Massive Martian dust storms have been challenging—and enticing—scientists for decades. Here’s the scoop on Martian dust:

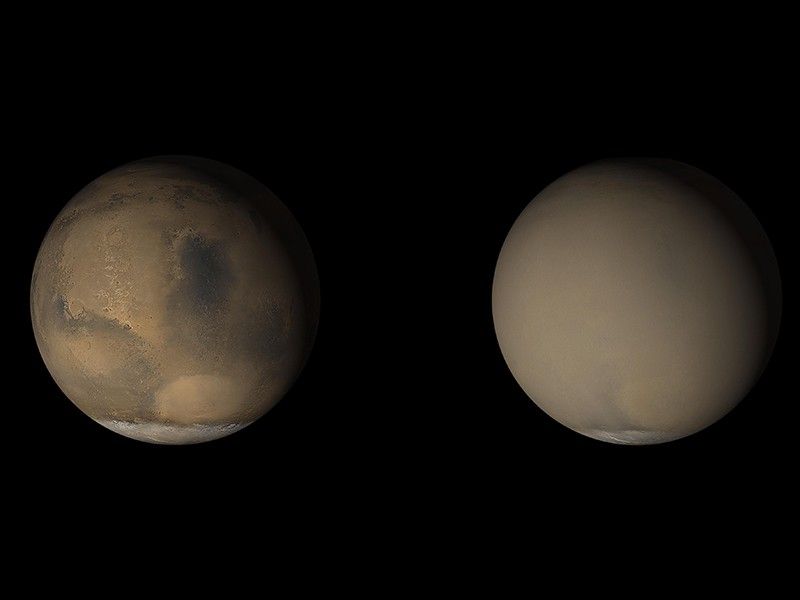
UPDATE (June 20, 2018): A storm of tiny dust particles has engulfed much of Mars over the last two weeks and prompted NASA’s Opportunity rover to suspend science operations. But across the planet, NASA’s Curiosity rover, which has been studying Martian soil at Gale Crater, is expected to remain largely unaffected by the dust. While Opportunity is powered by sunlight, which is blotted out by dust at its current location, Curiosity has a nuclear-powered battery that runs day and night.
The Martian dust storm has grown in size and is now officially a "planet-encircling" (or "global") dust event.

