Mars 2020: Perseverance Rover
NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover seeks signs of ancient life and collects samples of rock and regolith for possible Earth return.

NASA’s Mars Spacecraft Capture Images of Comet 3I/ATLAS
Two orbiters and a rover captured images of the interstellar object — from the closest location any of the agency’s…
Read the Story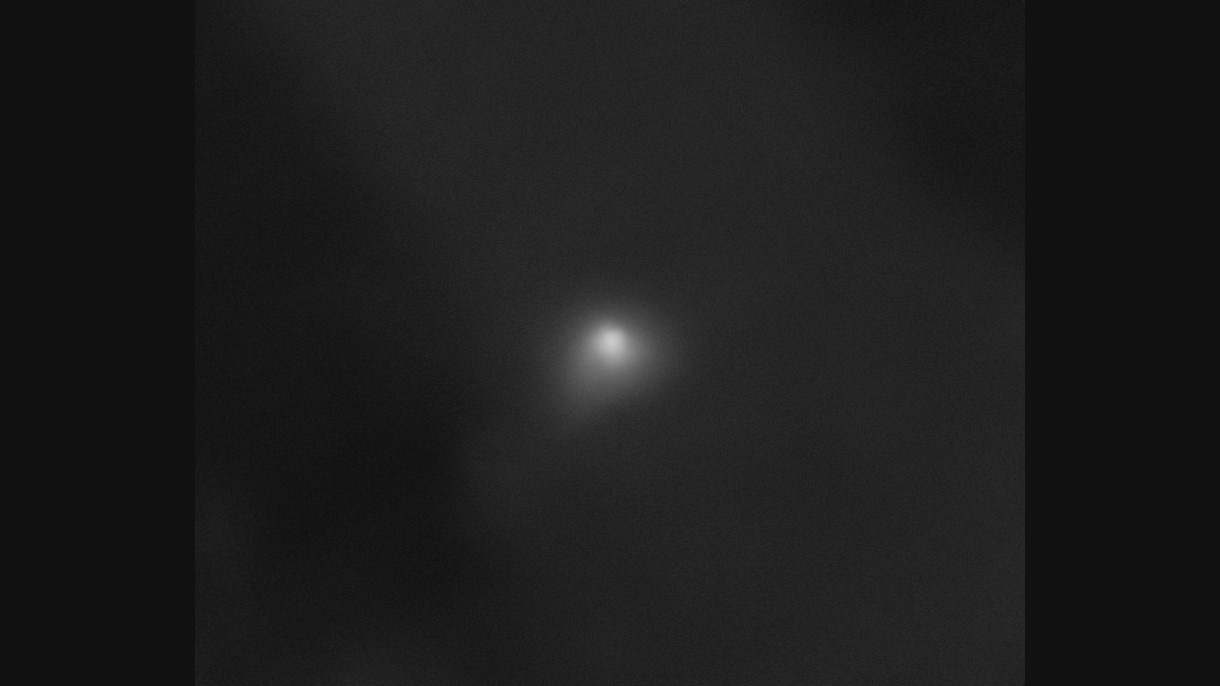
Report: Perseverance Rock Sample Contains 'Potential Biosignatures'
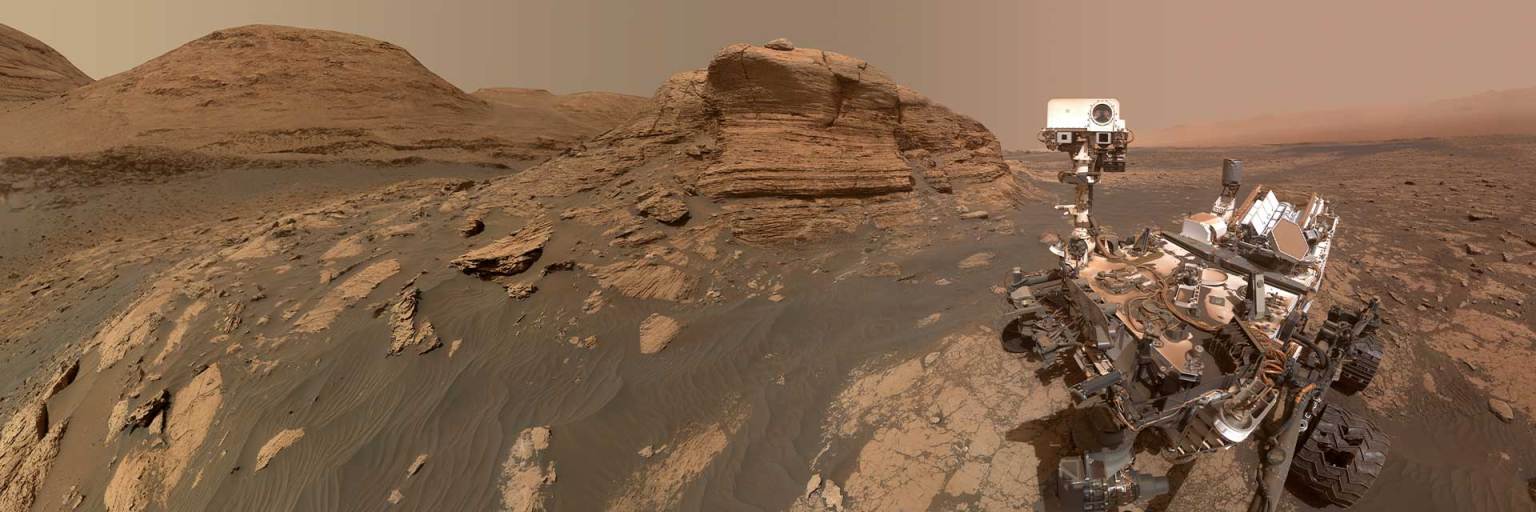
A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life. Taken from a rock named “Cheyava Falls” last year, the sample, called “Sapphire Canyon,” contains potential biosignatures, according to a paper published Sept. 10 in the journal Nature.
Read 'NASA Says Mars Rover Discovered Potential Biosignature Last Year'
NASA Shares Details of Perseverance Rover Finding
Experts discuss the analysis of a rock sampled by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover last year, and the science findings published Wednesday, Sept. 10, in the journal Nature. The sample, called “Sapphire Canyon,” was collected in July 2024 from a set of rocky outcrops on the edges of Neretva Vallis, a river valley carved by water rushing into Jezero Crater long ago.
Replay the Sept. 10 news conferenceMars Rock Samples: The Stories They Could Tell
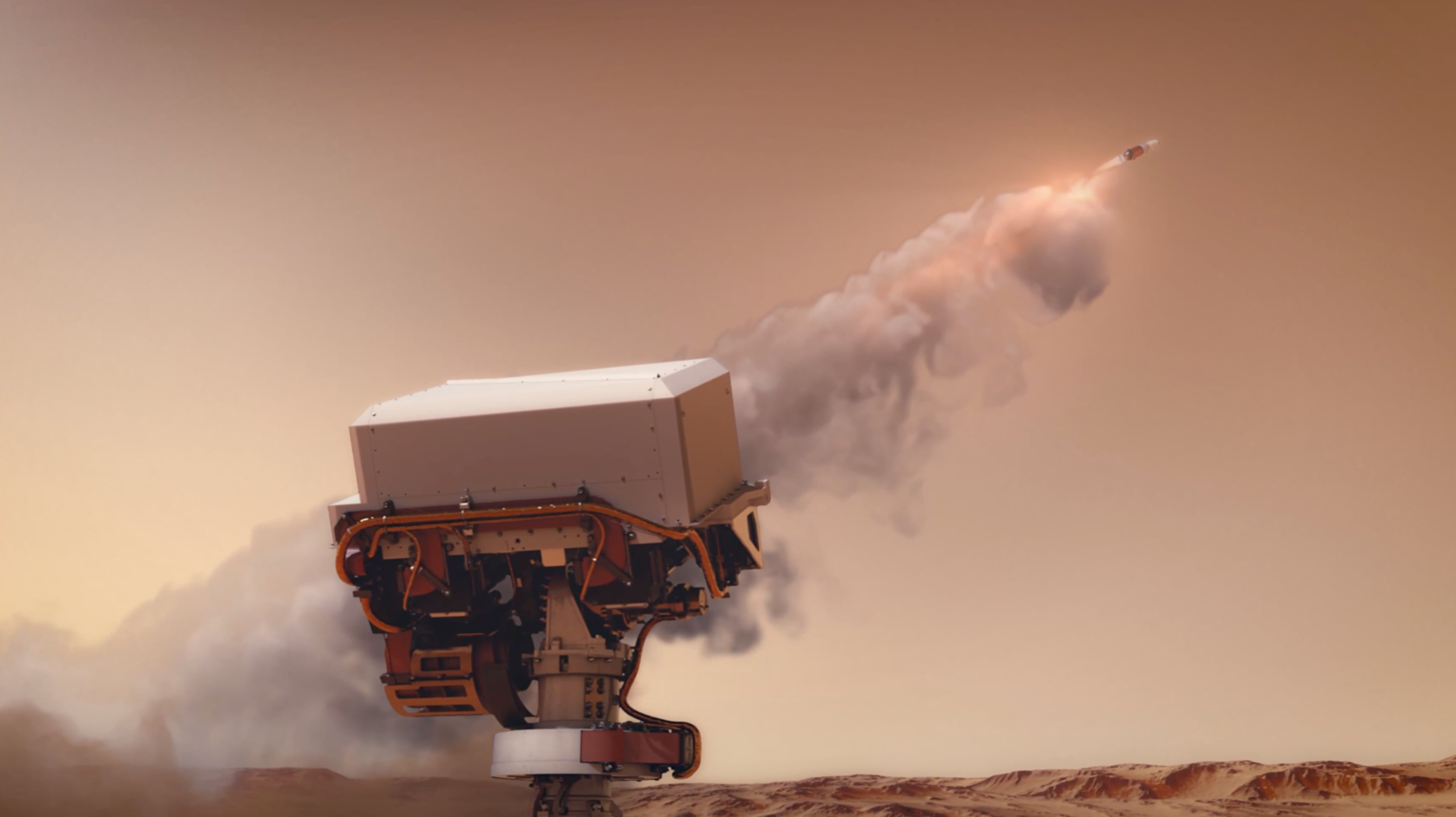
NASA's Mars Perseverance rover is building a unique rock collection, which also includes samples of Mars atmosphere and loose surface material. These samples record the history of the Jezero Crater landing site, and may even preserve signs of ancient life. Learn more about these precious samples, which Mars Sample Return could deliver to Earth for detailed study in the future.
Learn MoreLanding Site: Jezero Crater
