Shadow and Streamer-channels
| PIA Number | PIA11553 |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
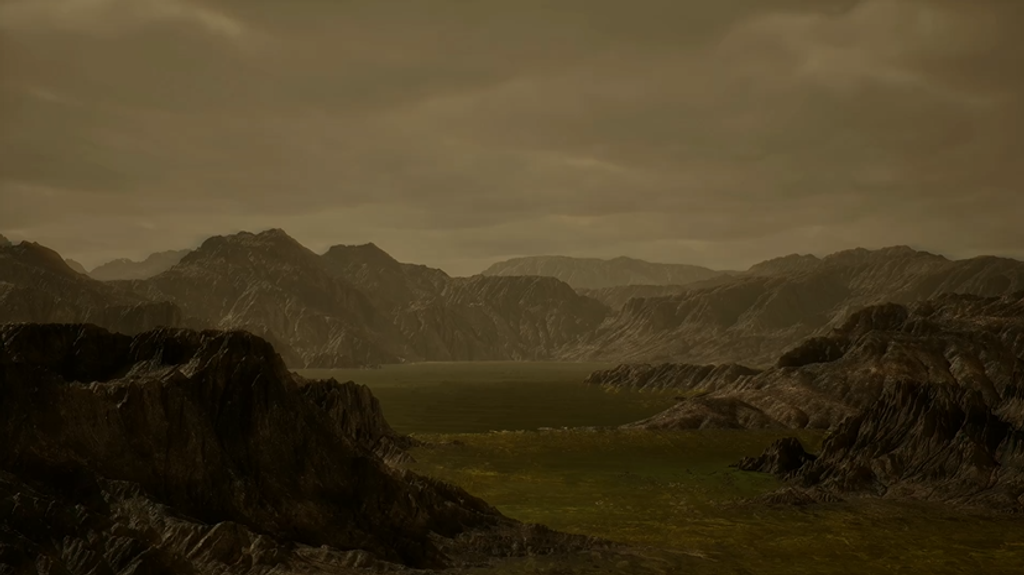
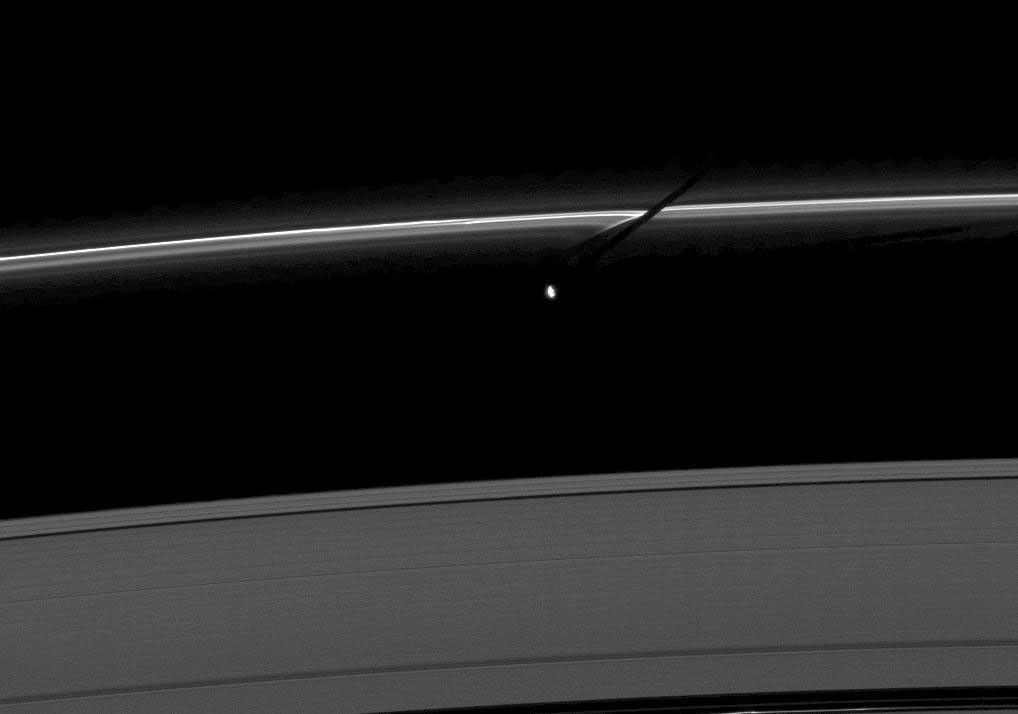
The moon Prometheus casts a shadow on the thin F ring marked with streamer-channels created by the moon in this image taken as Saturn approaches its August 2009 equinox.
The gravity of potato-shaped Prometheus (86 kilometers, or 53 miles across) periodically creates streamer-channels in the F ring. See Opening a Channel and Busy Moon to learn more. To watch a movie of this process, see Soft Collision.
The novel illumination geometry created as Saturn approaches its August 2009 equinox allows moons orbiting in or near the plane of Saturn's equatorial rings to cast shadows onto the rings. These scenes are possible only during the few months before and after Saturn's equinox which occurs only once in about 15 Earth years. To learn more about this special time and to see movies of moons' shadows moving across the rings, see Moon Shadow in Motion and Weaving a Shadow.
This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 52 degrees above the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on June 15, 2009. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.8 million kilometers (1.1 million miles) from Prometheus and at a Sun-Prometheus-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 85 degrees. Image scale is 11 kilometers (7 miles) per pixel.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Credit: NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute