Latest NASA Science News
Stay up-to-date with the latest news from NASA Science as we explore the universe, solar system, sun and our home planet Earth.
Filters
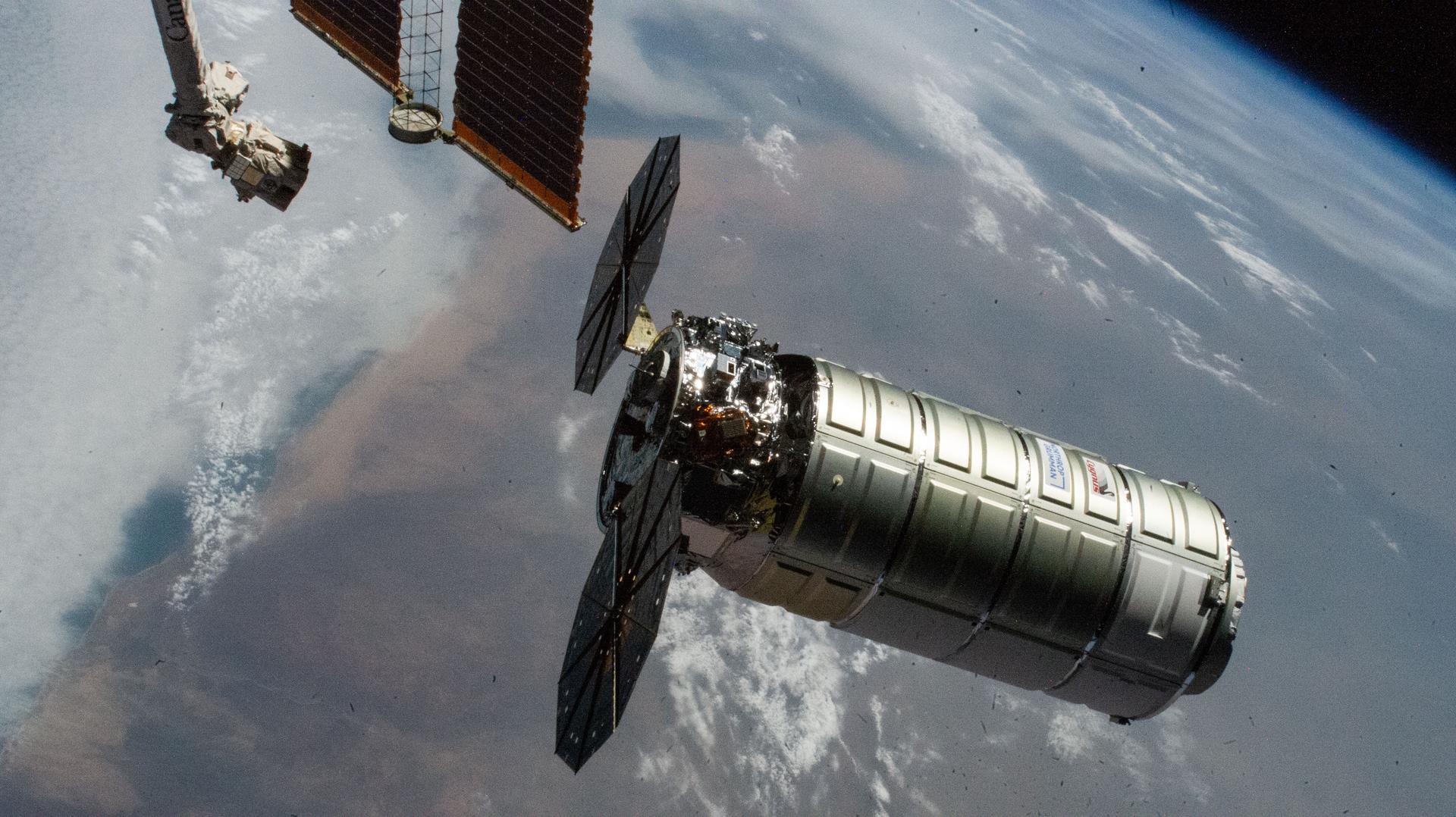

Media accreditation is open for the next launch to deliver NASA science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station. A Northrop Grumman Cygnus XL spacecraft will launch in April to the orbital laboratory on a SpaceX Falcon 9…

