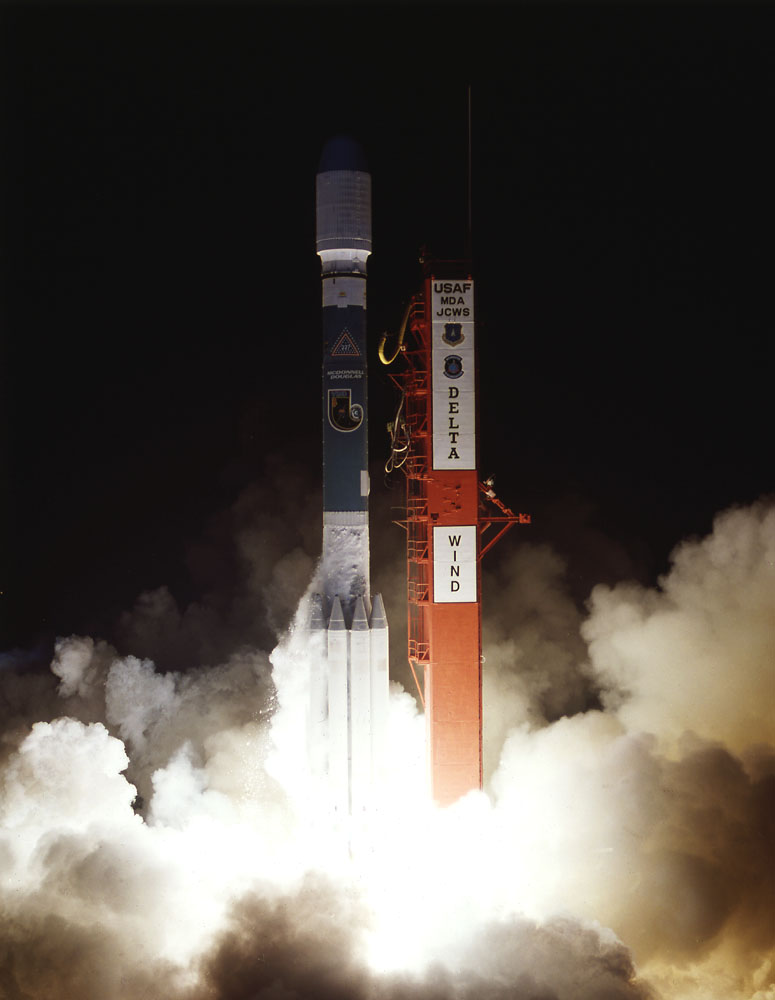
Picture it: 1994. The first World Wide Web conference took place in Geneva, the first Chunnel train traveled under the English Channel, and just three years after the end of the Cold War, the first Russian instrument on a U.S. spacecraft launched into deep space from Cape Canaveral. The mission to study the solar wind, aptly named Wind, held promise for heliophysicists and astrophysicists around the world to investigate basic plasma processes in the solar wind barreling toward Earth — key information for helping us understand and potentially mitigate the space weather environment surrounding our home planet.
Thirty years later, Wind continues to deliver on that promise from about a million miles away at the first Earth-Sun Lagrange Point (L1). This location is gravitationally balanced between Earth and the Sun, providing excellent fuel economy that requires mere puffs of thrust to stay in place.
According to Lynn Wilson, who is the Wind project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, fuel is only one indicator of Wind’s life expectancy, however. “Based on fuel alone, Wind can continue flying until 2074,” he said. “On the other hand, its ability to return data hinges on the last surviving digital tape recorder onboard.”
Wind launched with two digital tape recorders to record data from all the instruments on the spacecraft and provide reports on the spacecraft’s thermal conditions, orientation, and overall health. Each recorder has two tape decks, A and B, which Wilson affectionately refers to as “fancy eight-tracks.”
After six years of service, the first digital tape recorder failed in 2000 along with its two tape decks, forcing mission operators to switch to the second one. Tape Deck A on that one started showing signs of wear in 2016, so the mission operators now use Tape Deck B as the primary deck, with A as a backup.
“They built redundancy into the digital tape recorder system by building two of them, but you can never predict how technology will perform when it’s a million miles away, bathing in ionizing radiation,” said Wilson. “We’re fortunate that after 30 years, we still have two functioning tape decks.”
