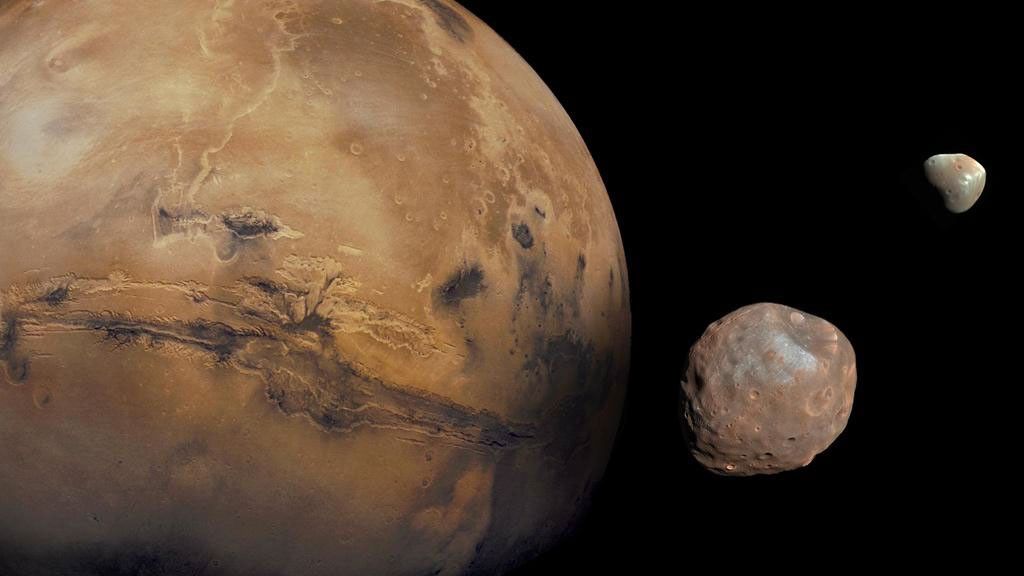
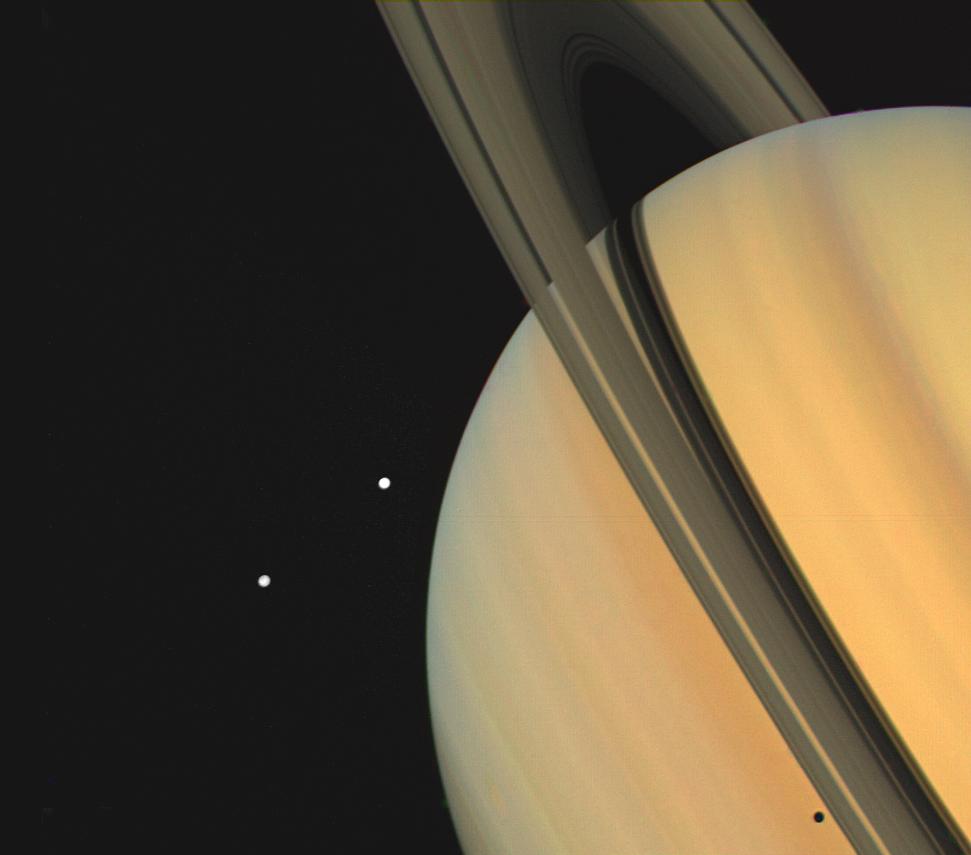
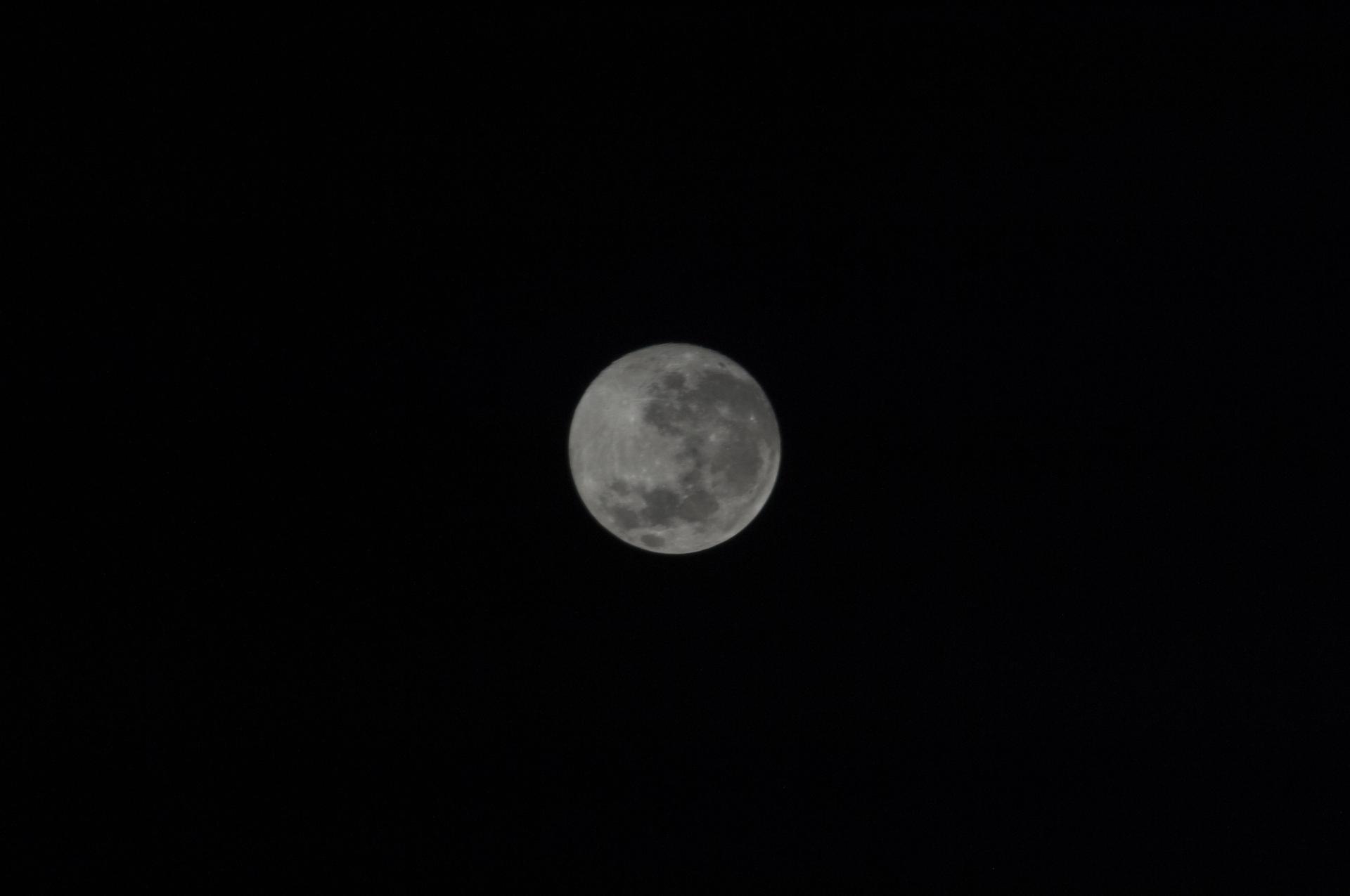
featured moons
Explore Our Solar System's Moons
Our solar system has hundreds of known moons orbiting planets and dwarf planets. Even some asteroids have moons.
Moons – also called natural satellites – come in many shapes, sizes and types. They are generally solid bodies, and a few have atmospheres.
How Many Moons?
Hundreds of moons orbit planets, dwarf planets - even asteroids.
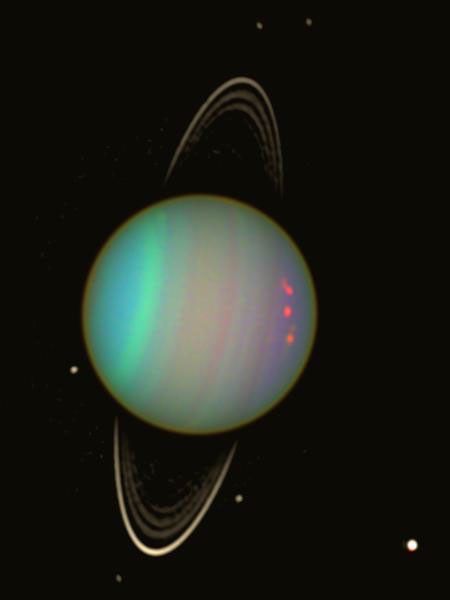
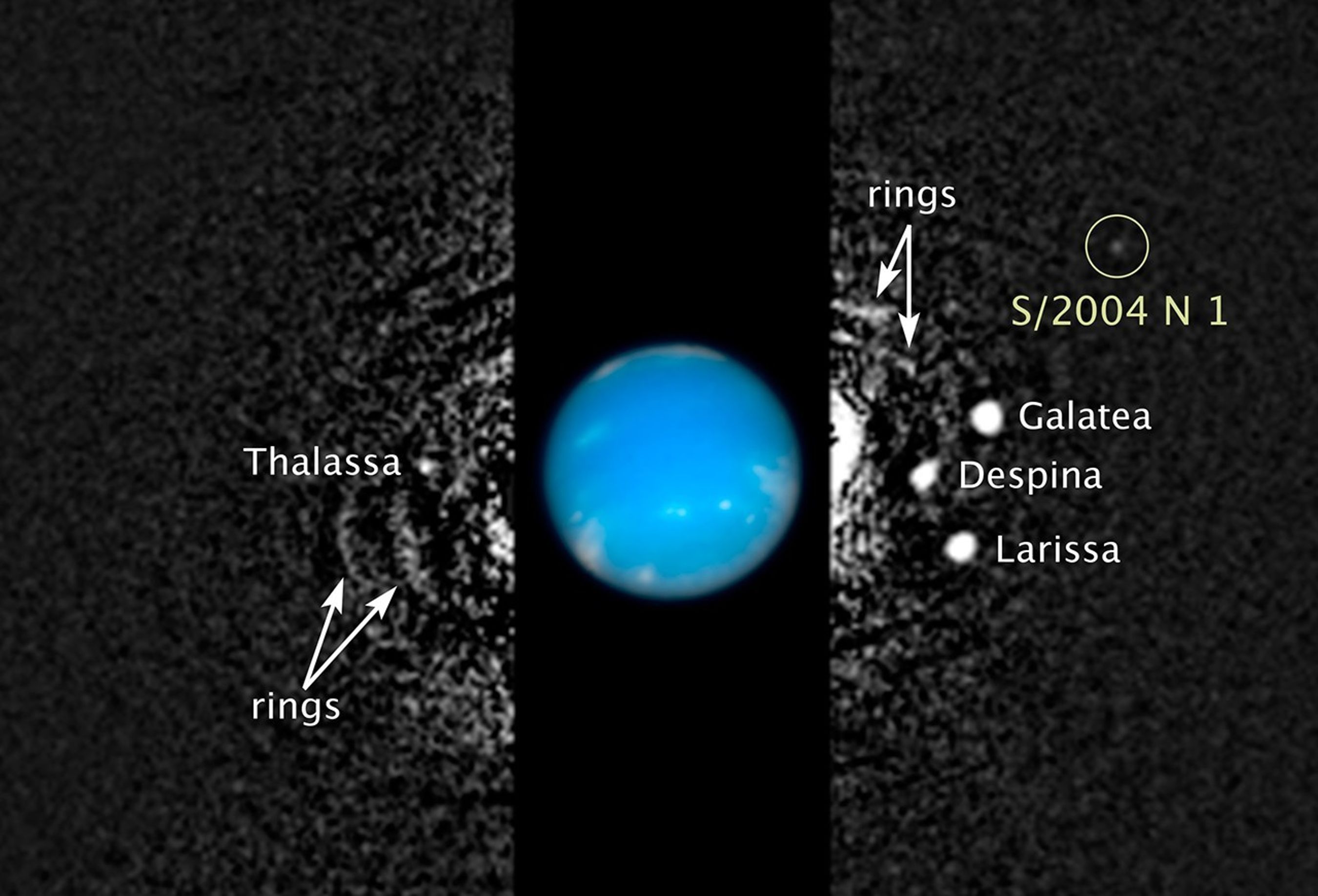
As of March 25, 2025, there was a total of 891 confirmed moons in our solar system. Of those, 421 moons are orbiting planets (including Pluto). More than 470 moons are orbiting other dwarf planets, asteroids and trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).

