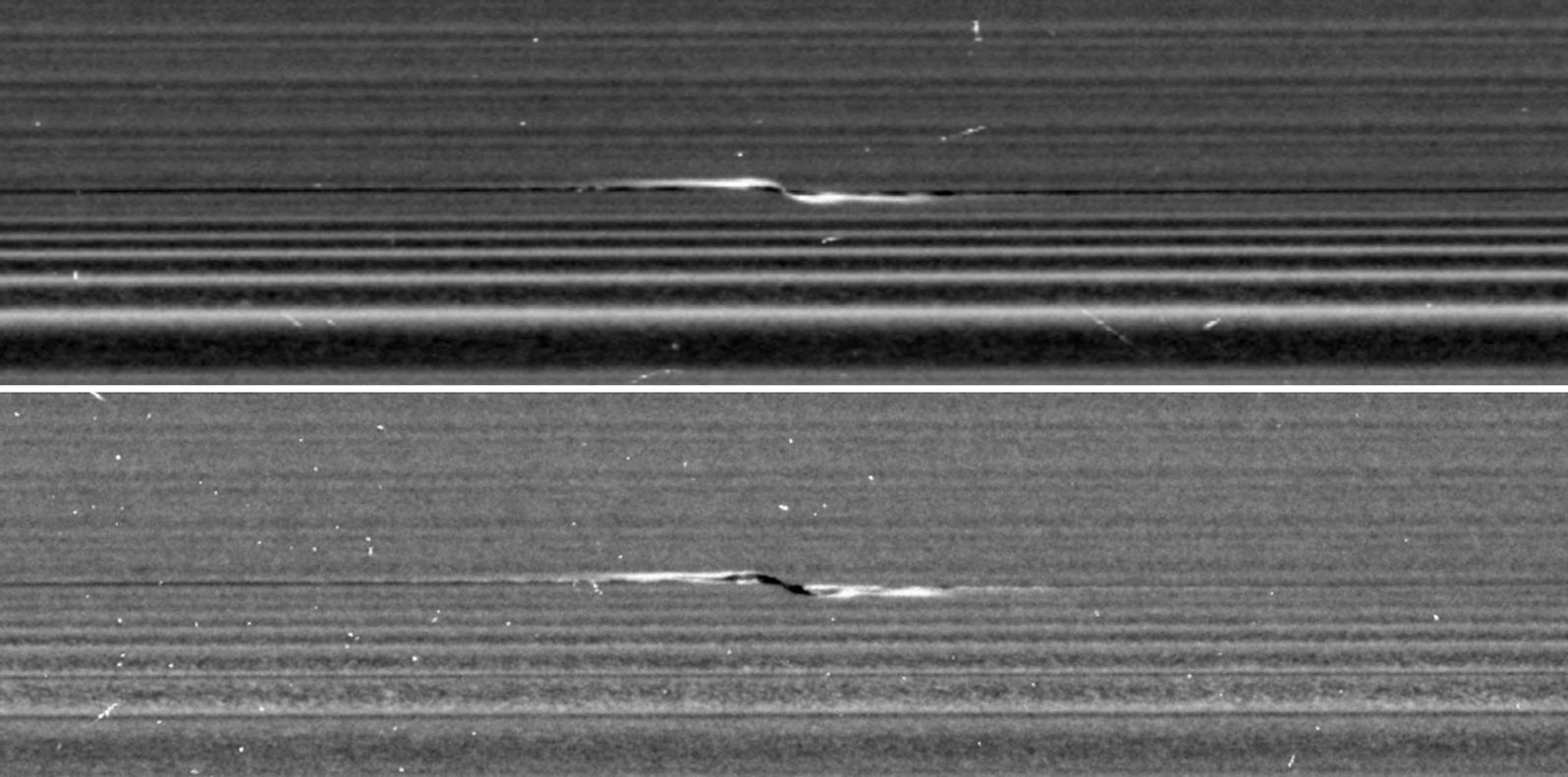
NASA's Cassini spacecraft captured these remarkable views of a propeller feature in Saturn's A ring on Feb. 21, 2017. These are the sharpest images taken of a propeller so far, and show an unprecedented level of detail. The propeller is nicknamed "Santos-Dumont," after the pioneering Brazilian-French aviator.
This observation was Cassini's first targeted flyby of a propeller. The views show the object from vantage points on opposite sides of the rings. The top image looks toward the rings' sunlit side, while the bottom image shows the unilluminated side, where sunlight filters through the backlit ring.
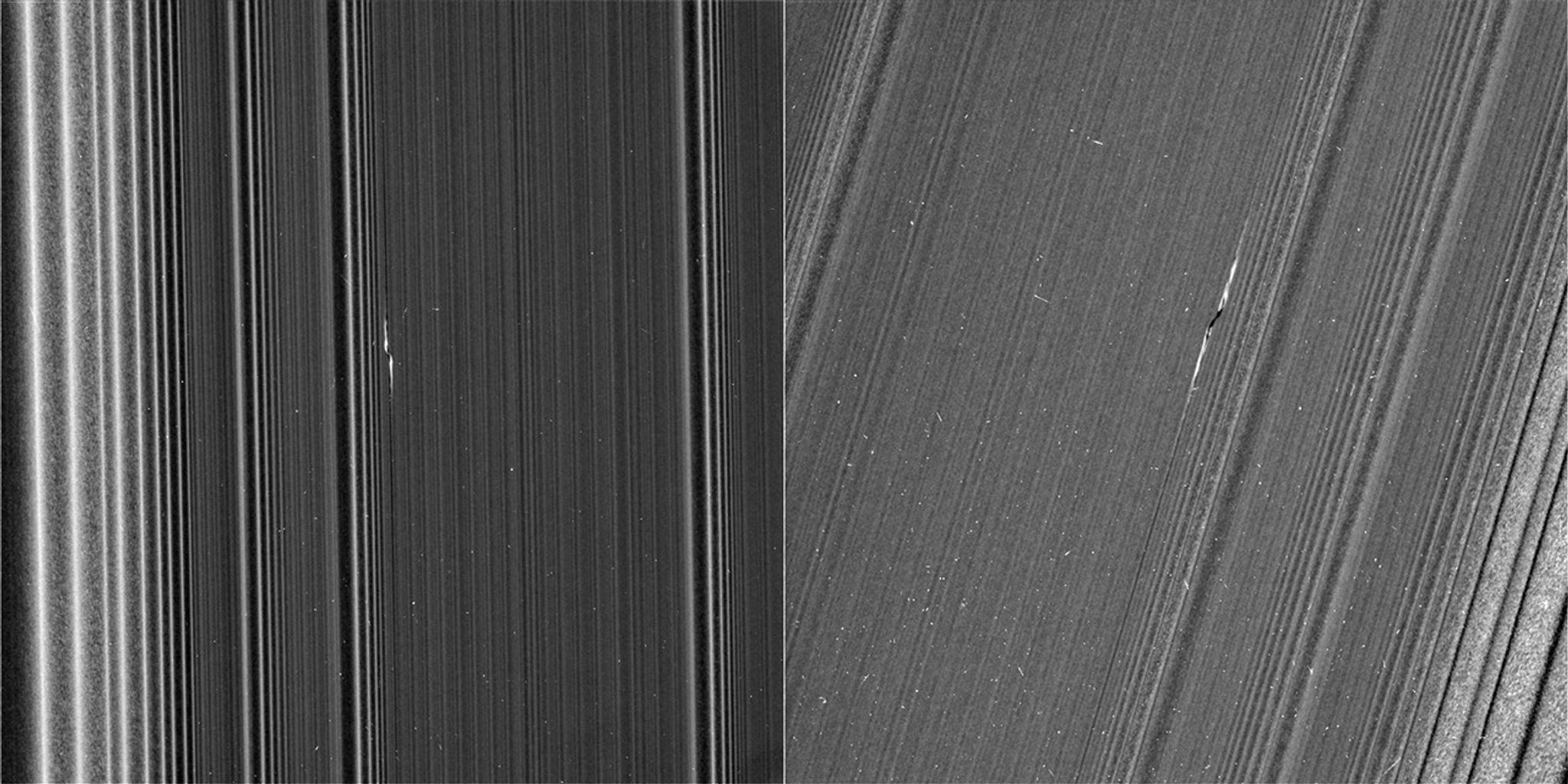
The two images presented as figure A are reprojected at the same scale (0.13 mile or 207 meters per pixel) in order to facilitate comparison. The original images, which have slightly different scales, are also provided here, without reprojection, as figure B; the sunlit-side image is at left, while the unlit-side image is at right.
Cassini scientists have been tracking the orbit of this object for the past decade, tracing the effect that the ring has upon it. Now, as Cassini has moved in close to the ring as part of its ring-grazing orbits, it was able to obtain this extreme close-up view of the propeller, enabling researchers to examine its effects on the ring. These views, and others like them, will inform models and studies in new ways going forward.
Like a frosted window, Saturn's rings look different depending on whether they are seen fully sunlit or backlit. On the lit side, the rings look darker where there is less material to reflect sunlight. On the unlit side, some regions look darker because there is less material, but other regions look dark because there is so much material that the ring becomes opaque.
Observing the same propeller on both the lit and unlit sides allows scientists to gather richer information about how the moonlet affects the ring. For example, in the unlit-side view, the broad, dark band through the middle of the propeller seems to be a combination of both empty and opaque regions.
The propeller's central moonlet would only be a couple of pixels across in these images, and may not actually be resolved here. The lit-side image shows that a bright, narrow band of material connects the moonlet directly to the larger ring, in agreement with dynamical models. That same thin band of material may also be obscuring the moonlet from view.
Lengthwise along the propeller is a gap in the ring that the moonlet has pried open. The gap appears dark on both the lit and unlit sides. Flanking the gap near the moonlet are regions of enhanced density, which appear bright on the lit side and more mottled on the unlit side.
One benefit of the high resolution of these images is that, for the first time, wavy edges are clearly visible in the gap. These waves are also expected from dynamical models, and they emphasize that the gap must be sharp-edged. Furthermore, the distance between the wave crests tells scientists the width of the gap (1.2 miles or 2 kilometers), which in turn reveals the mass of the central moonlet. From these measurements, Cassini imaging scientists deduce that the moonlet's mass is comparable to that of a snowball about 0.6 mile (1 kilometer) wide.
For the original images (figure B), the lit-side image has a scale of 0.33 mile (530 meters) per pixel in the radial (or outward from Saturn) direction and 0.44 mile (710 meters) per pixel in the azimuthal (or around Saturn) direction. The different scales are the result of Cassini's vantage point being off to the side of the propeller, rather than directly above it. The unlit-side image has a scale of 0.25 (410 meters) per pixel in both directions.
In order to preserve its original level of detail, the image has not been cleaned of bright blemishes due to cosmic rays and to charged particle radiation from Saturn.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and http://www.nasa.gov/cassini. The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute



























