Black Holes
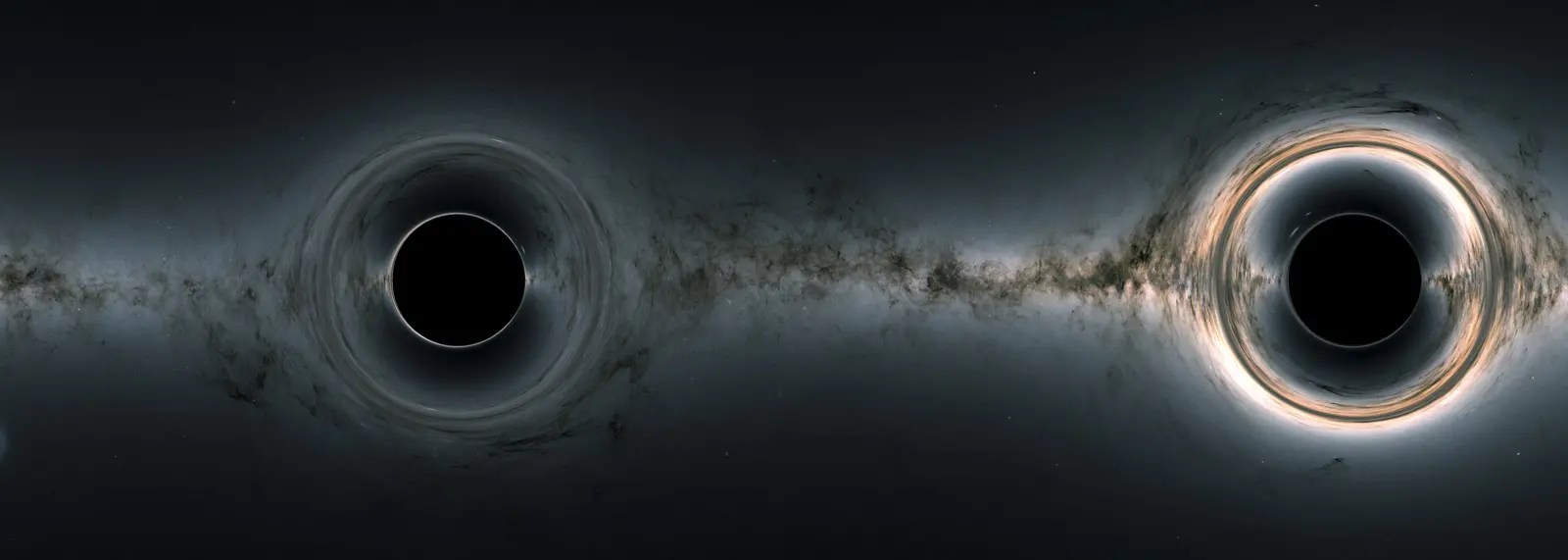
Black holes are among the most mysterious cosmic objects, much studied but not fully understood. These objects aren’t really holes. They’re huge concentrations of matter packed into very tiny spaces. A black hole is so dense that gravity just beneath its surface, the event horizon, is strong enough that nothing – not even light – can escape. The event horizon isn’t a surface like Earth’s or even the Sun’s. It’s a boundary that contains all the matter that makes up the black hole.
There is much we don’t know about black holes, like what matter looks like inside their event horizons. However, there is a lot that scientists do know about black holes.
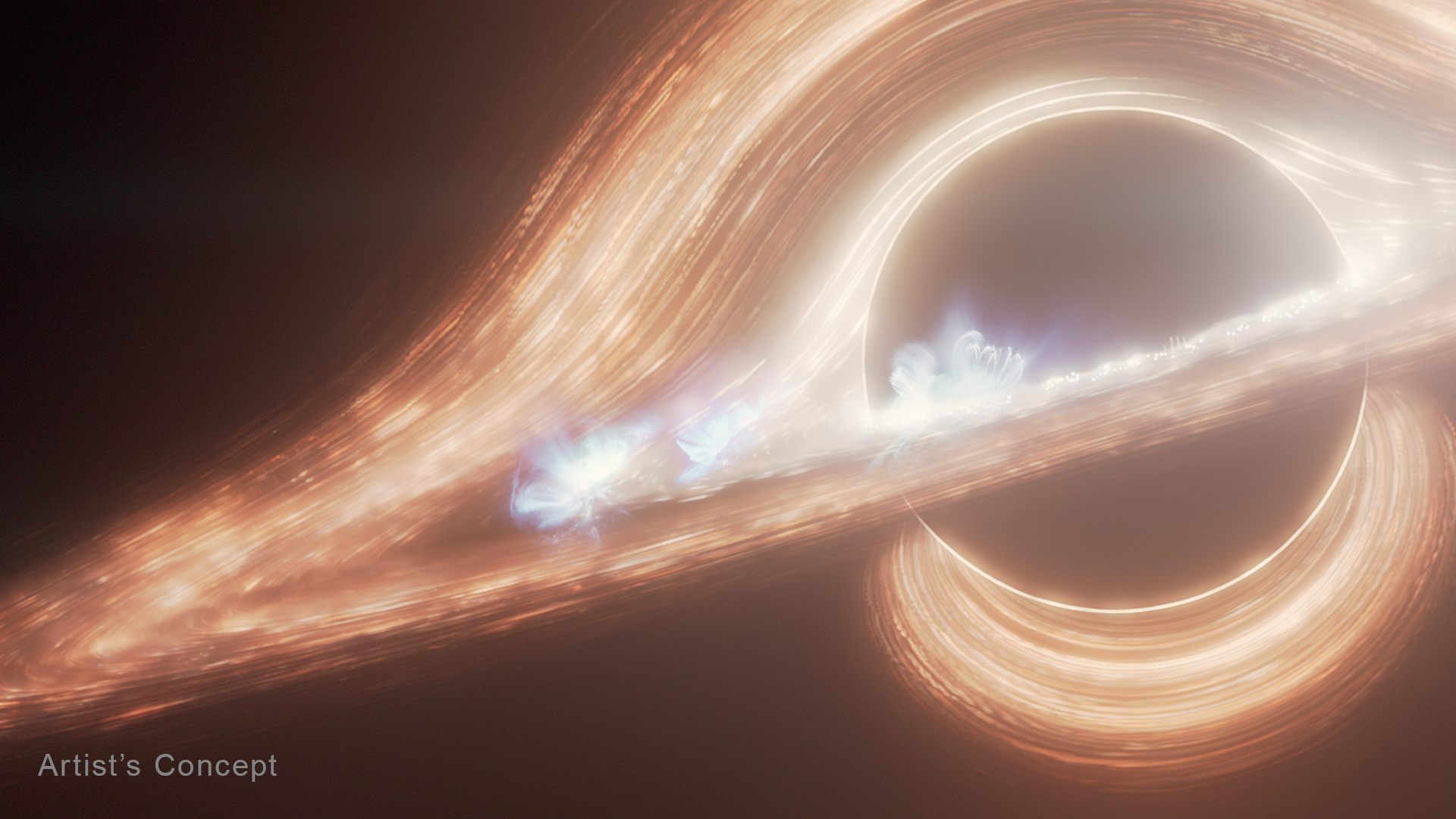
Finding Black Holes
Black holes don’t emit or reflect light, making them effectively invisible to telescopes. Scientists primarily detect and study them based on how they affect their surroundings:
- Black holes can be surrounded by rings of gas and dust, called accretion disks, that emit light across many wavelengths, including X-rays.
- A supermassive black hole’s intense gravity can cause stars to orbit around it in a particular way. Astronomers tracked the orbits of several stars near the center of the Milky Way to prove it houses a supermassive black hole, a discovery that won the 2020 Nobel Prize.
- When very massive objects accelerate through space, they create ripples in the fabric of space-time called gravitational waves. Scientists can detect some of these by the ripples’ effect on detectors.
- Massive objects like black holes can bend and distort light from more distant objects. This effect, called gravitational lensing, can be used to find isolated black holes that are otherwise invisible.
Black Holes Are Not ...
- Wormholes. They don’t provide shortcuts between different points in space, or portals to other dimensions or universes.
- Cosmic vacuum cleaners. Black holes don’t suck in other matter. From far enough away, their gravitational effects are just like those of other objects of the same mass.
NASA
Essential Black Hole Facts
-
01
Closest
The nearest known black hole, called Gaia BH1, is about 1,500 light-years away.
-
02
Farthest
The most distant black hole detected, at the center of a galaxy called QSO J0313-1806, is around 13 billion light-years away.
-
03
Biggest
The most massive black hole observed, TON 618, tips the scales at 66 billion times the Sun’s mass.
-
04
Smallest
The lightest-known black hole is only 3.8 times the Sun’s mass. It’s paired up with a star.
-
05
Spaghettification
A real term that describes what happens when matter gets too close to a black hole. It’s squeezed horizontally and stretched vertically, resembling a noodle.
-
06
Spin
All black holes spin. The fastest-known – named GRS 1915+105 – clocks in at over 1,000 rotations per second.
-
07
Particle accelerators
Monster black holes at the centers of galaxies can launch particles to near light speed.
-
08
Gravity's the same
If you replaced the Sun with a black hole of the same mass, the solar system would get a lot colder, but the planets would stay in their orbits.
-
09
Star booms
One type of black hole is born when massive stars run out of fuel and explode in supernovae.
-
10
Not so rare
Most Milky Way-sized galaxies have monster black holes at their centers. Our is called Sagittarius A* (pronounced ey-star), and it’s 4 million times the Sun’s mass.