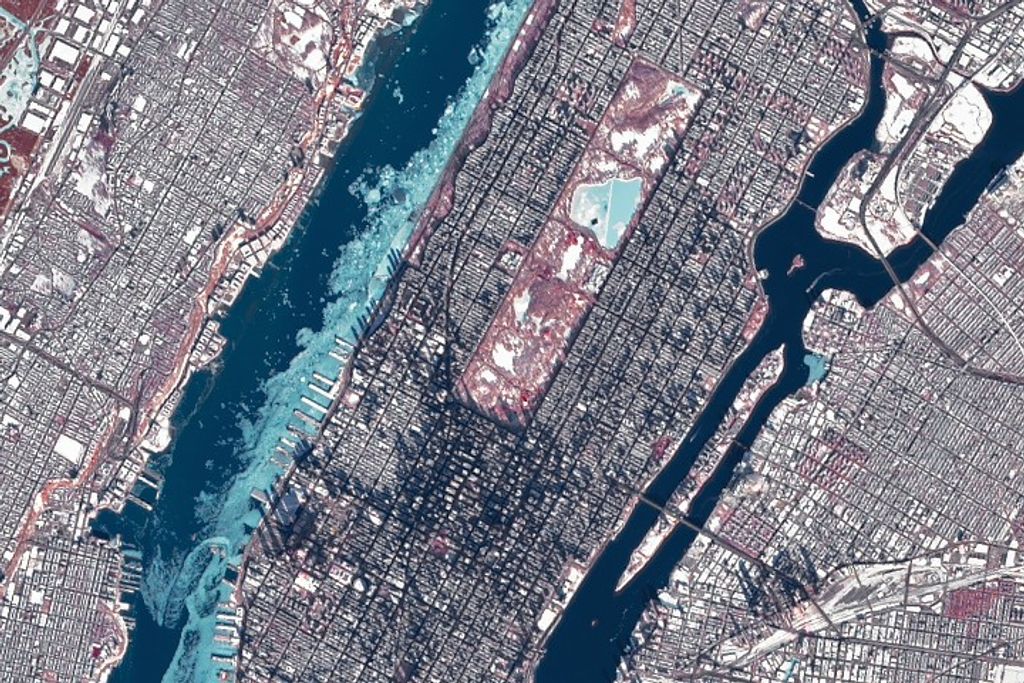
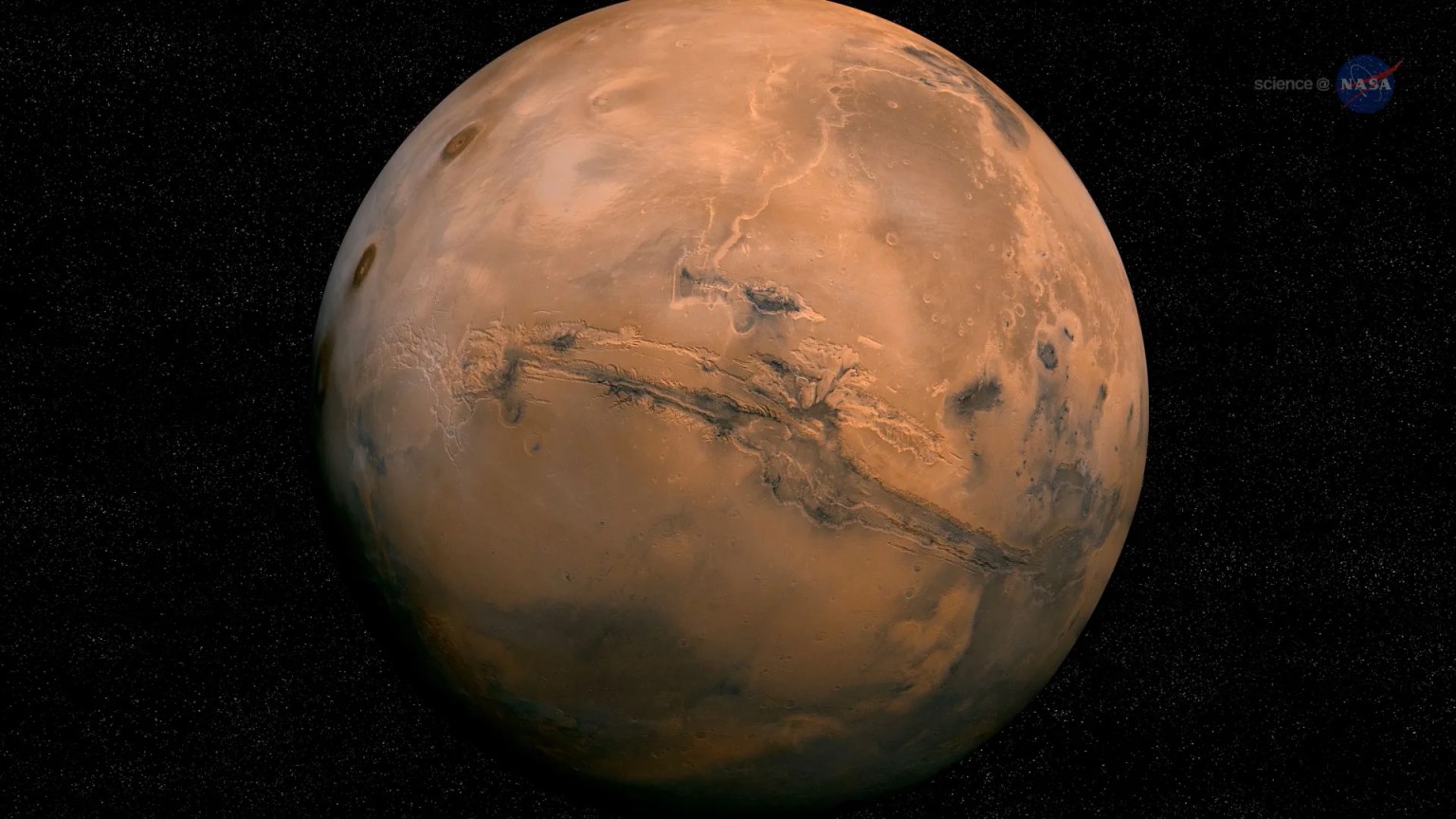
NASA chose Jezero Crater as the landing site for the Perseverance rover. Scientists believe the area was once flooded with water and was home to an ancient river delta. The process of landing site selection involved a combination of mission team members and scientists from around the world, who carefully examined more than 60 candidate locations on the Red Planet. After the exhaustive five-year study of potential sites, each with its own unique characteristics and appeal, Jezero rose to the top.
Jezero Crater tells a story of the on-again, off-again nature of the wet past of Mars. More than 3.5 billion years ago, river channels spilled over the crater wall and created a lake. Scientists see evidence that water carried clay minerals from the surrounding area into the crater lake. Conceivably, microbial life could have lived in Jezero during one or more of these wet times. If so, signs of their remains might be found in lakebed or shoreline sediments. Scientists will study how the region formed and evolved, seek signs of past life, and collect samples of Mars rock and soil that might preserve these signs.
Jezero Crater is 28 miles (45 kilometers) wide, and is located on the western edge of a flat plain called Isidis Planitia, which lies just north of the Martian equator. The landing site is about 2,300 miles (3,700 kilometers) from Curiosity's landing site in Gale Crater.
Perseverance Mars Rover Drive Path Animation
This animated orbital-map view shows the route NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has taken since its February 2021 landing at Jezero Crater to July 2024, when it took its “Cheyava Falls” sample. As of October 2024, the rover has driven over 30 kilometers (18.65 miles), and has collected 24 samples of rock and regolith as well as one air sample.
Learn MoreOld Glory on the Red Planet
The United States flag adorns an aluminum plate mounted at the base of the mast, or “head,” of NASA’s Perseverance…
Read the Story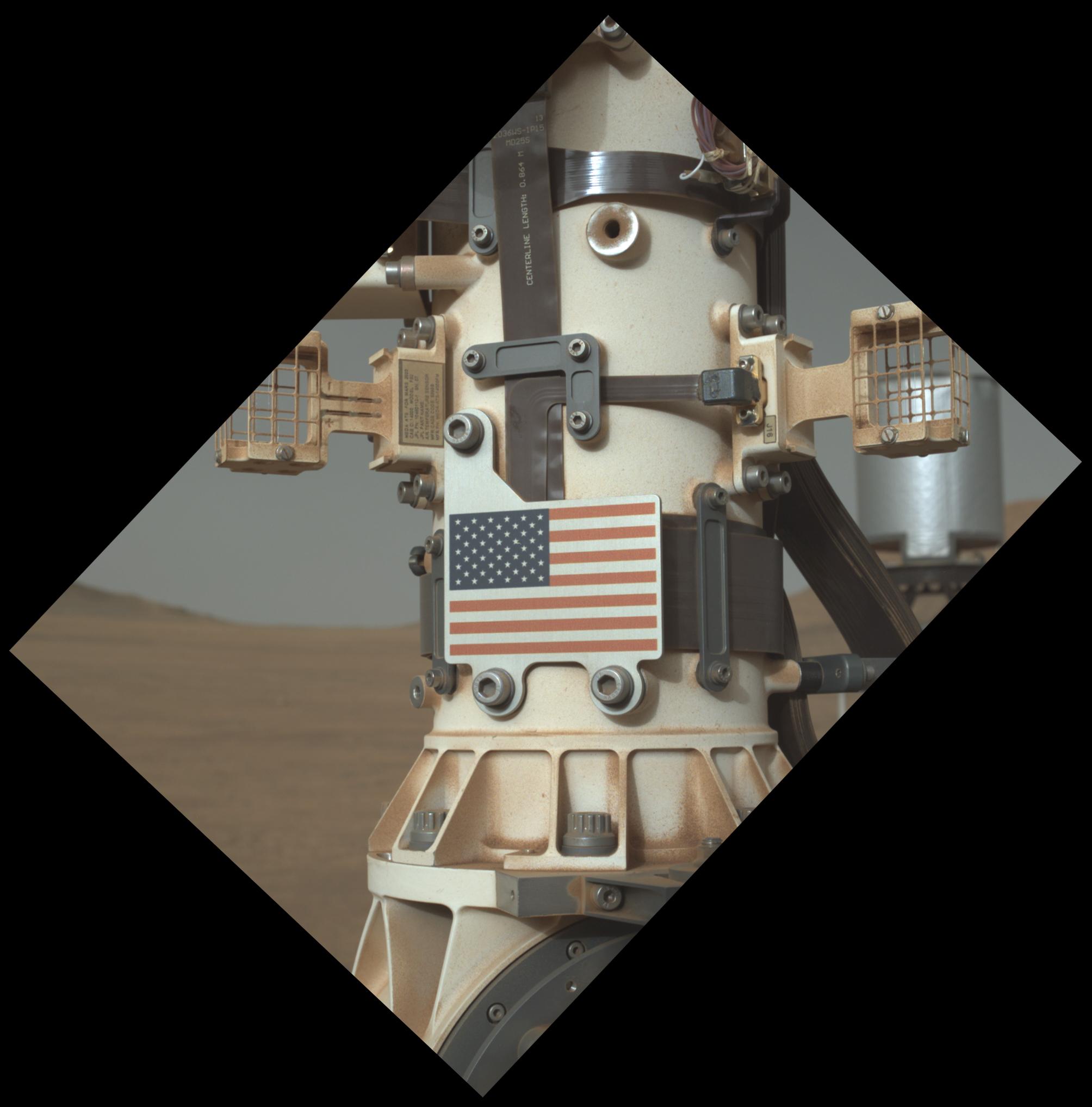
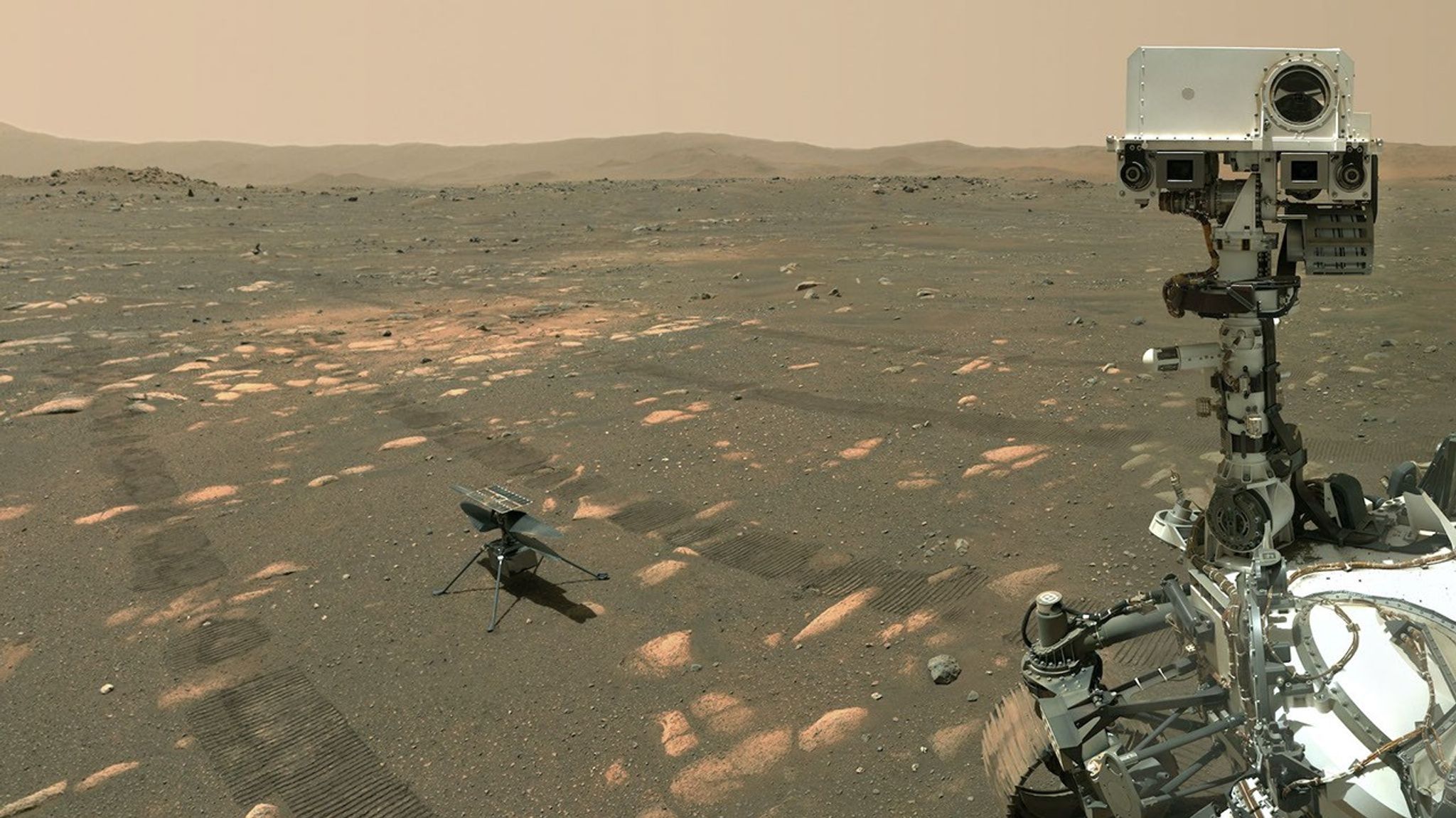
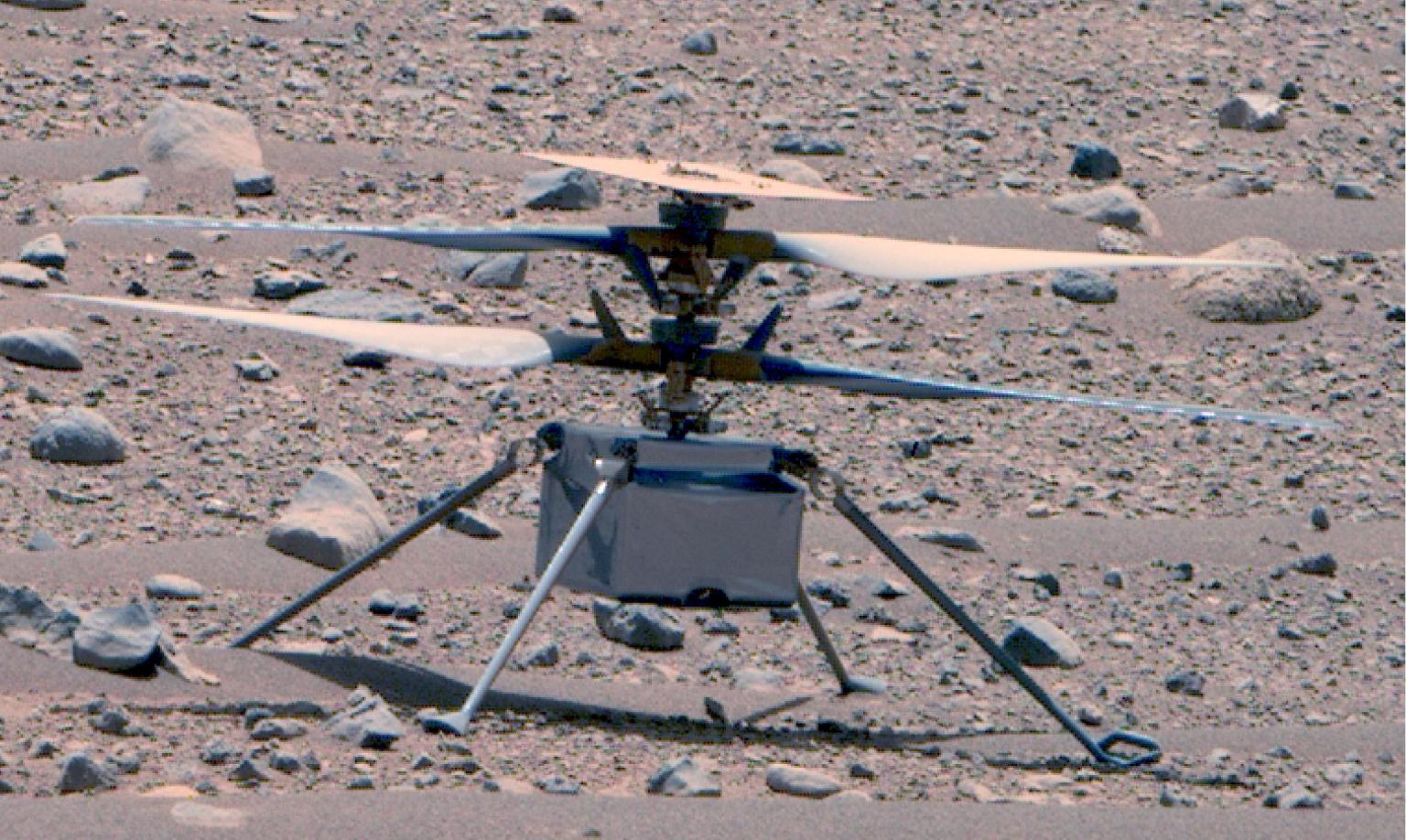
Mars Ingenuity Helicopter
Strapped to the rover's belly for the journey to Mars was a technology demonstration — the Mars Helicopter, Ingenuity, which completed 72 historic flights making it the first aircraft to achieve powered, controlled flight on another planet.
Learn More about Mars Ingenuity Helicopter