Latest NASA Science News
Stay up-to-date with the latest news from NASA Science as we explore the universe, solar system, sun and our home planet Earth.
Filters

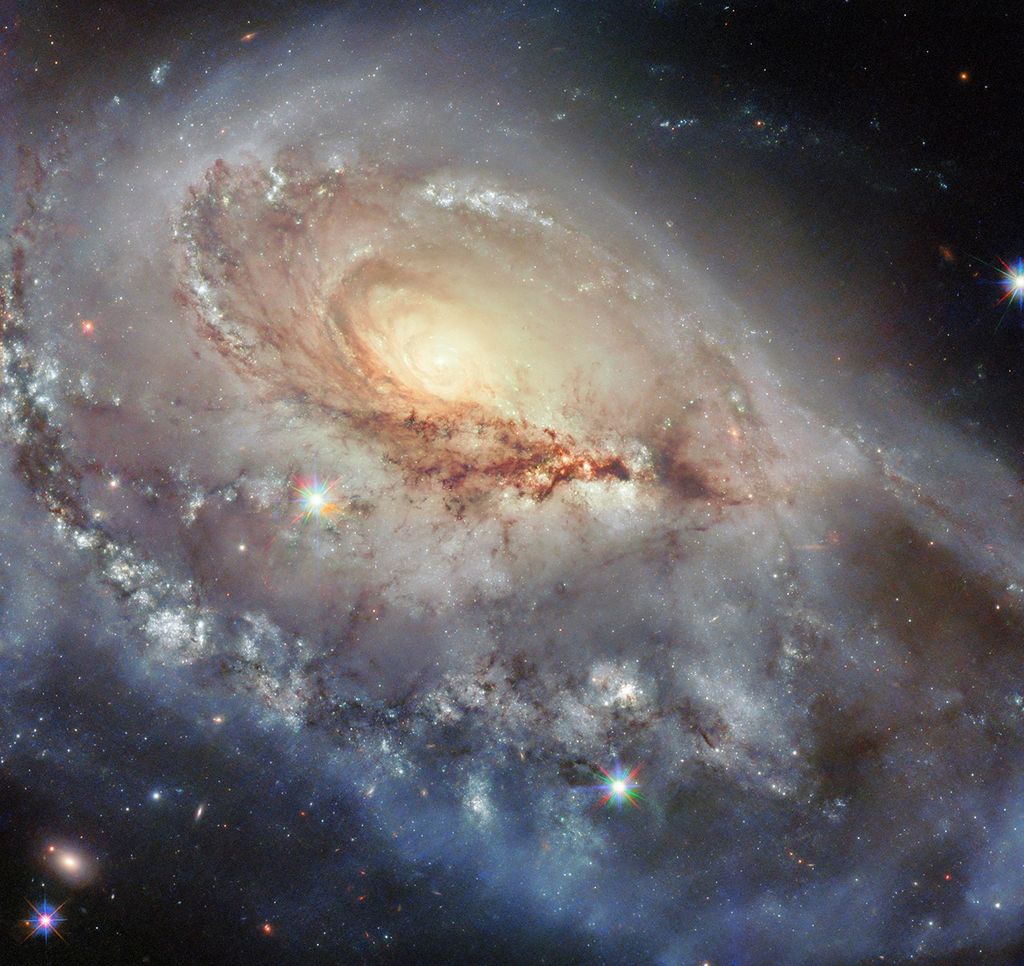
The spiral galaxy NGC 3596 is on display in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image that incorporates six different wavelengths of light. NGC 3596 is situated 90 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Leo, the Lion. British astronomer Sir…