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process. These results were reported as part of NASA’s role in the International Asteroid Warning Network. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope…
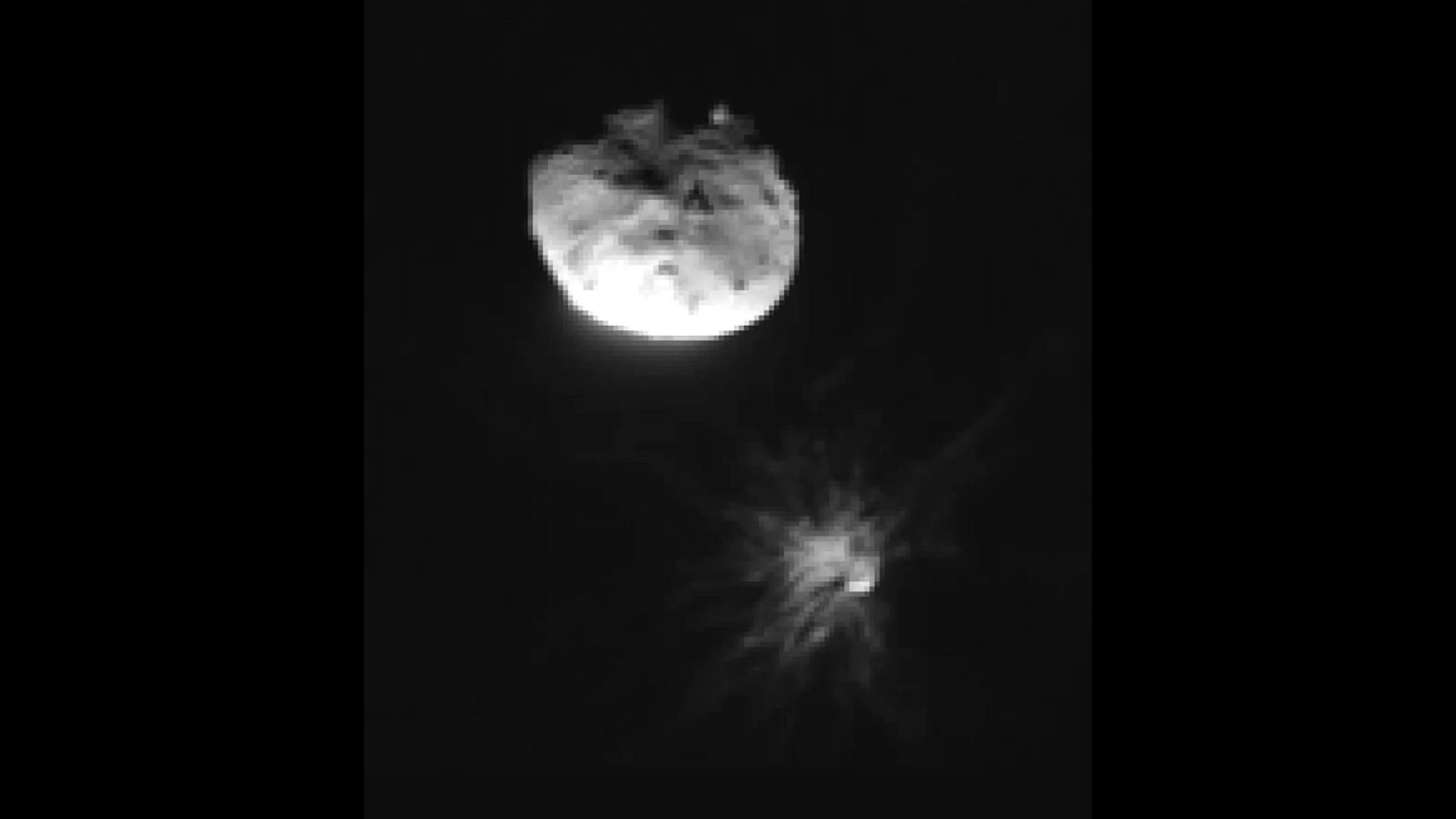
New research reveals that when NASA’s DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) spacecraft intentionally impacted the asteroid moonlet Dimorphos in September 2022, it didn’t just change the motion of Dimorphos around its larger companion, Didymos; the crash also shifted the orbit…
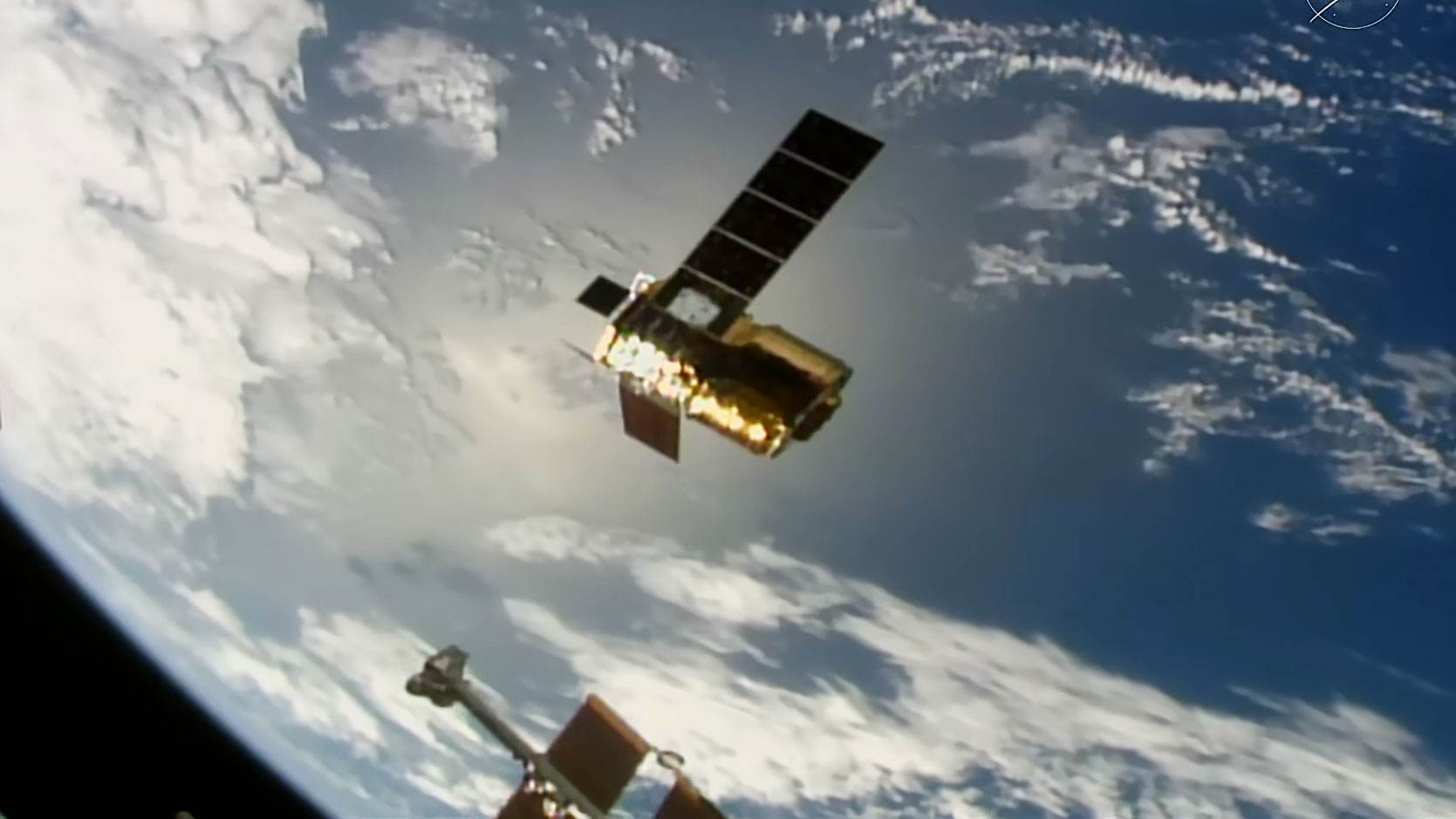

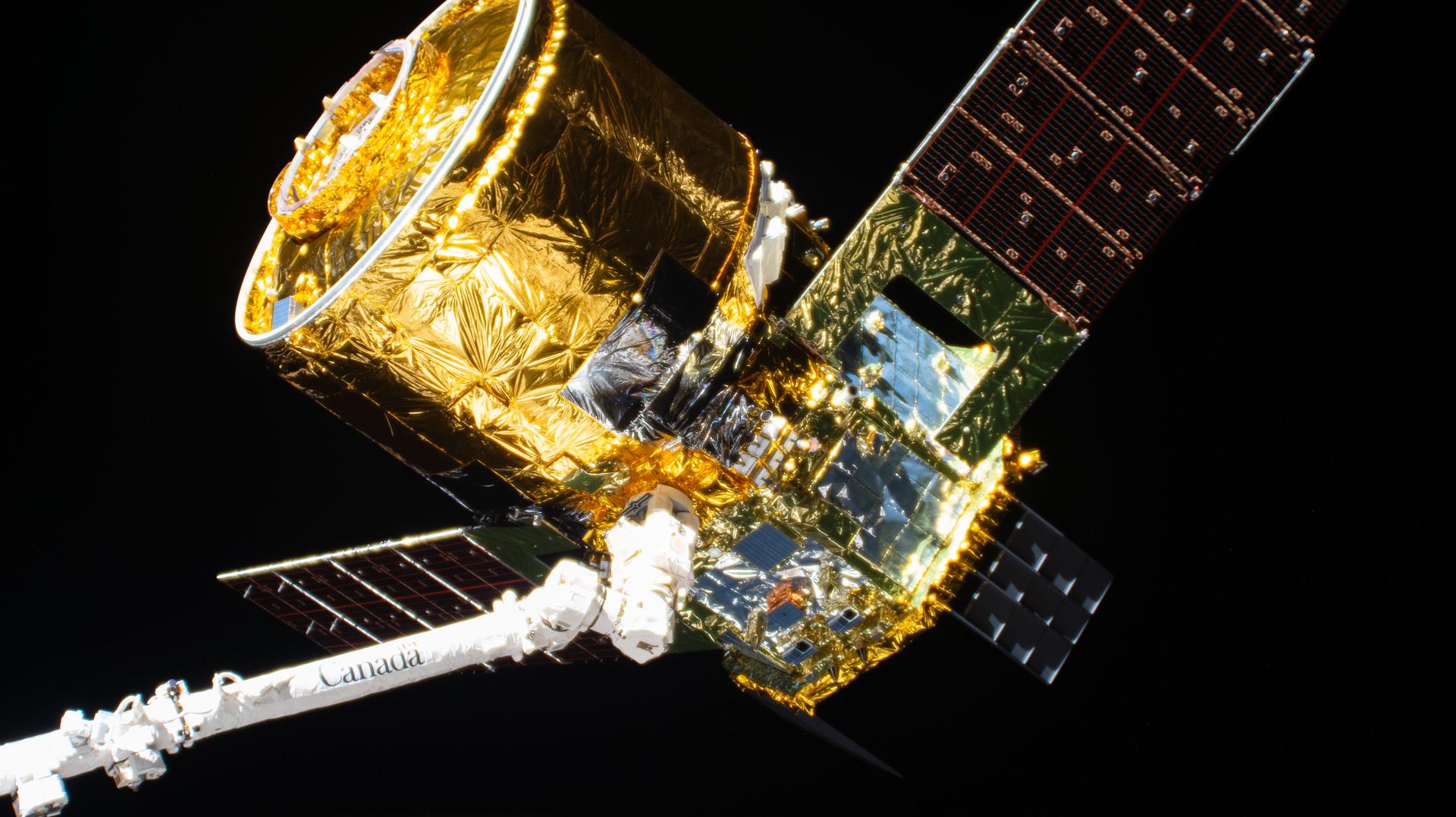
At 12 p.m. EST, JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s) HTV-X1 cargo spacecraft was released from the International Space Station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm, which earlier detached it from the Earth-facing port of the orbiting laboratory’s Harmony module.

NASA’s live coverage of the departure of JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s) uncrewed HTV-X1 cargo spacecraft from the International Space Station is underway on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and the agency’s YouTube channel.
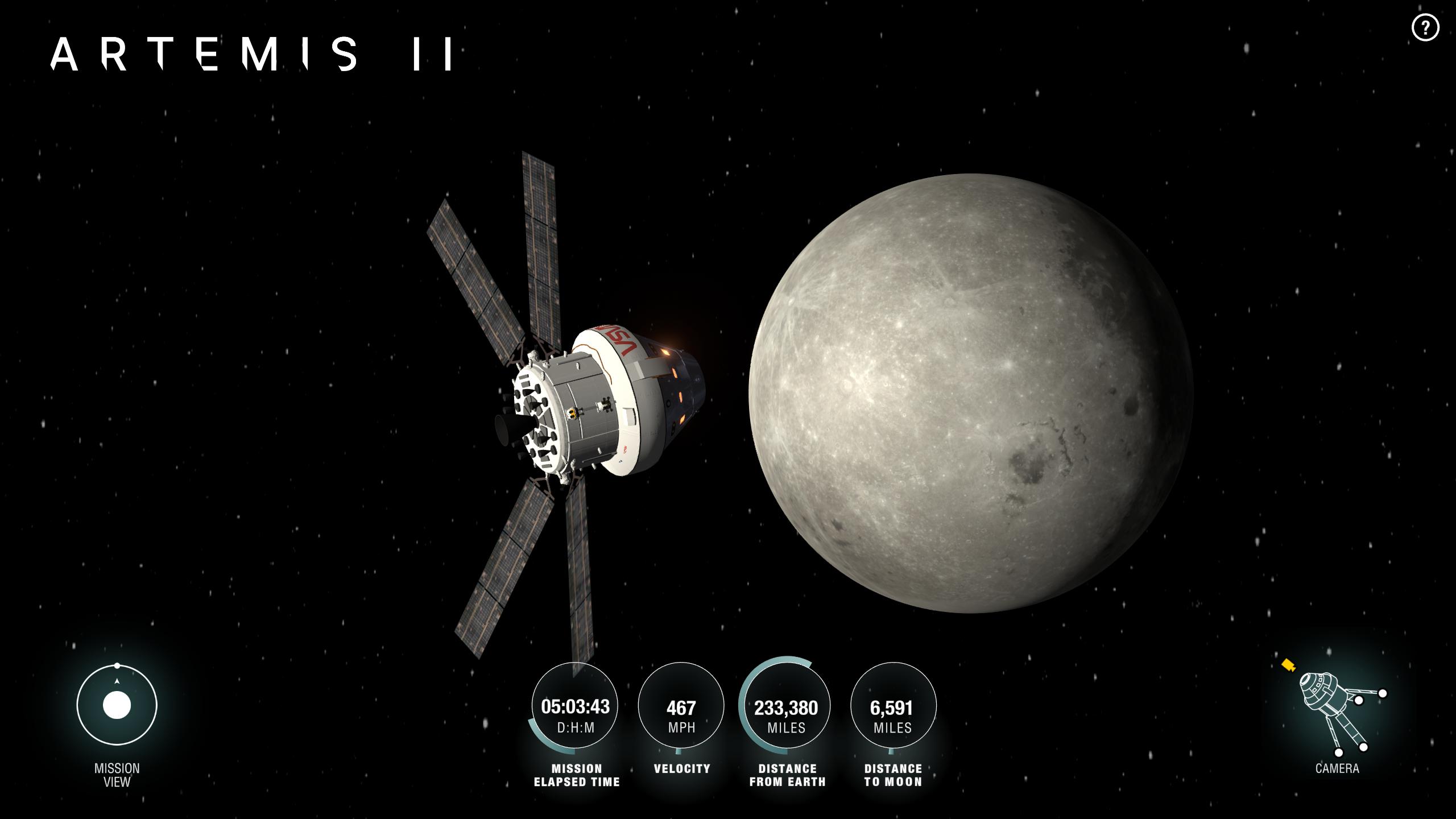
As NASA invites the public to follow the Artemis II mission as a crew of four astronauts venture around the Moon inside the agency’s Orion spacecraft, people around the world can pinpoint Orion during its journey using the Artemis Real-time…

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir trims the hair of fellow NASA astronaut Jack Hathaway in this March 1, 2026, image. Meir uses an electric razor attached to a vacuum that collects loose clippings to keep the station’s atmosphere clean in microgravity.…
