Sample Collection and Rock Analysis at ‘Wildcat Ridge’
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
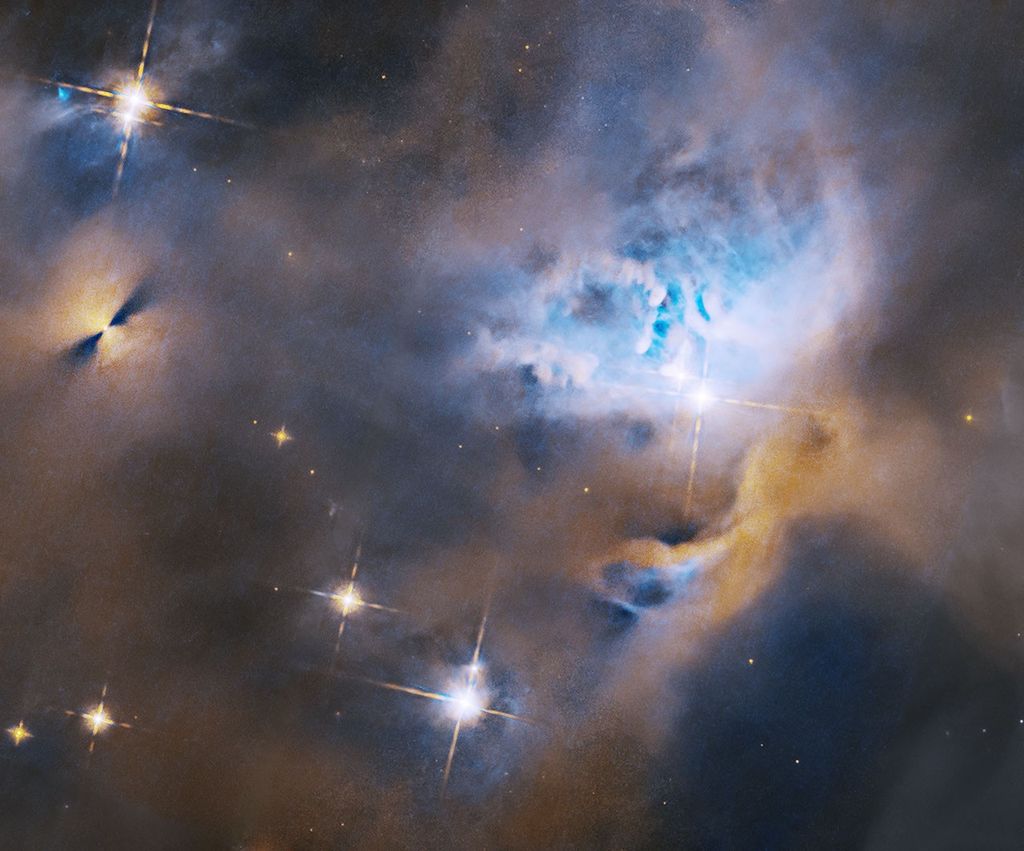
Composed of multiple images from NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover, this mosaic shows a rocky outcrop called “Wildcat Ridge,” where the rover extracted two rock cores and abraded a circular patch to investigate the rock’s composition.
The site is in the delta, a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake in Jezero Crater. Scientists consider this area one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life.
The images were obtained by the Mastcam-Z instrument on Aug. 4, 2022, the 518th Martian day, or sol, of the rover’s mission. For scale, the bright circular abrasion patch on the right is approximately 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter.
The color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences.
The rock cores obtained by Perseverance – each about the size of a piece of classroom chalk – were sealed in ultra-clean sample tubes. They are currently stored in the rover’s Sampling and Caching System.
The verification of ancient life on Mars carries an enormous burden of proof.
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect Perseverance’s sealed samples and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets.
For more about Perseverance: mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/
The verification of ancient life on Mars carries an enormous burden of proof.
For more about the Mars Sample Return campaign: mars.nasa.gov/msr