Discovery of the Wavemaker
| PIA Number | PIA06239 |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
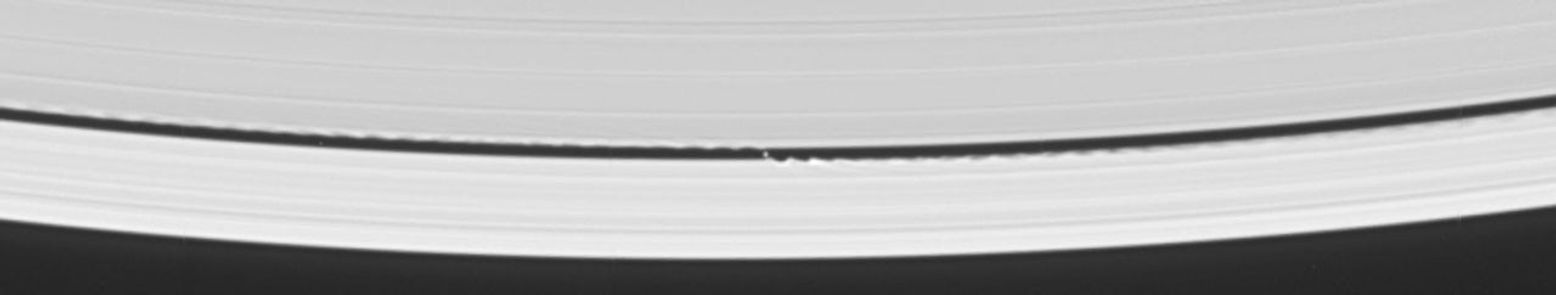
Cassini's celestial sleuthing has paid off with a series of images which confirmed earlier suspicions that a small moon was orbiting within the narrow Keeler gap within Saturn's rings.
This view was created by combining six individual, unmagnified frames from the movie sequence of images in which the moon was discovered. The digital composite view improves the overall resolution of the scene compared to that available in any of the single images (see Wavemaker Moon for the movie sequence).
The Keeler gap is located about 250 kilometers (155 miles) inside the outer edge of the A ring, which is also the outer edge of the bright main rings. The new object is about 7 kilometers (4 miles) across and reflects about 50 percent of the sunlight light that falls upon it -- a brightness that is typical of particles in the nearby rings.
The new body has been provisionally named S/2005 S1.
Imaging scientists predicted the moon's presence and its orbital distance from Saturn after July 2004, when they saw a set of peculiar spiky and wispy features in the Keeler gap's outer edge. The similarities of the Keeler gap features to those noted in Saturn's F ring and the Encke gap led the scientists to conclude that a small body, a few kilometers across, was lurking in the center of the Keeler gap, awaiting discovery.
Also included here is a view of the same scene created by combining six individual, unmagnified frames used in the movie sequence. This digital composite view improves the overall resolution of the scene compared to that available in any of the single images.
These images were obtained with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 1, 2005, at a distance of approximately 1.1 million kilometers (708,000 miles) from Saturn. Resolution in the original image was 8 kilometers (5 miles) per pixel. The images in the movie sequence have been magnified in (the vertical direction only) by a factor of two to aid visibility of features caused within the gap by the moonlet.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging team is based at the Space Science Institute, Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov . For additional images visit the Cassini imaging team homepage http://ciclops.org .
Credit: NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute