Swimming in Dunes
| PIA Number | PIA08738 |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
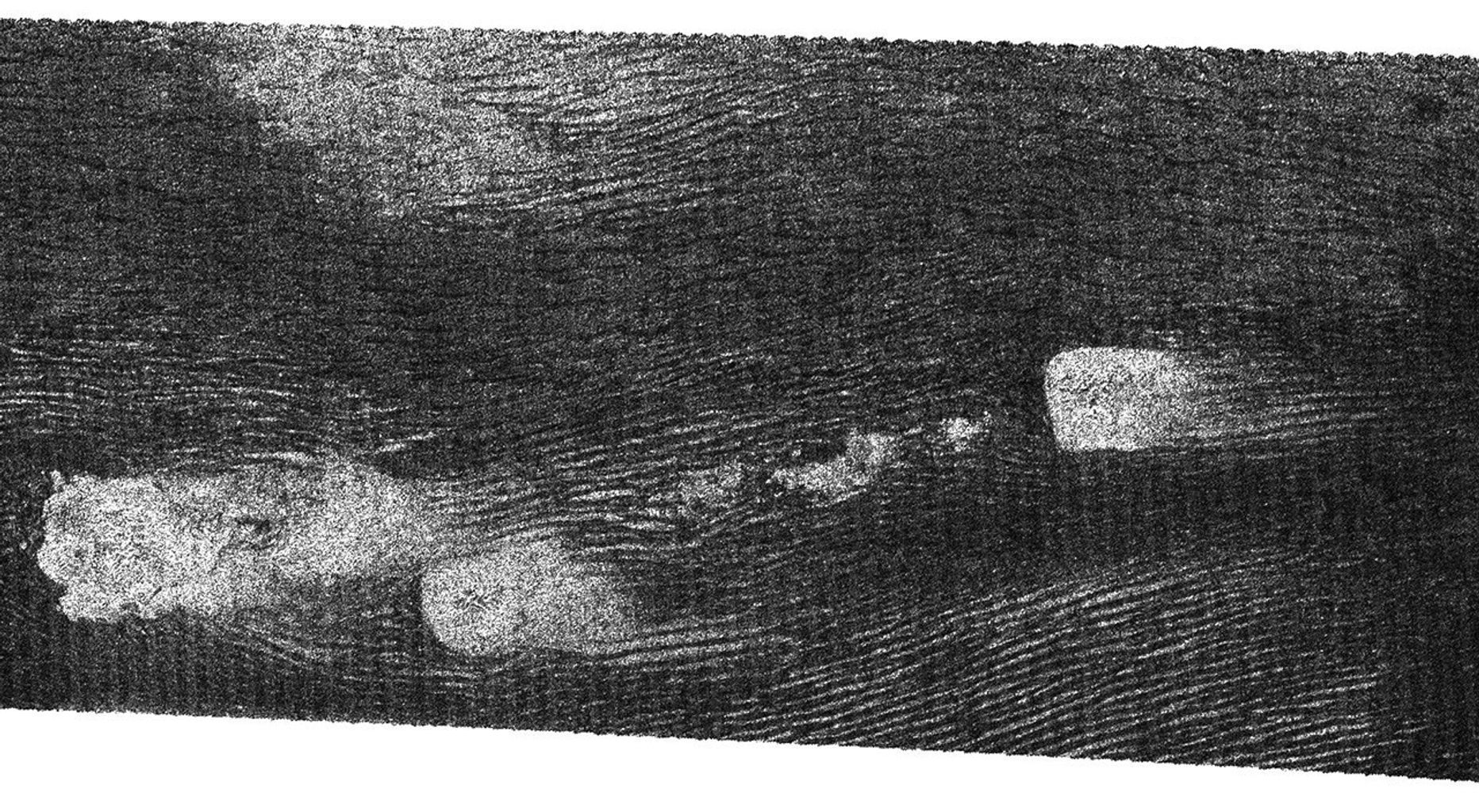
This image from Cassini's radar instrument was acquired by the Cassini radar instrument in synthetic aperture mode during a Sept. 7, 2006, flyby of Titan.
The image shows long, dark ridges similar to those seen in previous flybys. These are interpreted to be longitudinal dunes. Dunes are mostly an equatorial phenomenon on Titan, and the material forming them may be solid organic particles or ice coated with organic material. Spaced up to 3 kilometers (about 2 miles) apart, these dunes curve around bright features that may be high-standing topographic obstacles, in conformity with the wind patterns. The interaction between the two types of features is complex and not well understood, but clearly the topography and the dunes have influenced each other in other ways as well.
This image is centered at 44 degrees west longitude, 8 degrees north latitude and covers approximately 160 by 325 kilometers (99 by 202 miles) on Titan's surface. The smallest details in this image are about 500 meters (about 550 yards) across.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Credit: NASA/JPL