1: Challenging Opportunity
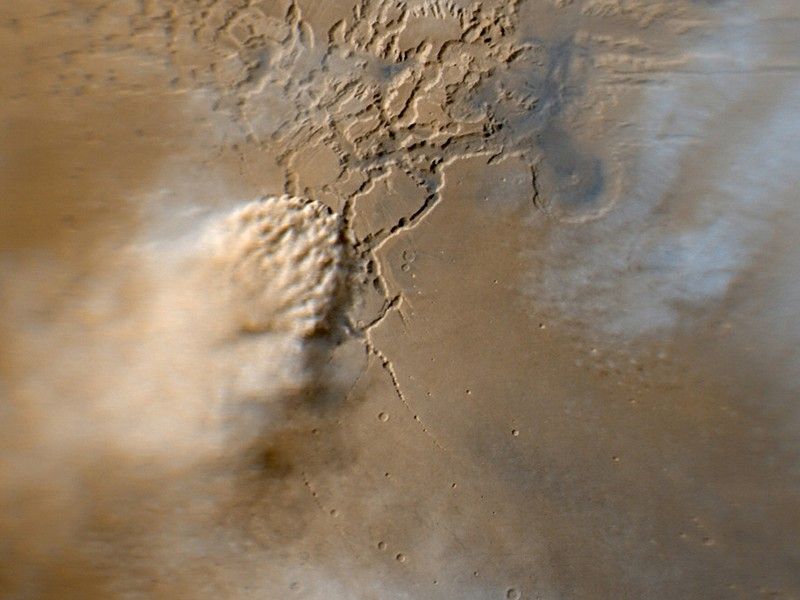
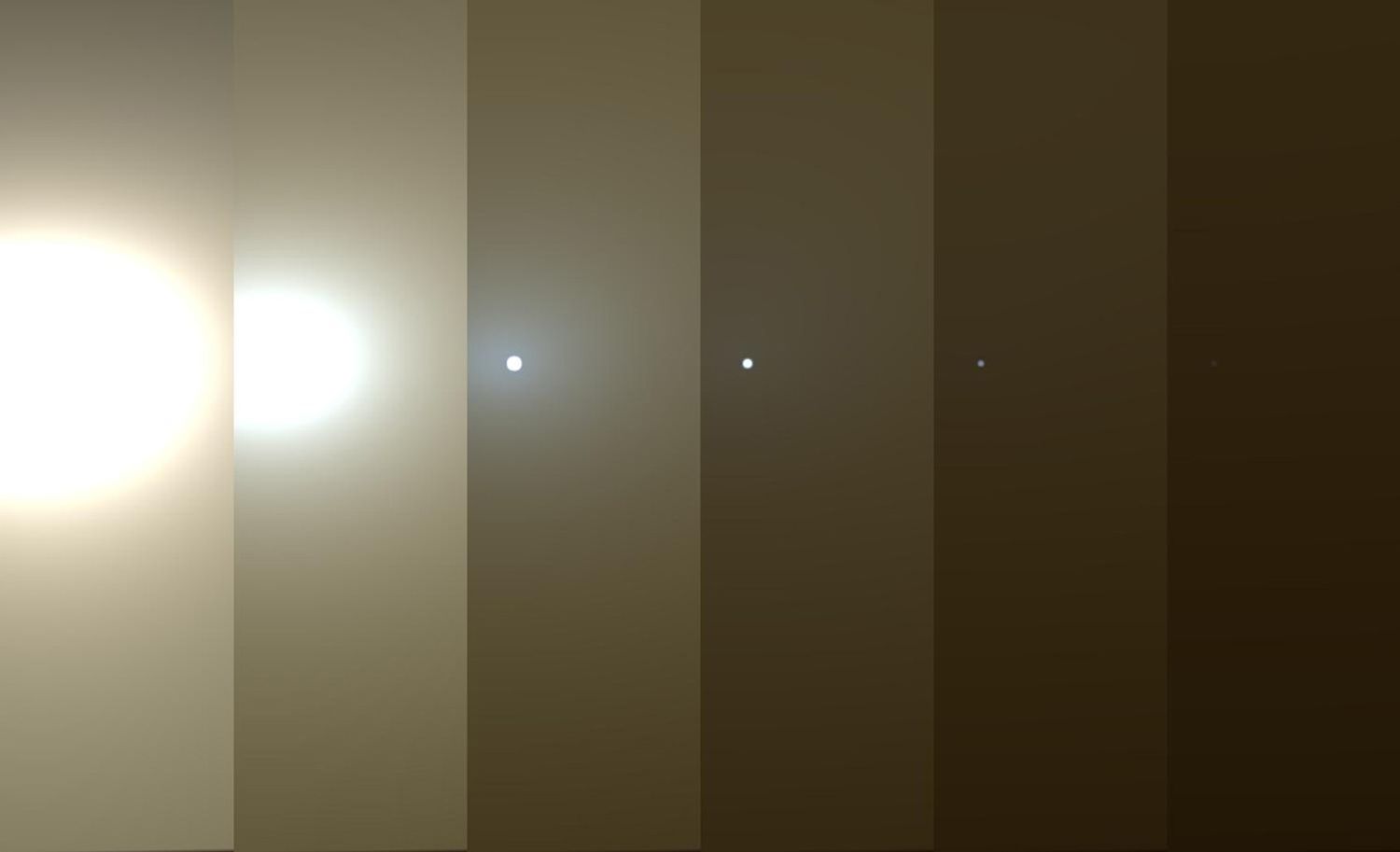
Our Opportunity rover is facing one of the greatest challenges of its 14 ½ year mission on the surface of Mars--a massive dust storm that has turned day to night. Opportunity is currently hunkered down on Mars near the center of a storm bigger than North America and Russia combined. The dust-induced darkness means the solar-powered rover can’t recharge its batteries.
2: One Tough Robot
This isn’t the first time Opportunity has had to wait out a massive storm. In 2007, a monthlong series of severe storms filled the Martian skies with dust. Power levels reached critical lows, but engineers nursed the rover back to health when sunlight returned.