Bonus Science
When Wind launched on Nov. 1, 1994, nobody could have possibly predicted that exactly 30 years later, NASA would be kicking off “Bonus Science” month in the Heliophysics Big Year. Beyond the mission’s incredible track record of mesmerizing discoveries about the solar wind — some detailed on its 25th anniversary — Wind continues to deliver with bonus science abound.
Opportunity and Collaborative Discovery
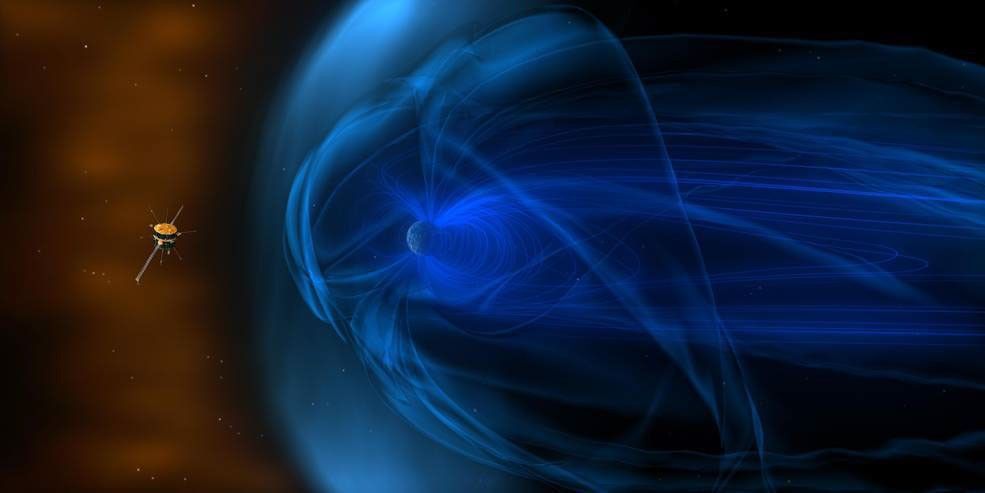
Along its circuitous journey to L1, Wind dipped in and out of Earth’s magnetosphere more than 65 times, capturing the largest whistler wave — a low-frequency radio wave racing across Earth’s magnetic field — ever recorded in Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts. Wind also traveled ahead of and behind Earth — about 150 times our planet’s diameter in both directions, informing potential future missions that would operate in those areas with extreme exposure to the solar wind. It even took a side quest to the Moon, cruising through the lunar wake, a shadow devoid of solar wind on the far side of the Moon.
Later, from its permanent home at L1, Wind was among several corroborating spacecraft that helped confirm what scientists believe is the brightest gamma-ray burst to occur since the dawn of human civilization. The burst, GRB 221009A, was first detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope in October 2022. Although not in its primary science objectives, Wind carries two bonus instruments designed to observe gamma-ray bursts that helped scientists confirm the burst’s origin in the Sagitta constellation.
Academic Inspiration
More than 7,200 research papers have been published using Wind data, and the mission has supported more than 100 graduate and post-graduate degrees.
Wilson was one of those degree candidates. When Wind launched, Wilson was in sixth grade, on the football, baseball, and wrestling teams, with spare time spent playing video games and reading science fiction. He had a knack for science and considered becoming a medical doctor or an engineer before committing to his love of physics, which ultimately led to his current position as Wind’s project scientist. While pursuing his doctorate, he worked with Adam Szabo who was the Wind project scientist at NASA Goddard at the time and used Wind data to study interplanetary collisionless shock waves. Szabo eventually hired Wilson to work on the Wind mission team at Goddard.
Also in sixth grade at the time, Joe Westlake, NASA Heliophysics division director, was into soccer and music, and was a voracious reader consumed with Tolkein’s stories about Middle Earth. Now he leads the NASA office that manages Wind.
“It’s amazing to think that Lynn Wilson and I were in middle school, and the original mission designers and scientists have long since retired,” said Westlake. “When a mission makes it to 30 years, you can’t help but be inspired by the role it has played not only in scientific discovery, but in the careers of multiple generations of scientists.”
By Erin Mahoney
NASA Headquarters, Washington