NASA
UPDATE - May 9, 2016: These views from the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, show Mercury passing in front of the sun on May 9, 2016.
By Lyle Tavernier, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
In the news
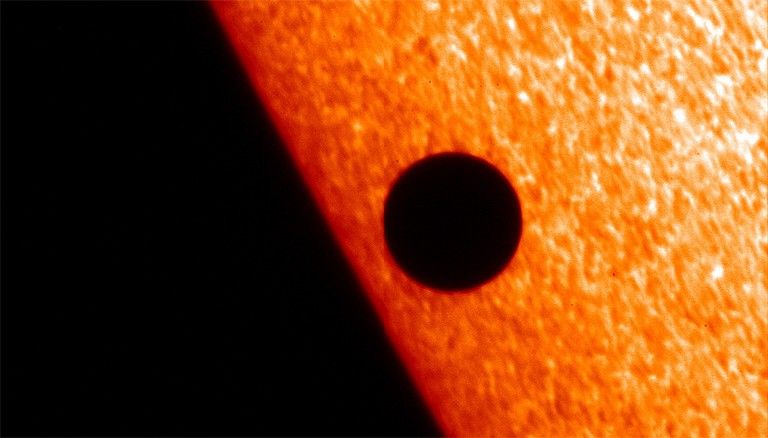
It only happens about 13 times per century and hasn’t happened in nearly a decade, but on Monday, May 9, Mercury will transit the sun. A transit happens when a planet crosses in front of a star. From our perspective on Earth, we only ever see two planets transit the sun: Mercury and Venus. (Transits of Venus are even more rare. The next one won't happen until 2117!) On May 9, as Mercury passes in front of the sun, viewers around Earth (using the proper safety equipment) will be able to see a tiny dark spot moving slowly across the disk of the sun.
CAUTION: Looking directly at the sun can cause permanent vision damage – see below for tips on how to safely view the transit.
Why Is It Important?
Then and Now
In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler discovered that both Mercury and Venus would transit the sun in 1631. It was fortunate timing: The telescope had been invented just 23 years earlier and the transits wouldn’t happen in the same year again until 13425. Kepler didn’t survive to see the transits, but French astronomer Pierre Gassendi became the first person to see the transit of Mercury (the transit of Venus wasn’t visible from Europe). It was soon understood that transits could be used as an opportunity to measure the apparent diameter – how large a planet appears from Earth – with great accuracy.
In 1677, Edmond Halley observed the transit of Mercury and realized that the parallax shift of the planet – the variation in Mercury’s apparent position against the disk of the sun as seen by observers at distant points on Earth – could be used to accurately measure the distance between the sun and Earth, which wasn’t known at the time.
Today, radar is used to measure the distance between Earth and the sun with greater precision than can be found using transit observations, but the transit of Mercury still provides scientists with opportunities for scientific investigation in two important areas: exospheres and exoplanets.
Exosphere Science
Some objects, like the moon and Mercury, were originally thought to have no atmosphere. But scientists have discovered that these bodies are actually surrounded in an ultra-thin atmosphere of gases called an exosphere. Scientists want to better understand the composition and density of the gases that make up Mercury’s exosphere and transits make that possible.
“When Mercury is in front of the sun, we can study the exosphere close to the planet,” said NASA scientist Rosemary Killen. “Sodium in the exosphere absorbs and re-emits a yellow-orange color from sunlight, and by measuring that absorption, we can learn about the density of gas there.”
Exoplanet Discoveries
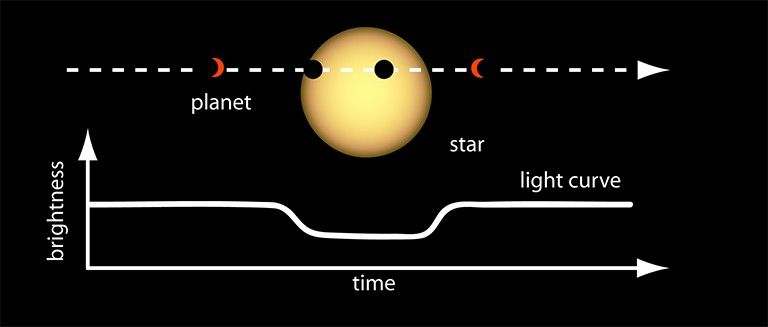
When Mercury transits the sun, it causes a slight dip in the sun’s brightness as it blocks a tiny portion of the sun's light. Scientists discovered they could use that phenomenon to search for planets orbiting distant stars, called exoplanets, that are otherwise obscured from view by the light of the star. When measuring the brightness of far-off stars, a slight recurring dip in the light curve (a graph of light intensity) could indicate an exoplanet orbiting and transiting its star. NASA’s Kepler mission has found more than 1,000 exoplanets by looking for this telltale drop in brightness.
NASA Ames/Dana Berry
Additionally, scientists have begun exploring the exospheres of exoplanets. By observing the spectra of the light that passes through an exosphere – similar to how we study Mercury’s exosphere – scientists are beginning to understand the evolution of exoplanet atmospheres as well as the influence of stellar wind and magnetic fields.
How to Watch It
Mercury will appear as a tiny dot on the sun’s surface and will require a telescope or binoculars with a special solar filter to see. Looking at the sun directly or through a telescope without proper protection can lead to serious and permanent vision damage. Do not look directly at the sun without a solar filter.
The transit of Mercury will begin at 4:12 a.m. PDT, meaning by the time the sun rises on the West Coast, Mercury will have been transiting the sun for nearly two hours. Fortunately, it will take seven and a half hours for Mercury to completely cross the sun’s face, so there will be plenty of time for West Coast viewers to witness this event. See the transit map to learn when and where the transit will be visible.
Don’t have access to a telescope, binoculars or a solar filter? Visit the Night Sky Network website for the location of events near you where amateur astronomers will have viewing opportunities available.
NASA also will stream a live program on NASA TV and the agency’s Facebook page from 7:30 to 8:30 a.m. PDT (10:30 to 11:30 a.m. EDT) -- an informal roundtable during which experts representing planetary, heliophysics and astrophysics will discuss the science behind the Mercury transit. Viewers can ask questions via Facebook and Twitter using #AskNASA.
Teach It
Here are two ways to turn the transit of Mercury into a lesson for students.
- Exploring Exoplanets with Kepler - Students use math concepts related to transits to discover real-world data about Mercury, Venus and planets outside our solar system.
- Pi in the Sky 3 - Try the "Sun Screen" problem on this illustrated math problem set that has students calculate the percentage drop in sunlight reaching Earth when Mercury transits.
Explore More
Transit Resources:
- NASA TV (live transit coverage)
- NASA Transit Website (near real-time images of the transit)
- Night Sky Network Events
- Video: What’s Up – May 2016
- Transit Map
- Solar System Transits
- NASA Museum Alliance Resources
Exoplanet Resources: