Asteroids Exploration
NASA has sent several robotic spacecraft to encounter asteroids up close. The agency also uses telescopes to scan the skies for asteroids. Here are highlights from some of those missions.
Featured NASA Asteroid Missions
-
NEO Surveyor
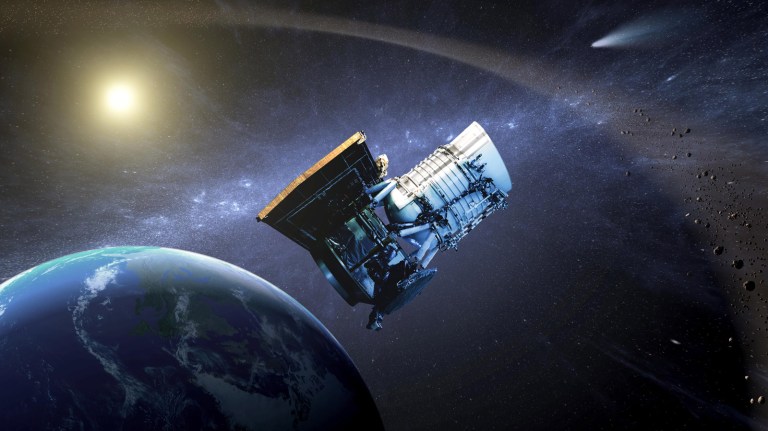
Near-Earth Object (NEO) Surveyor will be NASA's first space telescope specifically designed to hunt asteroids and comets that may be potential hazards to Earth. Scheduled to launch in next few years, NEO Surveyor's sensitive infrared detectors will let it track the most elusive near-Earth objects.
 In this illustration showing NEO Surveyor, NASA's next-generation Near-Earth Object hunter, the spacecraft floats in an infrared starfield containing stars, star clusters, gas, and dust. More than 100 asteroids can be seen as red dots, with some of them visible in a track that shows how they were captured at different times as they marched across the sky. This starfield was observed by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, during its primary all-sky survey in March 2010 before it was put into hibernation a year later. In December 2013, the space telescope was reactivated to search for more asteroids as the NEOWISE mission.
In this illustration showing NEO Surveyor, NASA's next-generation Near-Earth Object hunter, the spacecraft floats in an infrared starfield containing stars, star clusters, gas, and dust. More than 100 asteroids can be seen as red dots, with some of them visible in a track that shows how they were captured at different times as they marched across the sky. This starfield was observed by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, during its primary all-sky survey in March 2010 before it was put into hibernation a year later. In December 2013, the space telescope was reactivated to search for more asteroids as the NEOWISE mission. -
WISE/NEOWISE
Engineers on NASA’s NEOWISE (Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) mission commanded the spacecraft to turn off its transmitter for the last time on Aug. 8, 2024. This concluded more than 10 years of its planetary defense mission to search for asteroids and comets, including those that could pose a threat to Earth.
 Artist’s concept of NASA's WISE (Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) spacecraft, which was an infrared-wavelength astronomical space telescope active from December 2009 to February 2011. In September 2013 the spacecraft was assigned a new mission as NEOWISE to help find near-Earth asteroids and comets.
Artist’s concept of NASA's WISE (Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) spacecraft, which was an infrared-wavelength astronomical space telescope active from December 2009 to February 2011. In September 2013 the spacecraft was assigned a new mission as NEOWISE to help find near-Earth asteroids and comets. -
OSIRIS-REx/OSIRIS-APEX
Launched on Sept. 8, 2016, NASA's OSIRIS-REx arrived at near-Earth asteroid Bennu in 2018, and collected a sample of dust and rocks. On Sept. 24, 2023, the spacecraft flew by Earth and dropped off the asteroid sample capsule. It didn't land, and has a new assignment and a new name: It's now called OSIRIS-APEX and will explore asteroid Apophis.
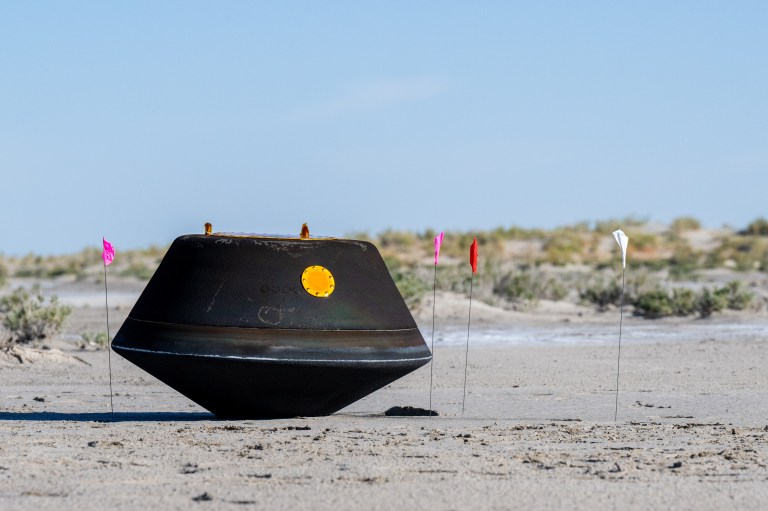 The sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is seen shortly after touching down in the desert, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft.
The sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is seen shortly after touching down in the desert, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. -
Psyche
The Psyche spacecraft is on its way to a unique metal-rich asteroid with the same name, orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. By August 2029 the spacecraft will begin exploring asteroid Psyche, which scientists think may be the partial core of a planetesimal, a building block of an early planet.
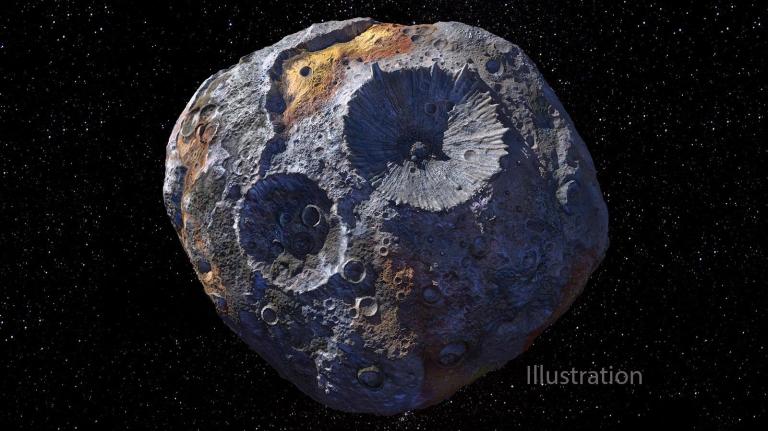 This illustration depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
This illustration depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. -
Lucy
NASA's Lucy mission will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids in the solar system’s main asteroid belt, and Trojan asteroids that share an orbit around the Sun with Jupiter. Launched on Oct. 16, 2021, Lucy has already made discoveries. On Nov. 1, 2023, Lucy made its first asteroid encounter - an asteroid with a contact binary asteroid as its moonlet.
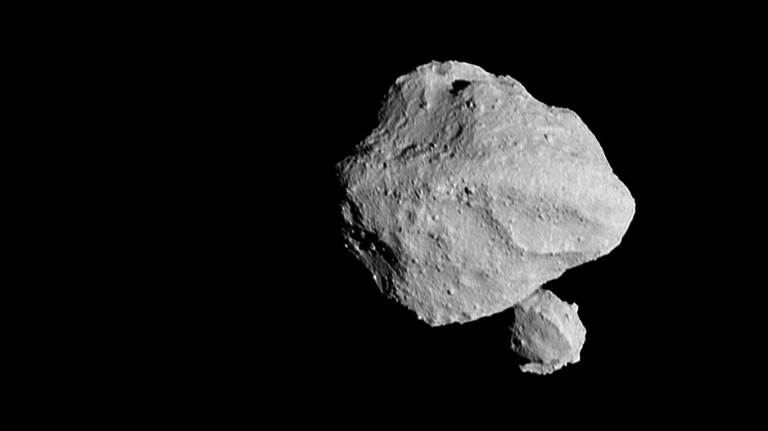

-
DART
NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) – the world’s first planetary defense technology demonstration – successfully impacted asteroid Dimorphos on Sept. 27, 2022, in the agency’s first attempt to move an asteroid in space. Dimorphos is a moonlet to asteroid Didymos.
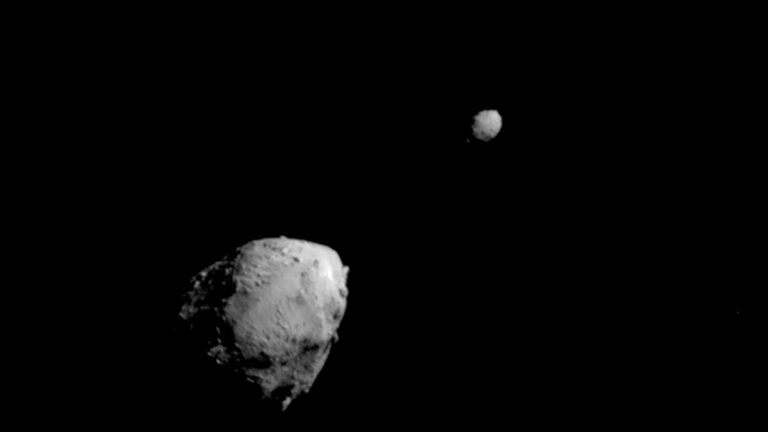 NASA's DART spacecraft captured this view of asteroids Didymos, and its moonlet Dimorphos, moments before DART intentionally impacted the moonlet.
NASA's DART spacecraft captured this view of asteroids Didymos, and its moonlet Dimorphos, moments before DART intentionally impacted the moonlet. -
Dawn
NASA's Dawn spacecraft was launched in 2007 to explore asteroid Vesta, the second most massive body in the main asteroid belt. Dawn arrived at Vesta in 2011, then orbited and explored Vesta for over a year before leaving in September 2012 to explore dwarf planet Ceres.
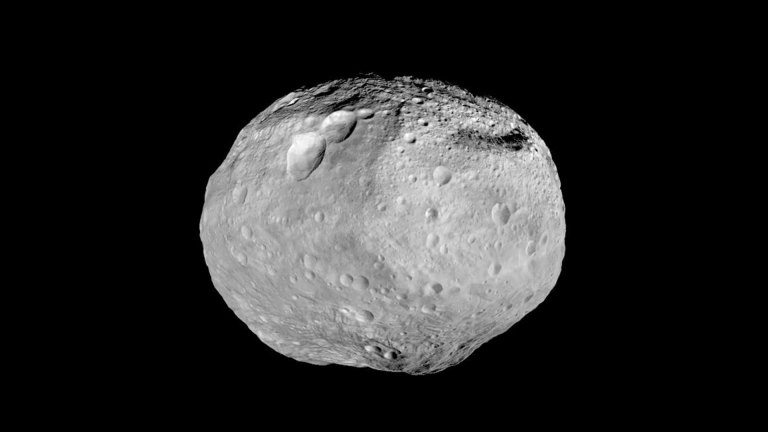 This mosaic blends some of the best views NASA's Dawn spacecraft took of the giant asteroid Vesta. Dawn studied Vesta from July 2011 to September 2012.
This mosaic blends some of the best views NASA's Dawn spacecraft took of the giant asteroid Vesta. Dawn studied Vesta from July 2011 to September 2012. -
Galileo
NASA's Galileo mission was the first spacecraft to fly past an asteroid. It flew past asteroid Gaspra in 1991, and asteroid Ida in 1993.
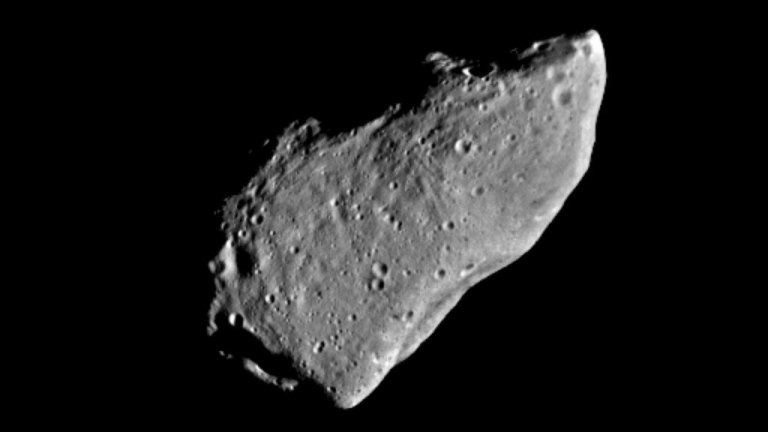 This picture of asteroid Gaspra is a mosaic of two images taken by the Galileo spacecraft from a range of 3,300 miles (5,300 kilometers) some 10 minutes before closest approach on Oct. 29, 1991.
This picture of asteroid Gaspra is a mosaic of two images taken by the Galileo spacecraft from a range of 3,300 miles (5,300 kilometers) some 10 minutes before closest approach on Oct. 29, 1991. -
NEAR Shoemaker
NASA's NEAR was the first spacecraft to orbit an asteroid, and also was the first spacecraft to land on one. Launched on Feb. 17, 1996, NEAR flew by asteroid Mathilde on June 27, 1997. Then on Feb. 14, 2000, NEAR began orbiting asteroid Eros. On Feb. 12, 2001, NEAR touched down on Eros – the first time a U.S. spacecraft was the first to land on a celestial body.
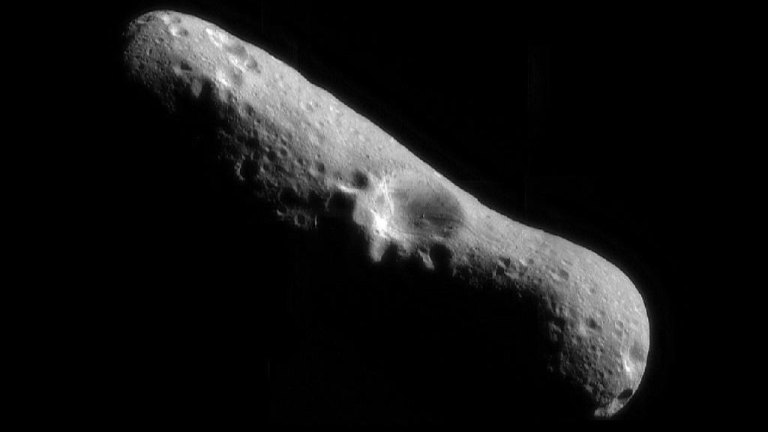 This picture of Eros, the first of an asteroid taken from an orbiting spacecraft, is a mosaic of four images obtained by NASA's NEAR spacecraft on Feb. 14, 2000, immediately after the spacecraft's insertion into orbit.
This picture of Eros, the first of an asteroid taken from an orbiting spacecraft, is a mosaic of four images obtained by NASA's NEAR spacecraft on Feb. 14, 2000, immediately after the spacecraft's insertion into orbit. -
Deep Space 1
Deep Space 1 (DS1) was designed to test new technologies for future deep space and interplanetary missions. As a bonus, the spacecraft also flew by asteroid 9969 Braille on July 29, 1999, at a range of about 16 miles (26 kilometers).
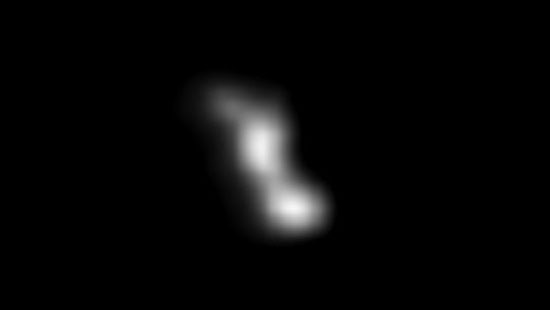 This image was created from a composite of two images taken seconds after NASA's Deep Space 1 (DS1) encountered asteroid 9969 Braille.
This image was created from a composite of two images taken seconds after NASA's Deep Space 1 (DS1) encountered asteroid 9969 Braille. -
Stardust/Stardust NExT
NASA's Stardust was the first spacecraft to bring samples from a comet to Earth. Launched on Feb. 7, 1999, the spacecraft flew within 155 miles (250 kilometers) of comet P/Wild 2 and collected samples of dust and volatiles from the comet's coma. On Nov. 2, 2002, it flew by and imaged asteroid 5535 Annefrank. The spacecraft was given an extended mission known as New Exploration of Tempel 1 (NExT) that included a flyby of Comet Tempel 1.
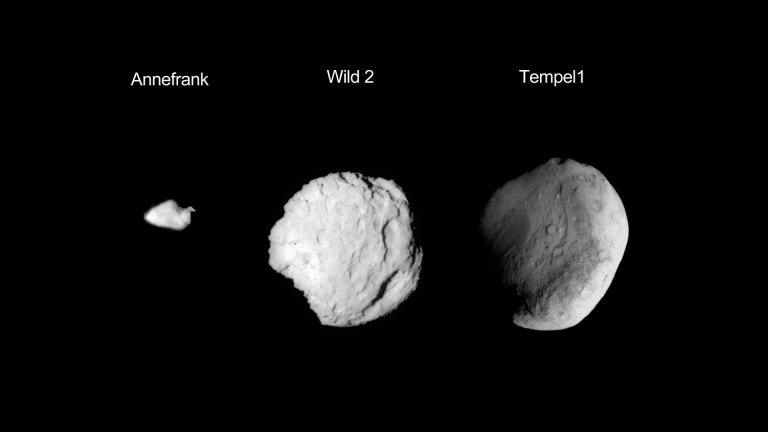 This composite image shows the three small worlds NASA's Stardust spacecraft encountered during its 12 year mission. Stardust performed a flyby of asteroid Annefrank on Nov. 2, 2002. Comet Wild 2 was visited by the spacecraft on Jan. 2, 2004. The comet Tempel 1 encounter occurred on Feb. 14, 2011.
This composite image shows the three small worlds NASA's Stardust spacecraft encountered during its 12 year mission. Stardust performed a flyby of asteroid Annefrank on Nov. 2, 2002. Comet Wild 2 was visited by the spacecraft on Jan. 2, 2004. The comet Tempel 1 encounter occurred on Feb. 14, 2011.





























