Faults in Ius Chasma (3-D)
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
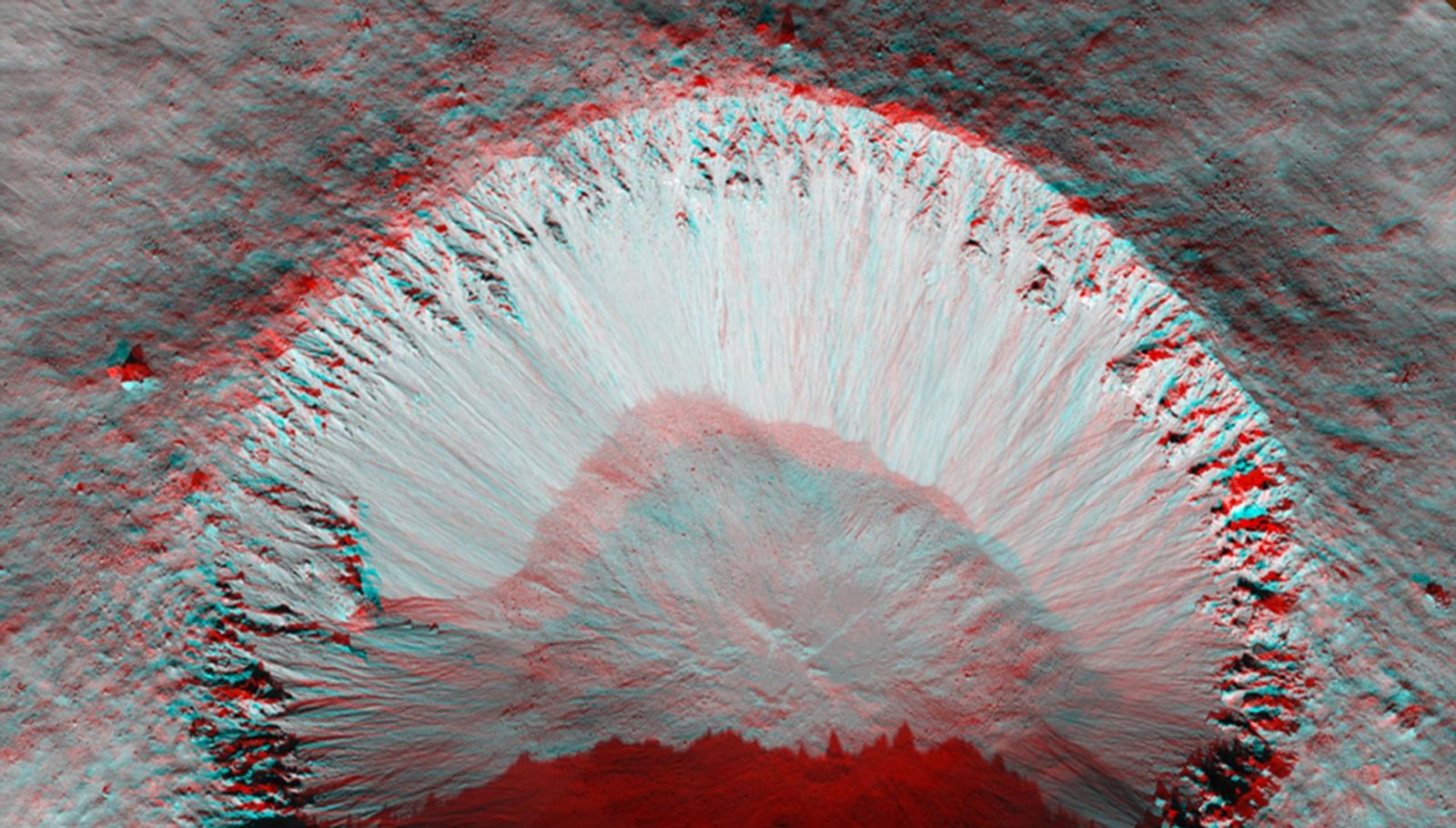
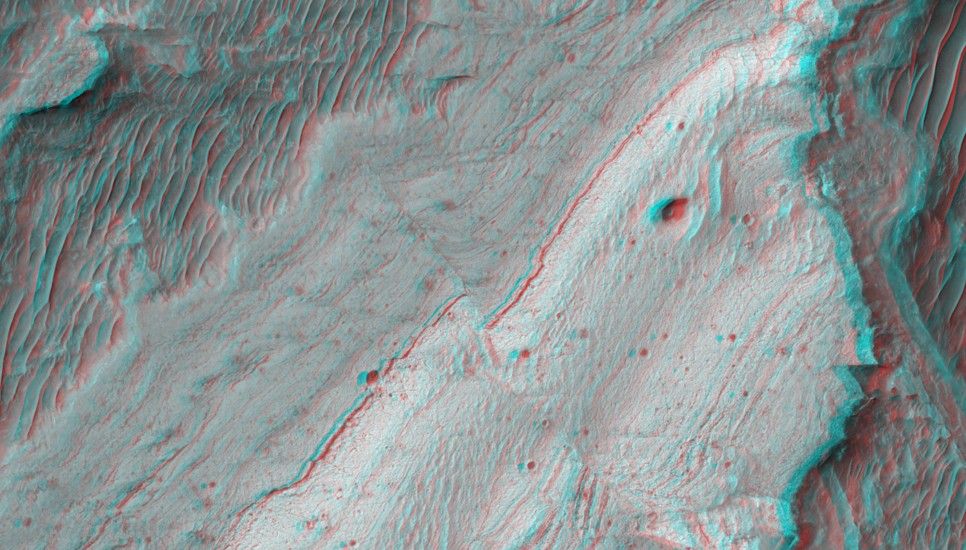
Ius Chasma is one of many steep-sided interconnected depressions (chasmata) that comprise Valles Marineris, the largest canyon system in the Solar System.
The chasma is approximately 900 kilometers long and is located in western Valles Marineris. The floor of Ius Chasma is between 8 to 10 kilometers deep and is divided by a prominent east-west trending ridge known as Geryon Montes.
The region in this image is located (approximately 7.8 degrees South, 279.5 degrees East) on the floor of Ius Chasma. A variety of light and medium-toned terrains and layered units of different rock types comprise the chasma floor. Prominent faults of various sizes have displaced and deformed these layered units and outcrops, some in a spectacular fashion.
The ejecta of small fresh-appearing impact craters formed in the light-toned units reveal the existence of a darker (likely basaltic) underlying substrate. Linear dunes are located on top of the lighter-tone outcropping units and are ubiquitous on the chasma floor. These dunes are oriented in a north-south direction and indicate prevailing westerly winds through the canyon.
Image source: https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_025020_1720