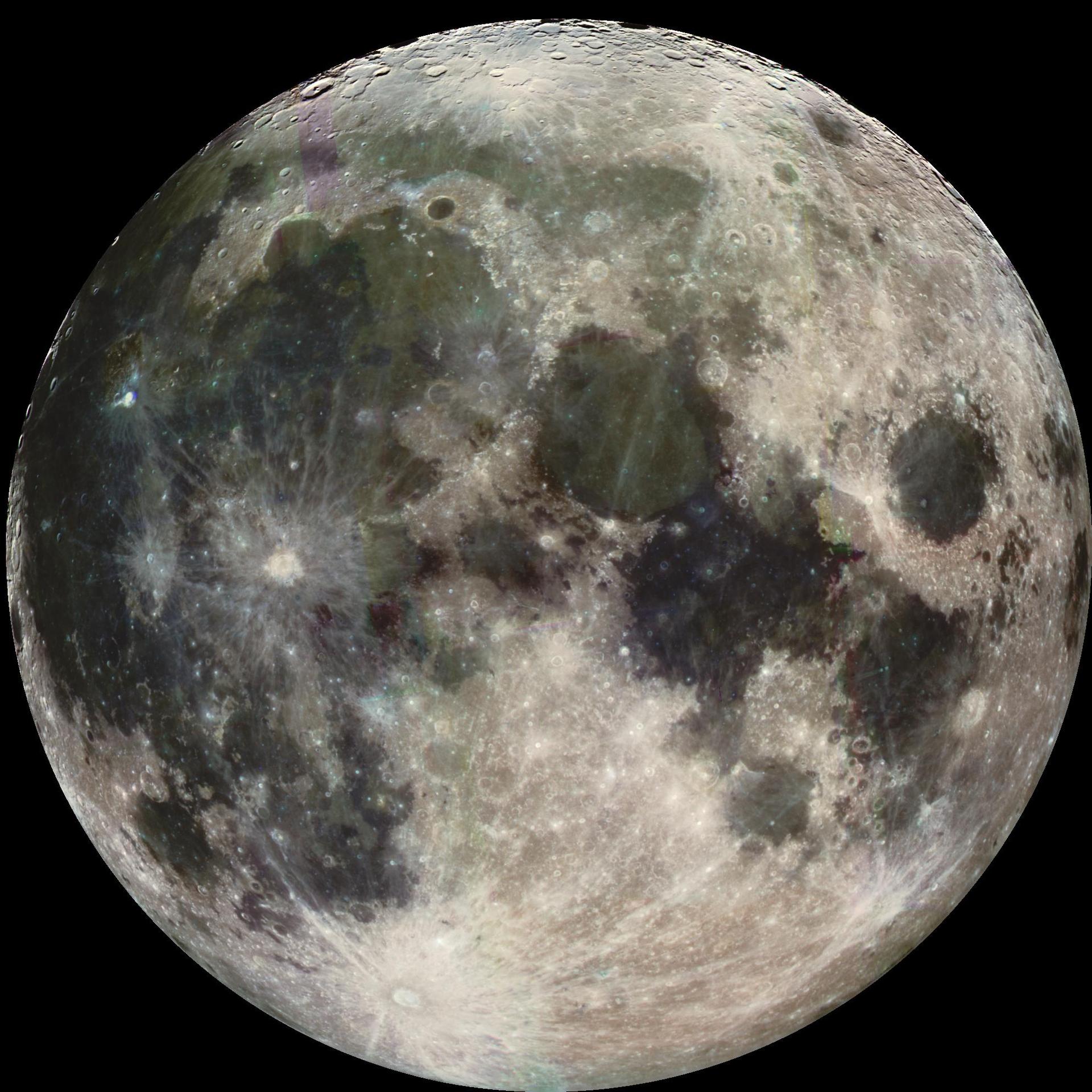
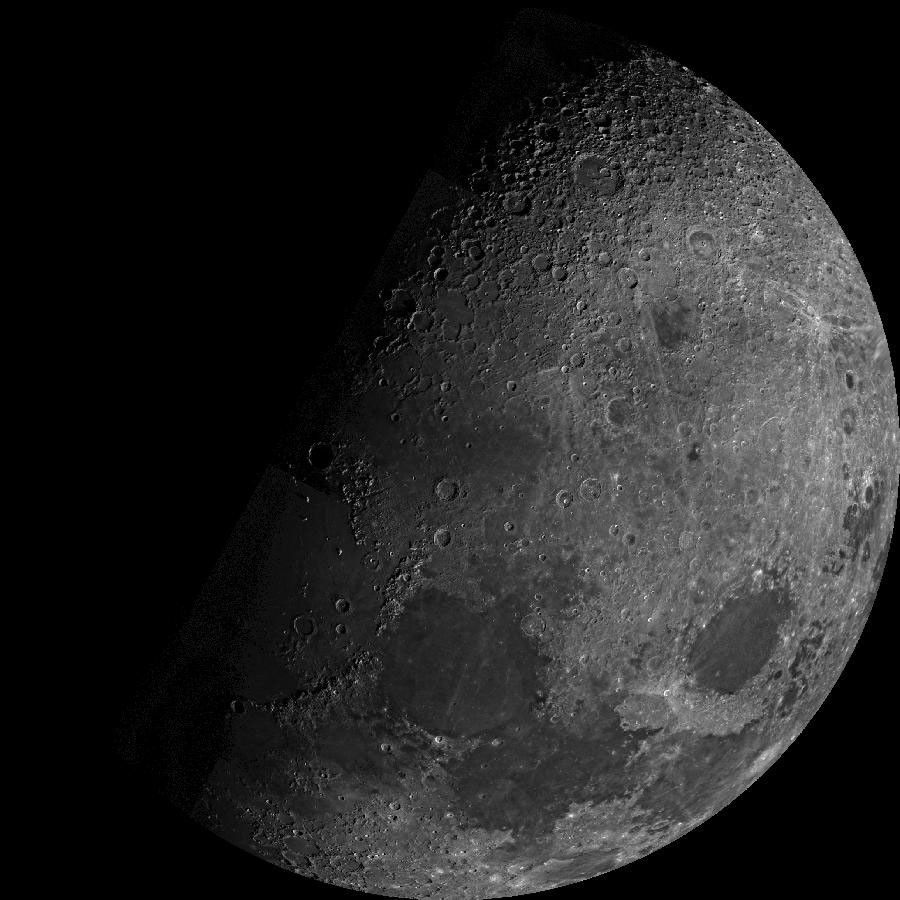
Earth's Moon
-
All About Our Moon
From lighting up our skies to maintaining a geological record of our solar