In this May 1, 2025, photo taken by fellow NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers, Anne McClain works near one of the International Space Station’s main solar arrays during a spacewalk. During the May 1 spacewalk – McClain’s third and Ayers’ first…

NASA’s coverage of the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse has earned two nominations for the 46th Annual News & Documentary Emmy Awards. The Academy of Television Arts & Sciences announced the nominations on May 1, recognizing NASA’s outstanding work…

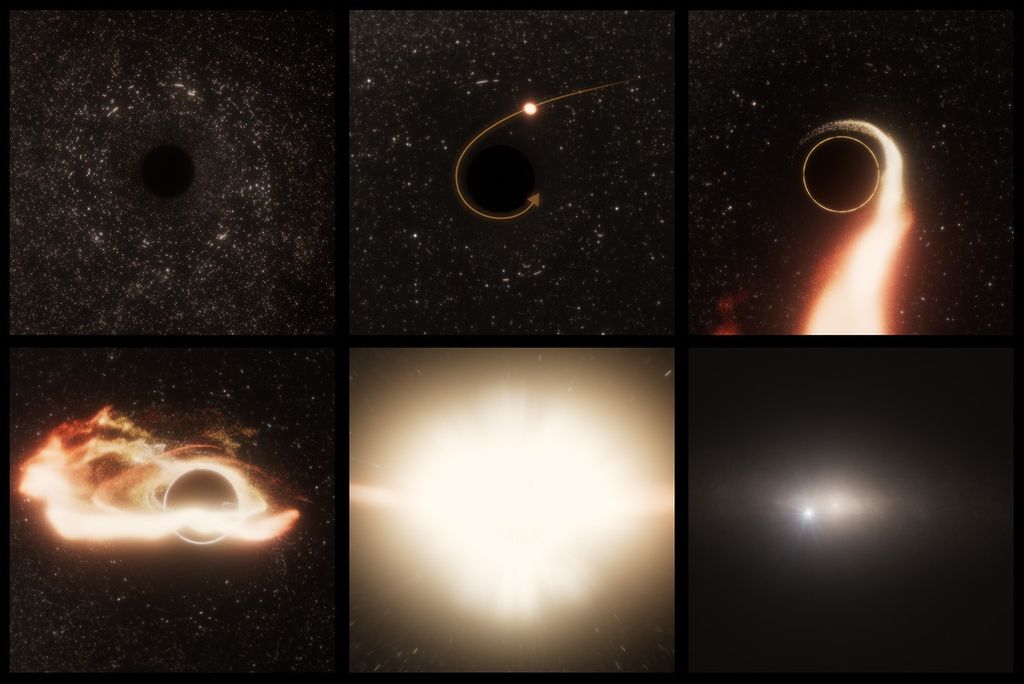
NASA released three new pieces of cosmic sound Thursday that are associated with the densest and darkest members of our universe: black holes. These scientific productions are sonifications — or translations into sound — of data collected by NASA telescopes…

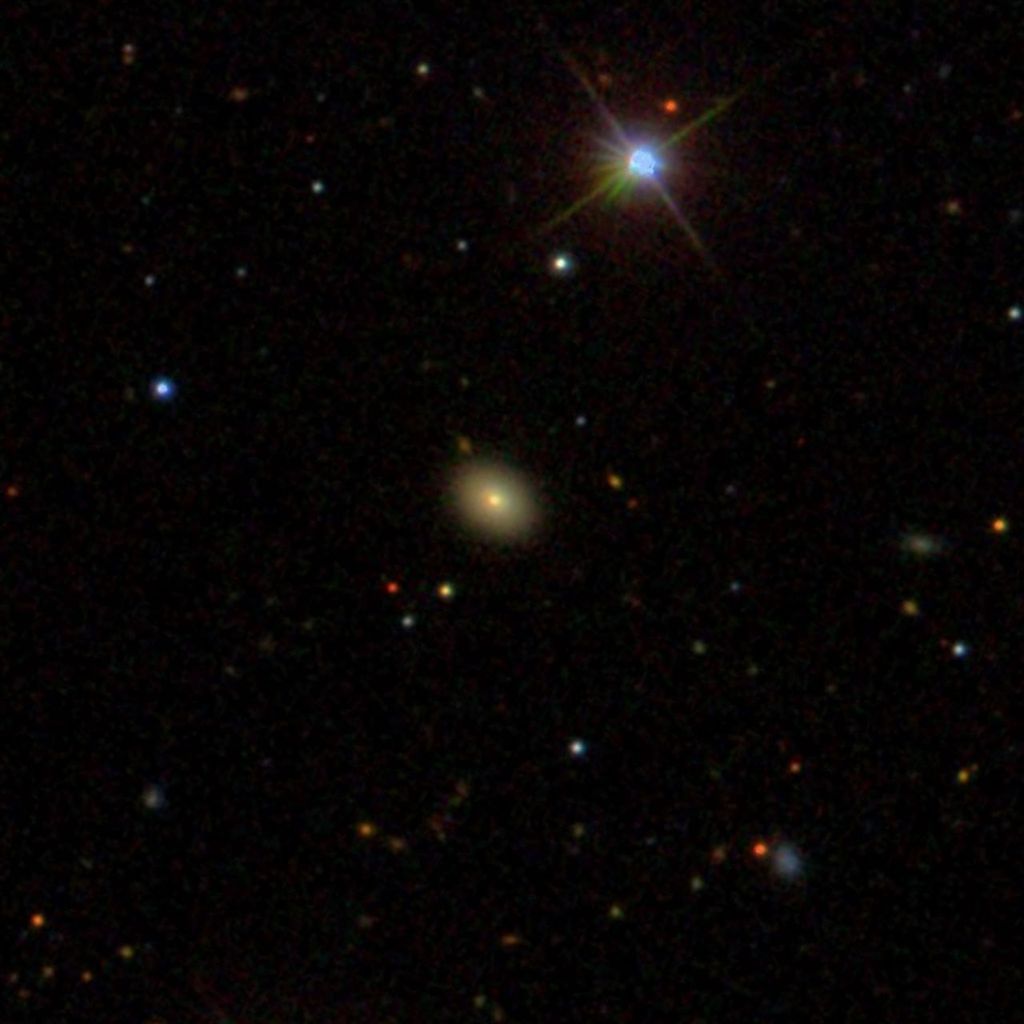
Like a scene out of a sci-fi movie, astronomers using NASA telescopes have found “Space Jaws.” Lurking 600 million light-years away, within the inky black depths between stars, there is an invisible monster gulping down any wayward star that plummets…