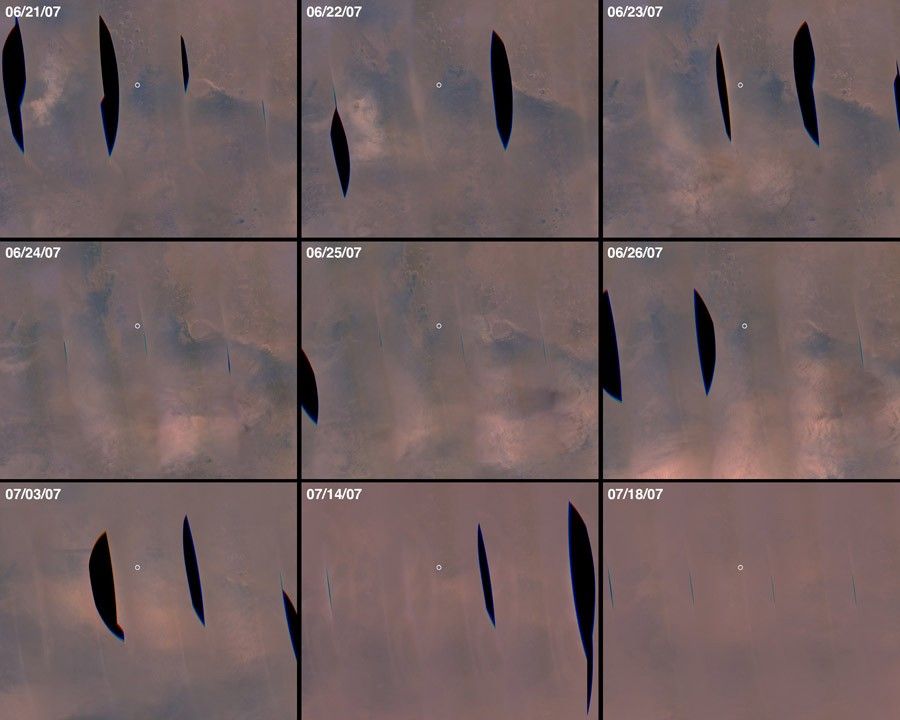
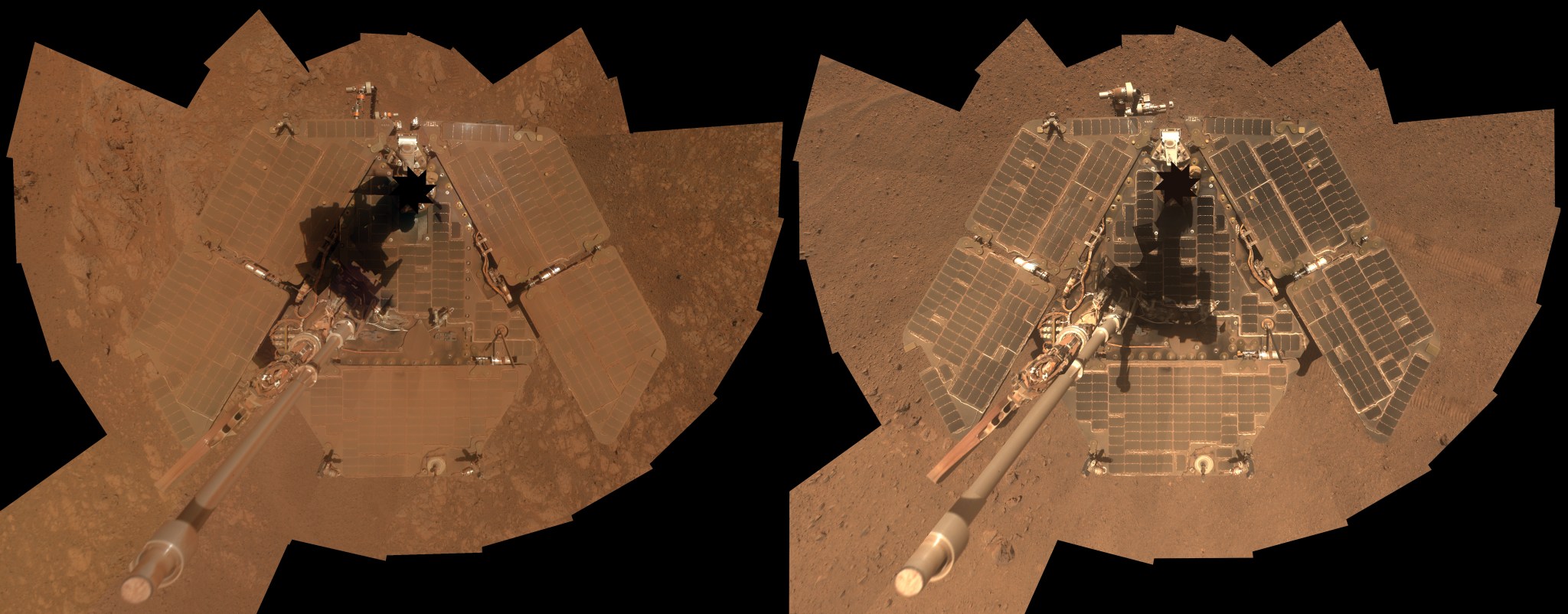
3: Windswept
Martian breezes proved a saving grace for the solar-powered Mars rovers in the past, sweeping away accumulated dust and enabling rovers to recharge and get back to science. Below is Opportunity in 2014. The image on the left is from January 2014. The image on the right from March 2014.