system’s history, Earth’s closest celestial neighbor plays a pivotal role in the study of our planet and our solar system.
-
It's Just a Phase
Sometimes the entire face of the Moon glows brightly. Other times we see only a thin crescent of light. Sometimes the Moon seems to disappear. These shifts are called moon phases.

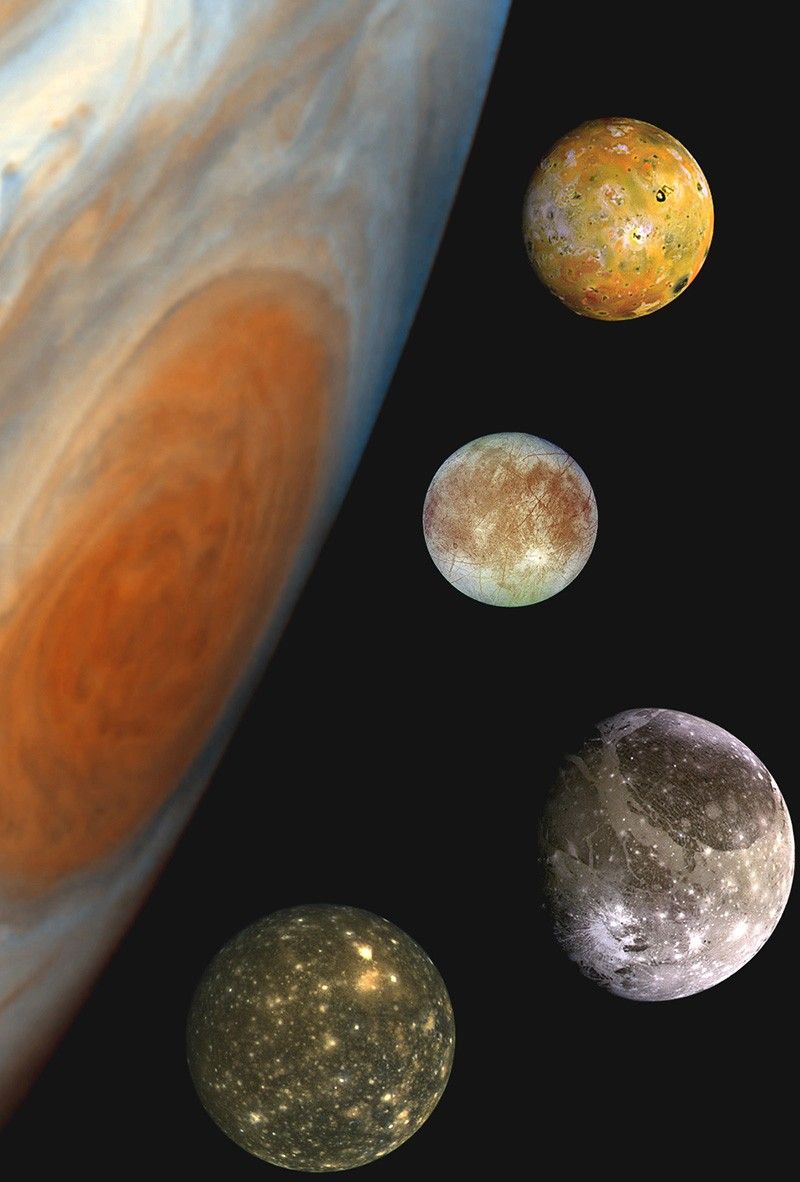
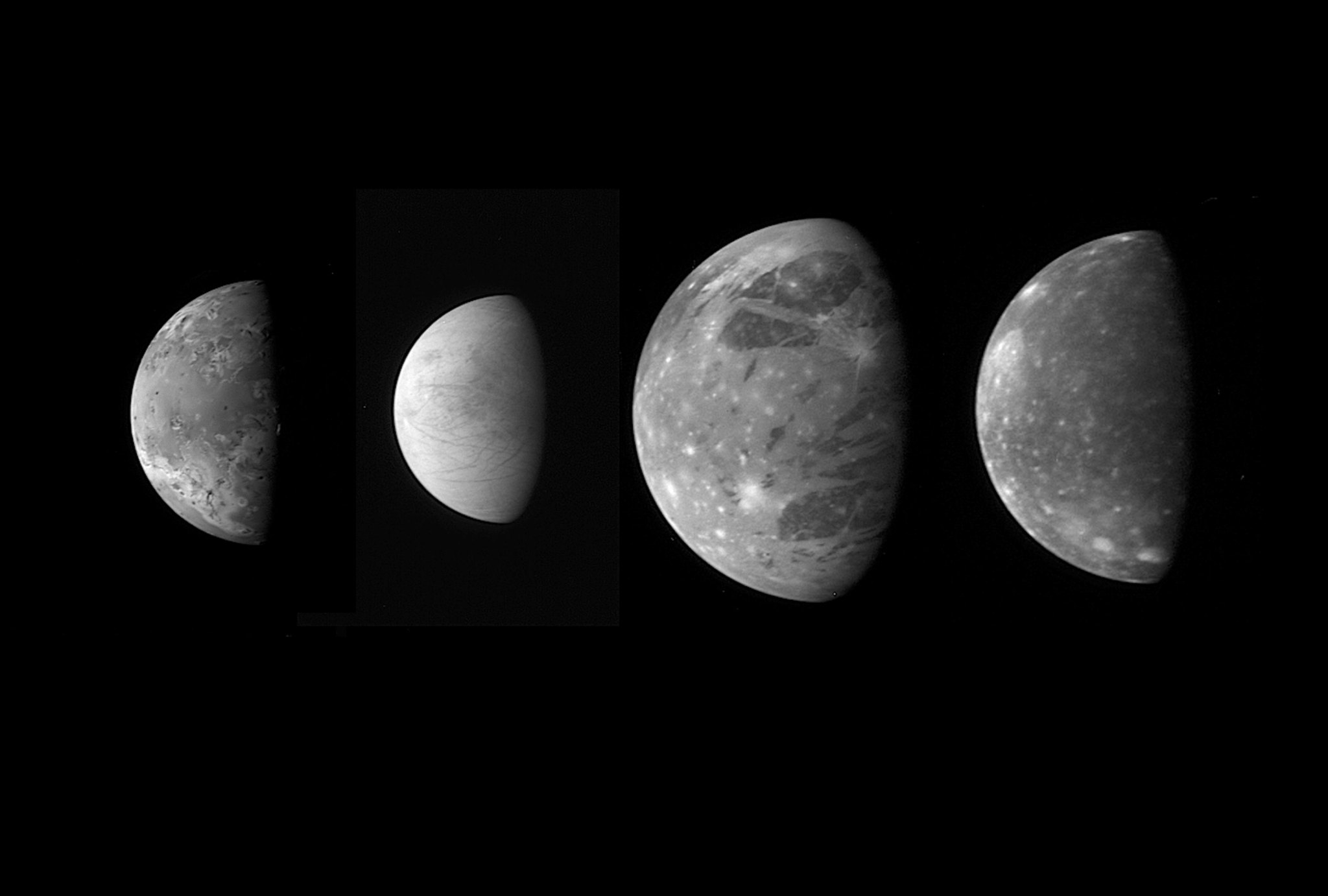
Moons in Our Solar System
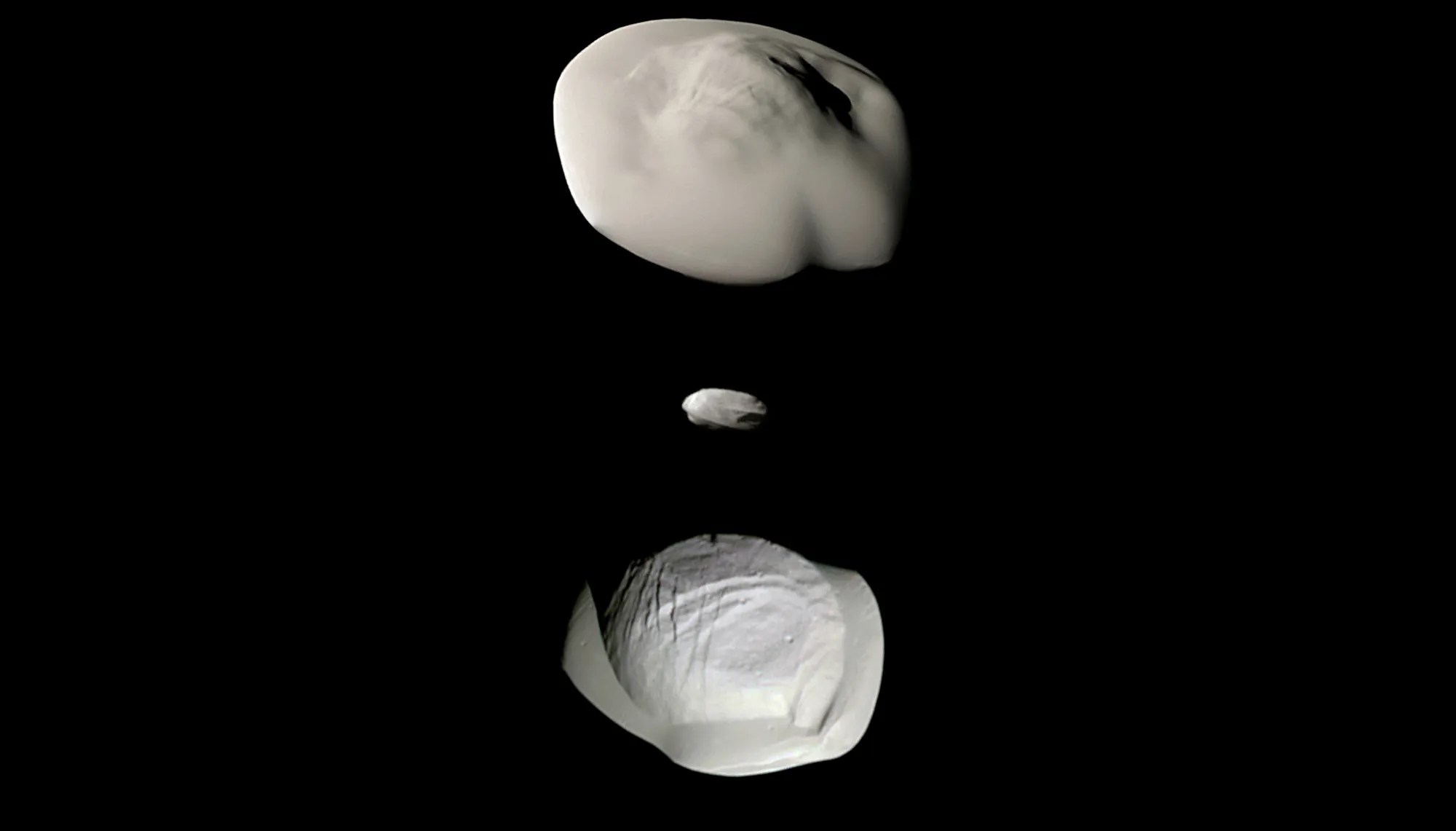
How big is Ganymede? How small is Deimos? Which moons might have what it takes to support life?
Explore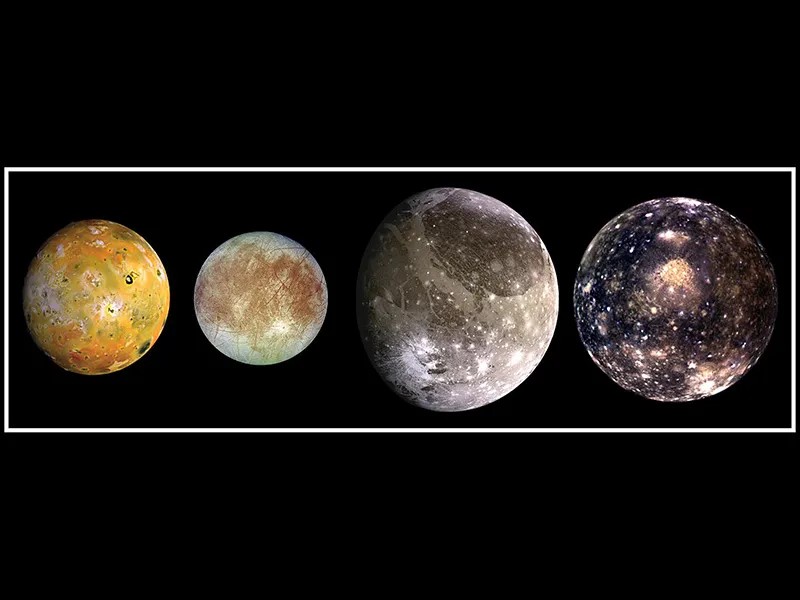
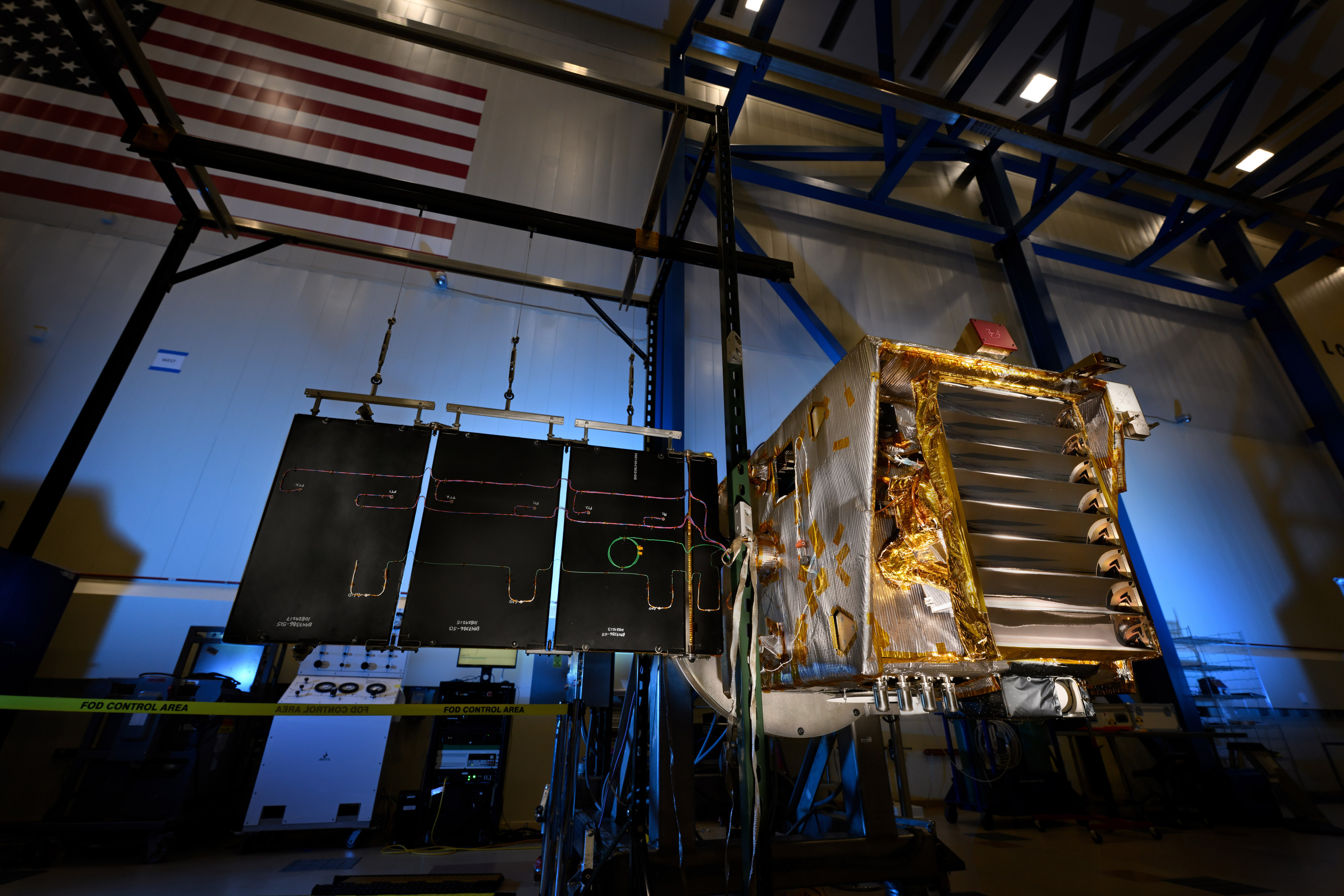
Europa Clipper
Learn More