1 min read
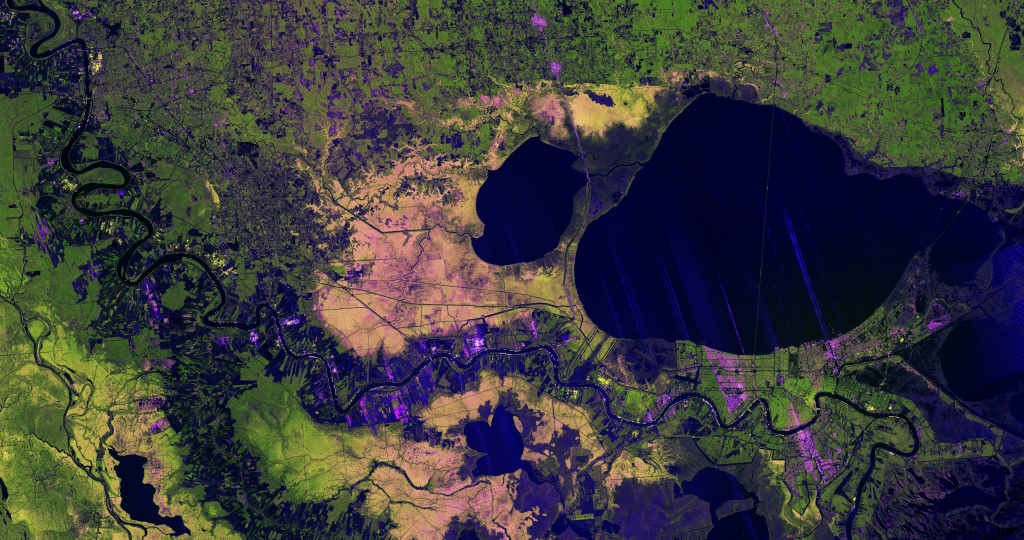
Galaxy Cluster MACS J1423 (NIRCam Image)

Thousands of glimmering galaxies are bound together by their own gravity, making up a massive cluster formally classified as MACS J1423.
The largest bright white oval is a supergiant elliptical galaxy and the dominant member of this galaxy cluster. The galaxy cluster acts like a lens, magnifying and distorting the light of objects that lie well behind it, an effect known as gravitational lensing that has big research benefits. Astronomers can study lensed galaxies in detail, like the Firefly Sparkle galaxy.
This 2023 image is from the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera). Researchers used Webb to survey the same field the Hubble Space Telescope imaged in 2010. Due to its specialization in high-resolution near-infrared imagery, Webb was able to show researchers many more galaxies in far more detail.
Webb’s observation is part of its CAnadian NIRISS Unbiased Cluster Survey (CANUCS), a follow up to the Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble (CLASH) program, which used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.14:23:47.79
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.24:05:4.64
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Boötes
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Galaxy cluster is 5 billion light-years away
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 2.3 arcminutes across
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from Webb data from proposal: 1208 (C. J. Willott). Image processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.26 Feb 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F115W, F150W, F200W, F277W, F356W, F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.MACSJ1423.8+2404
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Galaxy cluster
- Release DateDecember 11, 2024
- Science ReleaseFound: First Actively Forming Galaxy as Lightweight as Young Milky Way
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Christopher Willott (NRC-Canada), Lamiya Mowla (Wellesley College), Kartheik Iyer (Columbia)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F115W + F150W, Green: F200W + F277W, Red: F356W + F444W

Related Images & Videos
Firefly Sparkle Galaxy and Companions in Galaxy Cluster MACS J1423 (NIRCam Image)
For the first time, astronomers have identified a still-forming galaxy that weighs about the same as our Milky Way if we could “wind back the clock” to weigh our galaxy as it developed. The newly identified galaxy, the Firefly Sparkle, is in the process of assembling and forming...

Illustration of the Firefly Sparkle Galaxy in the Early Universe (Artist's Concept)
This illustration depicts a reconstruction of what the Firefly Sparkle galaxy looked like about 600 million years after the big bang if it wasn’t stretched and distorted by a natural effect known as gravitational lensing . This concept is based on images and data from NASA’s...

Galaxy Cluster MACS J1423 (NIRCam Compass Image)
This image of galaxy cluster MACS J1423, captured by the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), shows compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. The scale bar is...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Christopher Willott (NRC-Canada), Lamiya Mowla (Wellesley College), Kartheik Iyer (Columbia)