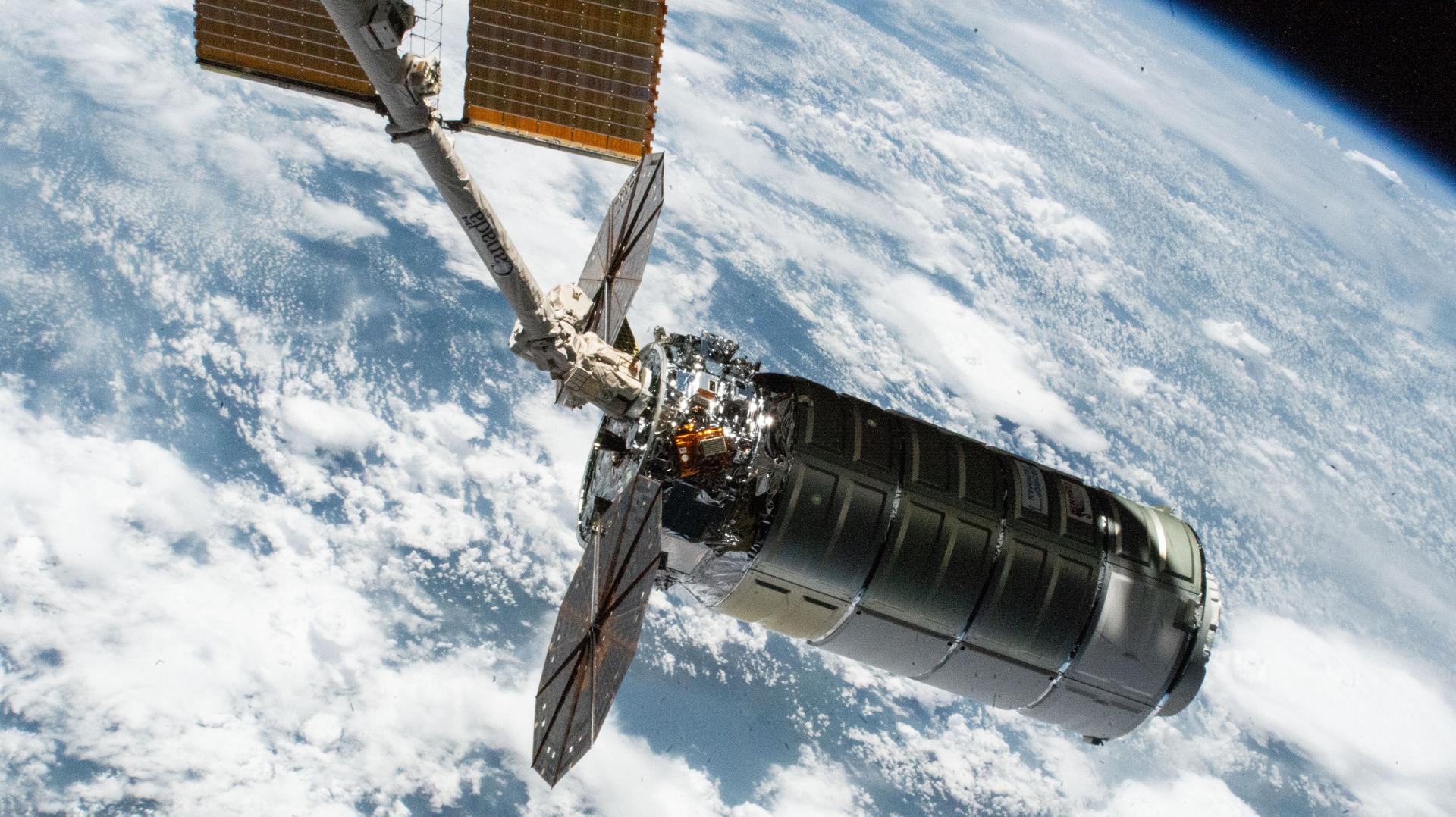

After delivering more than 11,000 pounds of supplies, science investigations, hardware, and other cargo to the International Space Station for NASA and its international partners, the Cygnus XL spacecraft supporting Northrop Grumman’s 23rd Commercial Resupply Services mission is scheduled to…
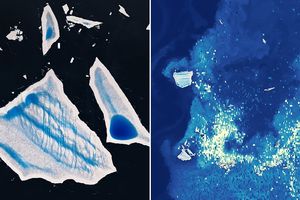
As Iceberg A-23A disintegrated, it shed meltwater that helped fuel an extensive phytoplankton bloom in the South Atlantic Ocean.