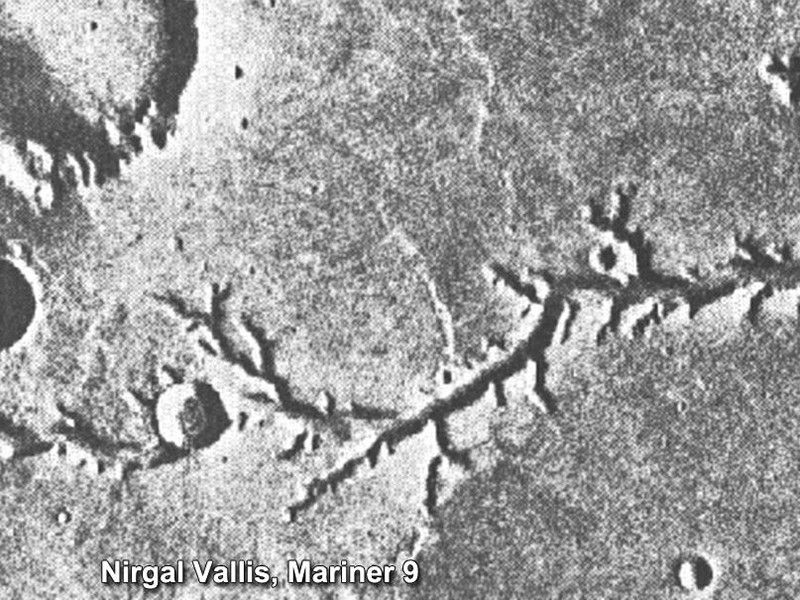
4: Dusty Disappointment
Back in 1971, scientists were eager for their first orbital views of Mars. But when Mariner 9 arrived in orbit, the Red Planet was engulfed by a global dust storm that hid most of the surface for a month. When the dust settled, geologists got detailed views of the Martian surface, including the first glimpses of ancient riverbeds carved into the dry and dusty landscape.
5: Dramatic License
As bad as the massive storm sounds, Mars isn’t capable of generating the strong winds that stranded actor Matt Damon’s character on the Red Planet in the movie The Martian. Mars’ atmosphere is too thin and winds are more breezy than brutal. The chore of cleaning dusty solar panels to maintain power levels, however, could be a very real job for future human explorers.
6: Semi-Regular Visitors
Scientists know to expect big dust storms on Mars, but the rapid development of the current one is surprising. Decades of Mars observations show a pattern of regional dust storms arising in northern spring and summer. In most Martian years, nearly twice as long as Earth years, the storms dissipate. But we’ve seen global dust storms in 1971, 1977, 1982, 1994, 2001 and 2007. The current storm season could last into 2019.
7: Science in the Dust
Dust is hard on machines, but can be a boon to science. A study of the 2007 storm published earlier this year suggests such storms play a role in the ongoing process of gas escaping from the top of Mars' atmosphere. That process long ago transformed wetter, warmer ancient Mars into today's arid, frozen planet. Three NASA orbiters, the Curiosity rover and international partners are already in position to study the 2018 storm.
8: Adjusting InSight
Mission controllers for Mars InSight lander — due to land on Mars in November — will be closely monitoring the storm in case the spacecraft’s landing parameters need to be adjusted for safety.
9: Martian Weather Report
One saving grace of dust storms is that they can actually limit the extreme temperature swings experienced on the Martian surface. The same swirling dust that blocks out sunlight also absorbs heat, raising the ambient temperature surrounding Opportunity.
Track the storm and check the weather on Mars anytime.
10: Dust: Not Just a Martian Thing
A dust storm in the Sahara can change the skies in Miami and temperatures in the North Atlantic. Earth scientists keep close watch on our home planet’s dust storms, which can darken skies and alter Earth’s climate patterns.