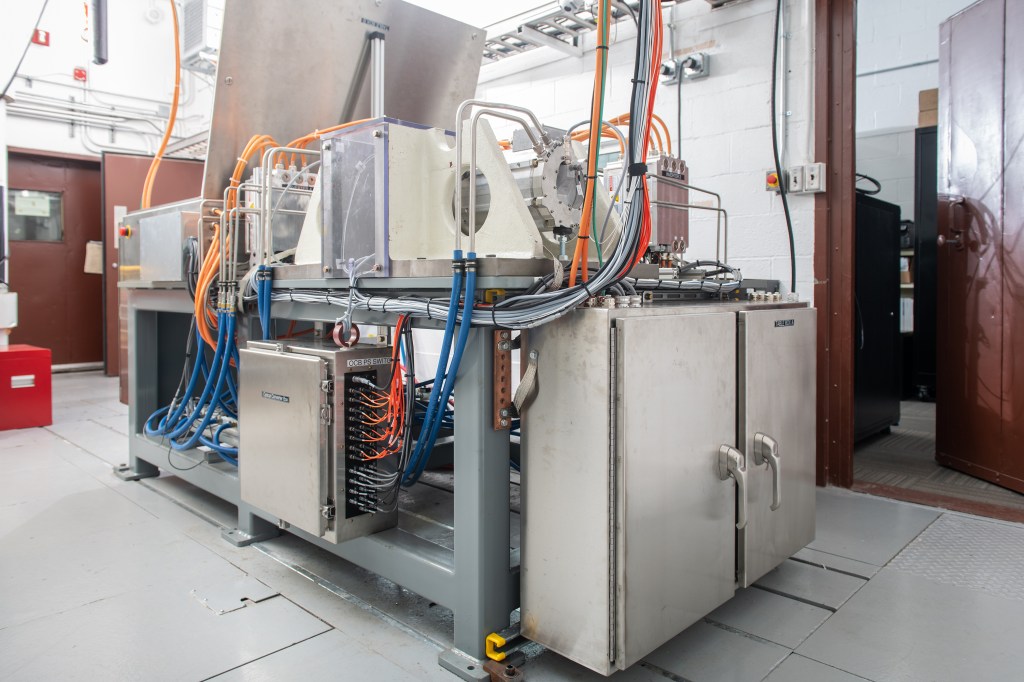
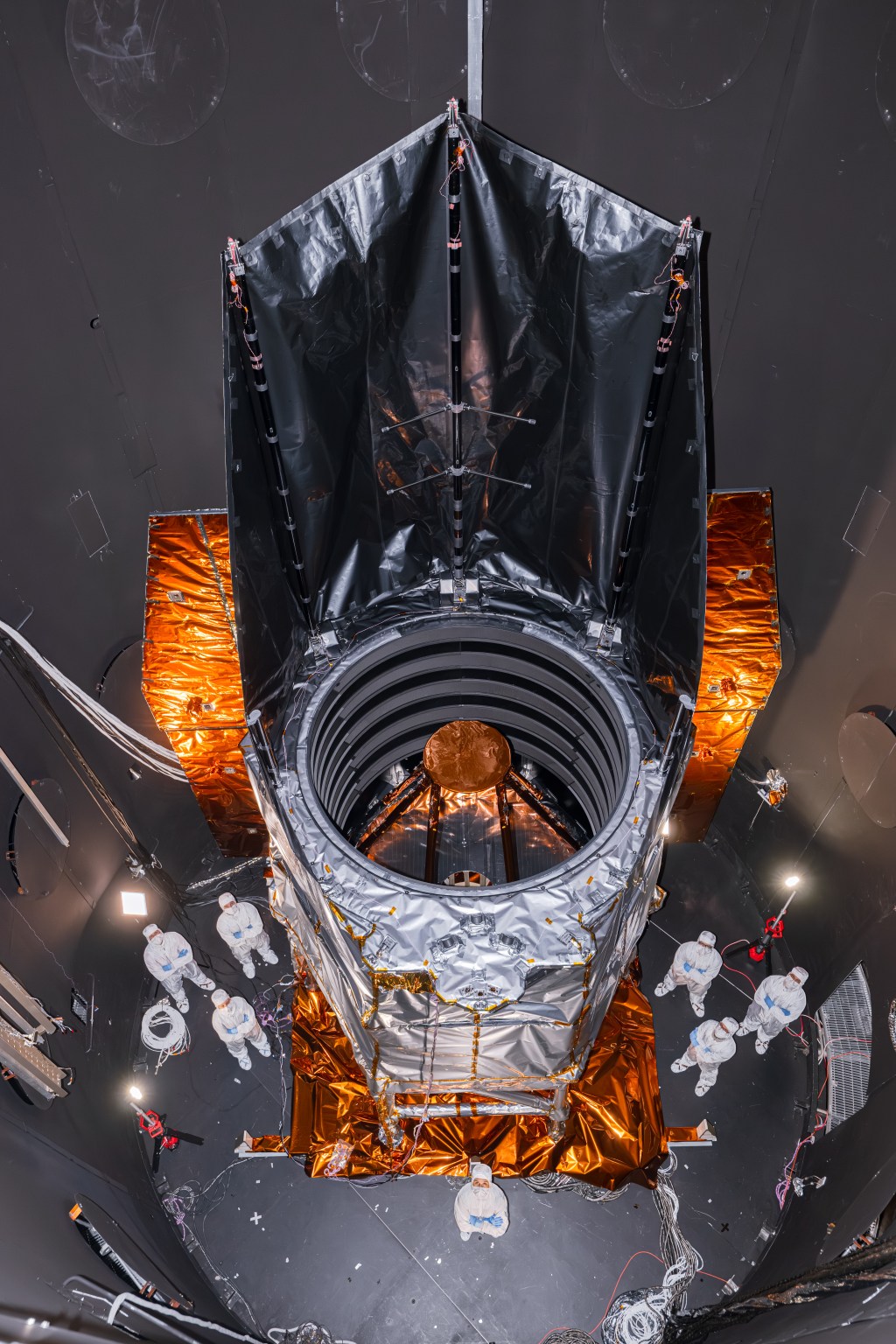
NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) has successfully completed thermal vacuum testing at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of its journey toward launch as soon as this fall. As a modern-day celestial cartographer,…

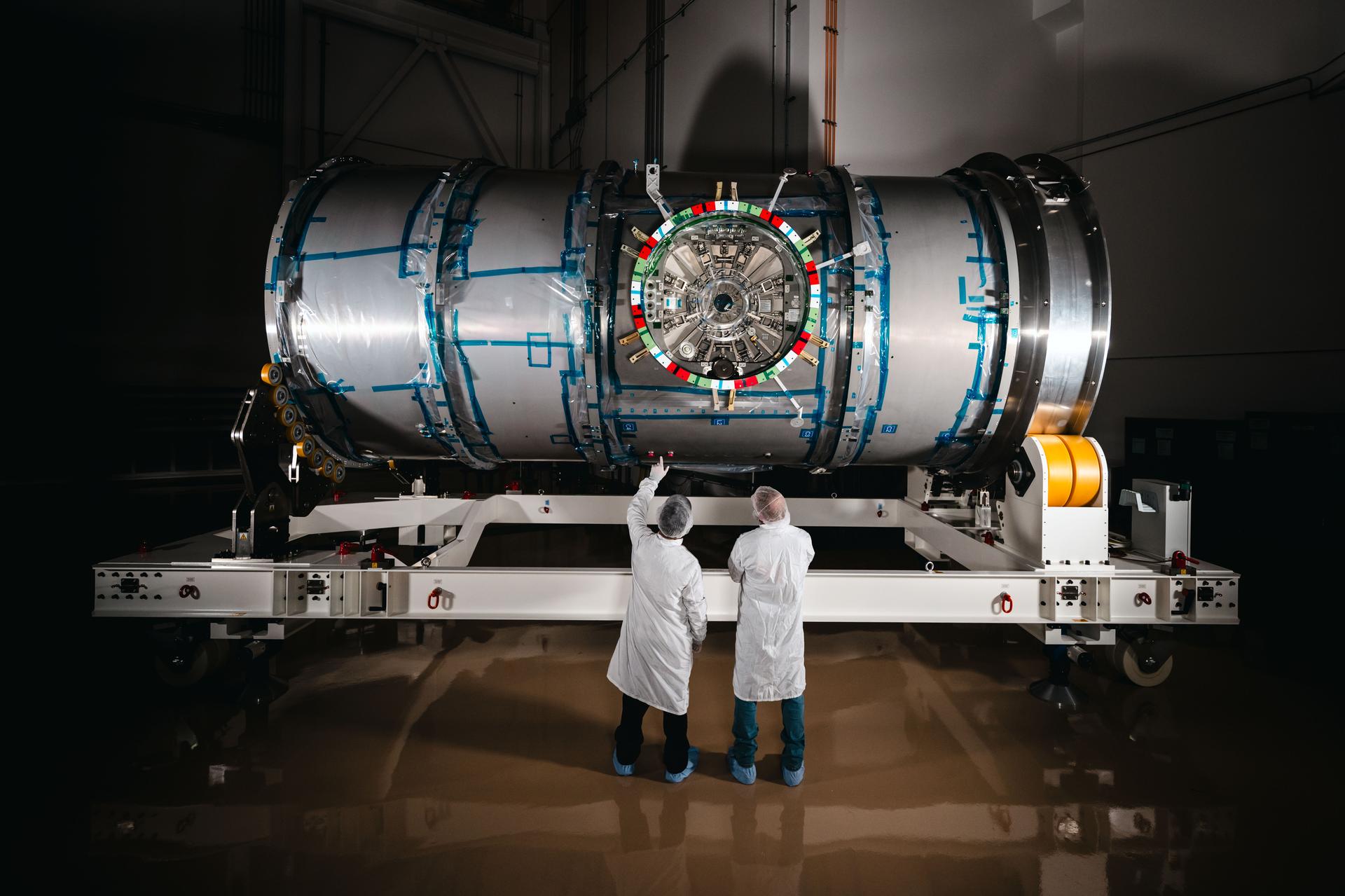
One half of NASA’s nearly complete Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope just passed a lengthy test to ensure it will function properly in the space environment. “This milestone tees us up to attach the flight solar array sun shield to…

In July 2022, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope made its public debut with a series of breathtaking images. Among them was an ethereal landscape nicknamed the Cosmic Cliffs. This glittering realm of star birth is the subject of a new…

The blazar BL Lacertae, a supermassive black hole surrounded by a bright disk and jets oriented toward Earth, provided scientists with a unique opportunity to answer a longstanding question: How are X-rays generated in extreme environments like this? NASA’s IXPE…

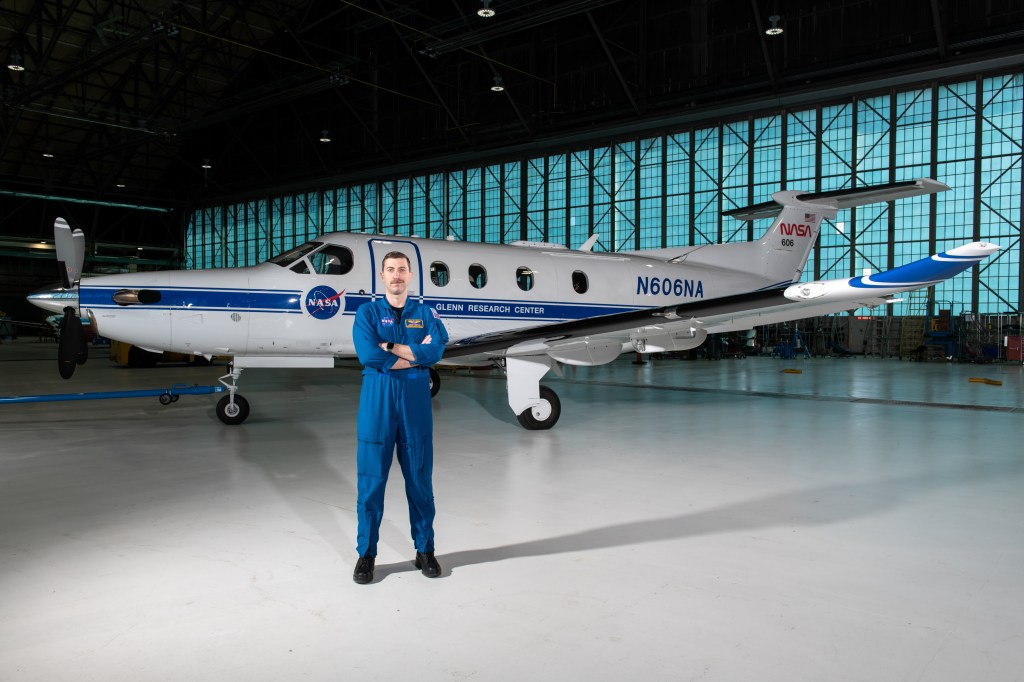
Engineers, technicians, mission planners, and the four astronauts set to fly around the Moon next year on Artemis II, NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission, are rapidly progressing toward launch. At the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, teams are working…