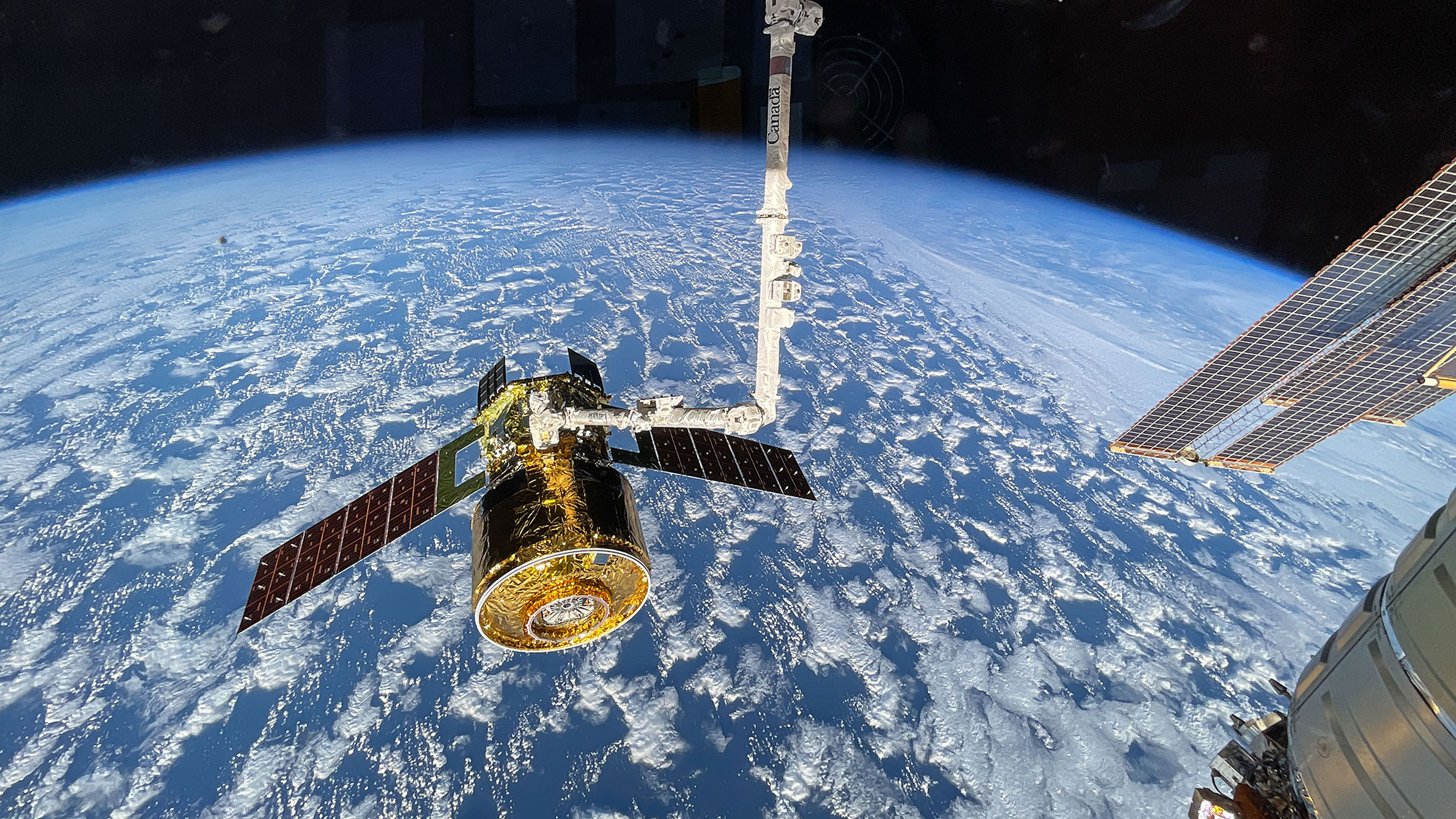

A JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) cargo spacecraft is in the grasp of the Canadarm2 robotic arm following its detachment from the International Space Station’s Harmony module on Thursday. The Expedition 74 crew continued its spacewalk preparations, transferred more cargo,…



























