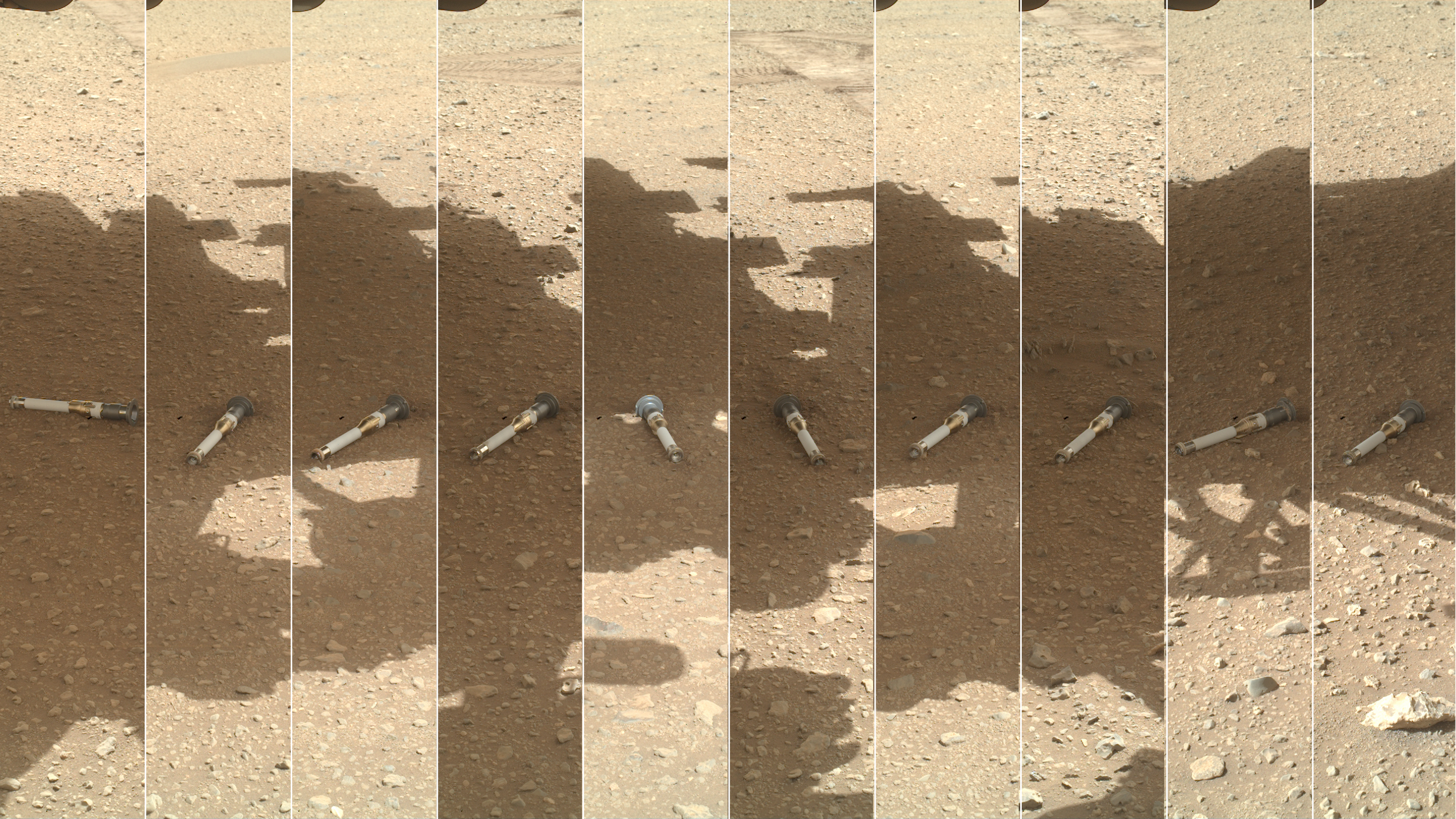
WATSON’s Photomontage of Mars Sample Depot
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
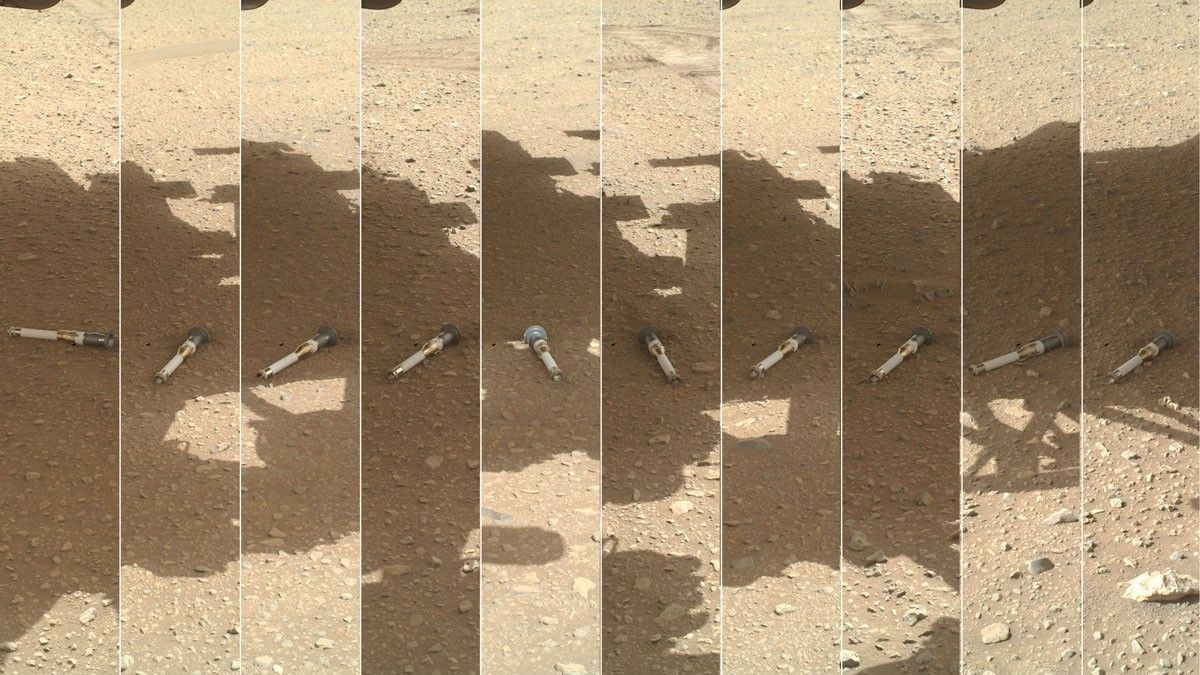
This photomontage shows each of the sample tubes shortly after they were deposited onto the surface by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover, as viewed by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera on the end of the rover’s 7-foot-long (2-meter-long) robotic arm.
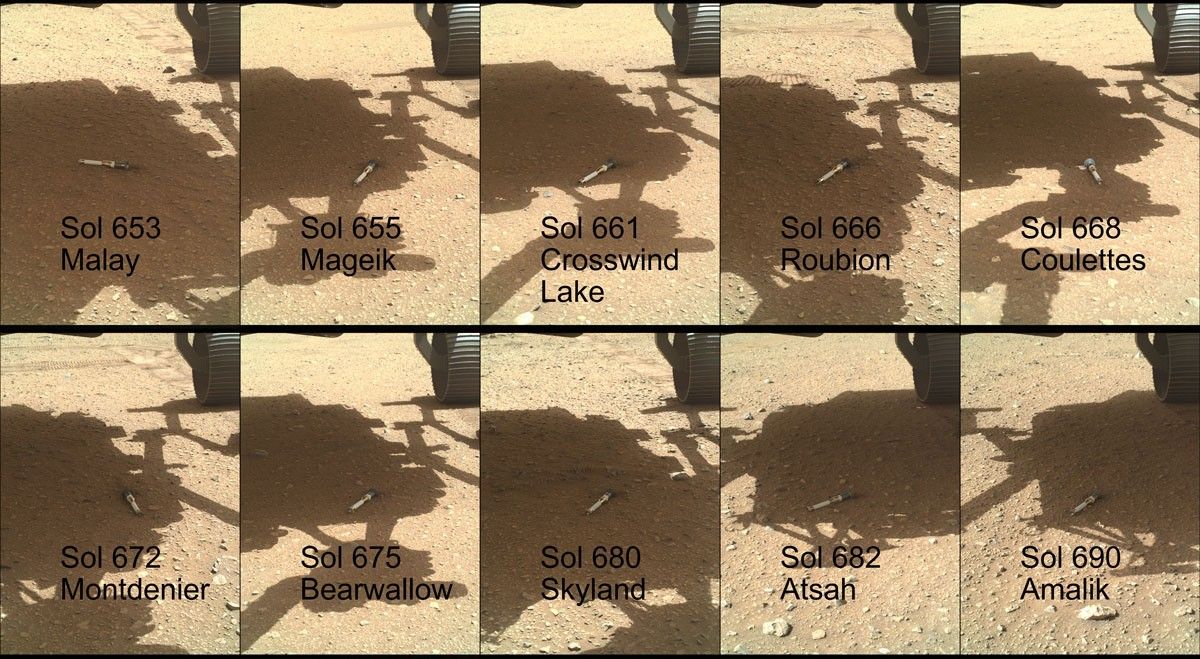
Shown, from left, are “Malay,” “Mageik,” “Crosswind Lake,” “Roubion,” “Coulettes,” “Montdenier,” “Bearwallow,” “Skyland,” “Atsah,” and “Amalik.” Deposited from Dec. 21, 2022, to Jan. 28, 2023, these samples make up the sample depot Perseverance built at “Three Forks,” a location within Mars’ Jezero Crater.
Figure A is an alternate montage annotated with the name of each sample and the Martian day, or sol, that it was deposited.
Perseverance’s sample depot is a collection of 10 sample tubes left on the Martian surface in a zig-zag pattern. These tubes represent a backup collection of rock cores and regolith (broken rock and dust) that could be recovered in the future by the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign, which aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study. Perseverance will be collecting more samples on its journey that will be considered the primary samples for return, but the mission team wants to make sure backups are available in case anything happens to the rover.
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL.