1 min read
Exoplanet WASP-39 b and Its Star (Illustration)

This illustration shows what exoplanet WASP-39 b could look like, based on current understanding of the planet.
WASP-39 b is a hot, puffy gas giant with a mass 0.28 times Jupiter (0.94 times Saturn) and a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter, orbiting just 0.0486 astronomical units (4,500,000 miles) from its star. The star, WASP-39, is fractionally smaller and less massive than the Sun. Because it is so close to its star, WASP-39 b is very hot and is likely to be tidally locked, with one side facing the star at all times.
Data collected by Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) show unambiguous evidence for carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, while previous observations from NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, as well as other telescopes, indicate the presence of water vapor, sodium, and potassium. The planet probably has clouds and some form of weather, but it may not have atmospheric bands like those of Jupiter and Saturn.
This illustration is based on indirect transit observations from Webb as well as other space and ground-based telescopes. Webb has not captured a direct image of this planet.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.14:29:18.42
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+03:26:40.2
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Virgo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.700 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.WASP-39 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Hot gas giant exoplanet
- Release DateAugust 25, 2022
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Detects Carbon Dioxide in Exoplanet Atmosphere
- CreditArtwork: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Related Images & Videos

Exoplanet WASP-39 b (NIRSpec Transmission Spectrum)
A transmission spectrum of the hot gas giant exoplanet WASP-39 b captured by Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) on July 10, 2022, reveals the first clear evidence for carbon dioxide in a planet outside the solar system. This is also the first detailed exoplanet...
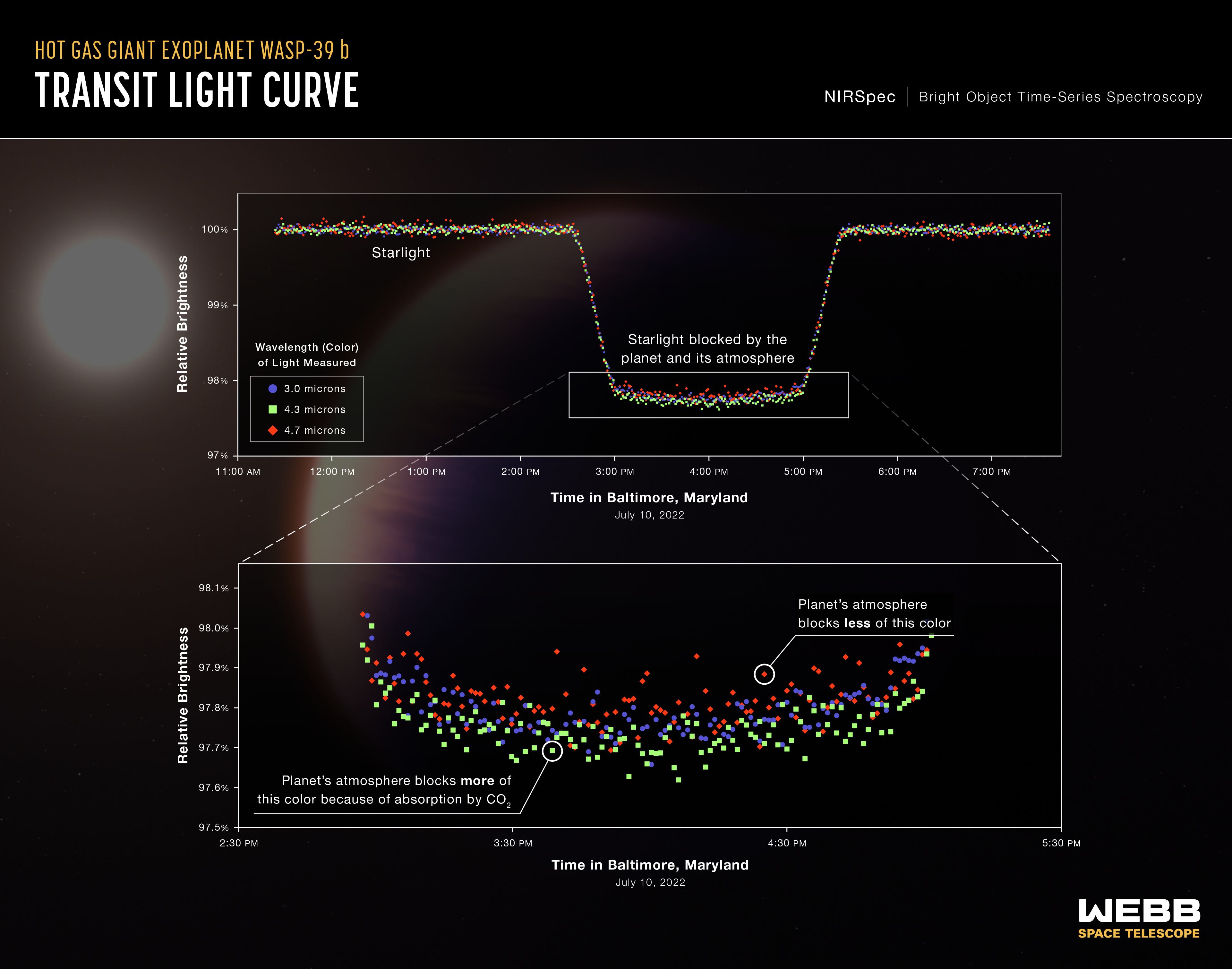
Exoplanet WASP-39 b (NIRSpec Transit Light Curves)
A series of light curves from Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) shows the change in brightness of three different wavelengths (colors) of light from the WASP-39 star system over time as the planet transited the star on July 10, 2022. A transit occurs when an orbiting...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)