1 min read
Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Artist’s Concept)
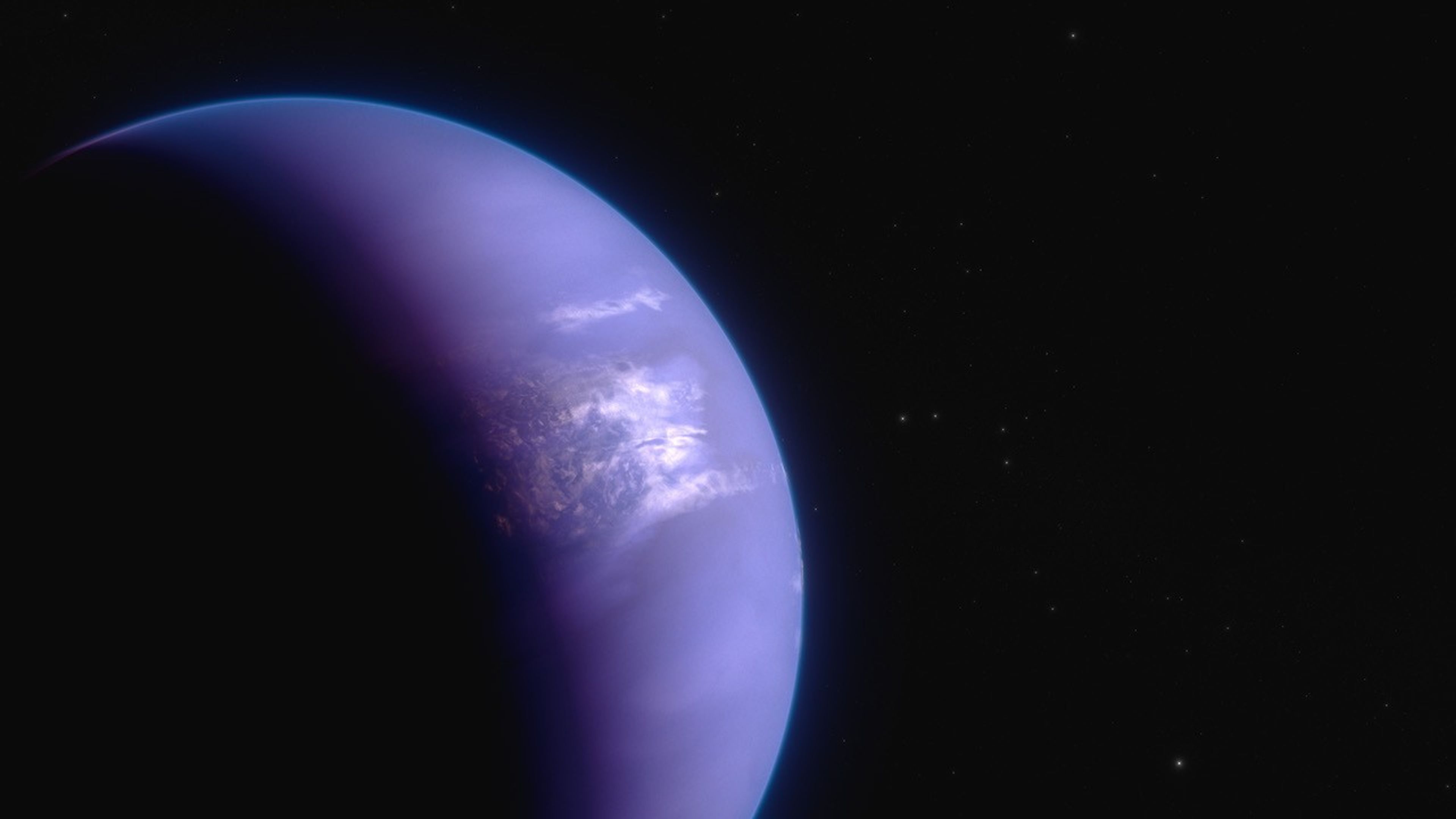

This artist’s concept shows what the hot gas-giant exoplanet WASP-43 b could look like. WASP-43 b is a Jupiter-sized planet circling a star roughly 280 light-years away, in the constellation Sextans. The planet orbits at a distance of about 1.3 million miles (0.014 astronomical units, or AU), completing one circuit in about 19.5 hours. Because it is so close to its star, WASP-43 b is probably tidally locked: its rotation rate and orbital period are the same, such that one side faces the star at all times.
Temperature measurements based on the amount of 5- to 12-micron mid-infrared light emitted by the planet show that the nightside is probably covered in thick, high clouds. Spectroscopy measurements indicate the presence of water vapor on both the dayside and nightside. But because it is too hot for liquid water to exist, the clouds are probably made of tiny mineral grains instead of water droplets. A surprising lack of methane on the nightside suggests that strong eastward winds are mixing atmospheric gases around the planet.
This illustration is based on new data gathered by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) as well as previous observations from other ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble and Spitzer. Webb has not captured any images of the planet.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10:19:37.96
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-09:48:23.20
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Sextans
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.280 light-years (87 parsecs)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.WASP-43 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Hot Jupiter Exoplanet
- Release DateApril 30, 2024
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Maps Weather on Planet 280 Light-Years Away
- CreditArtwork: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)
Related Images & Videos
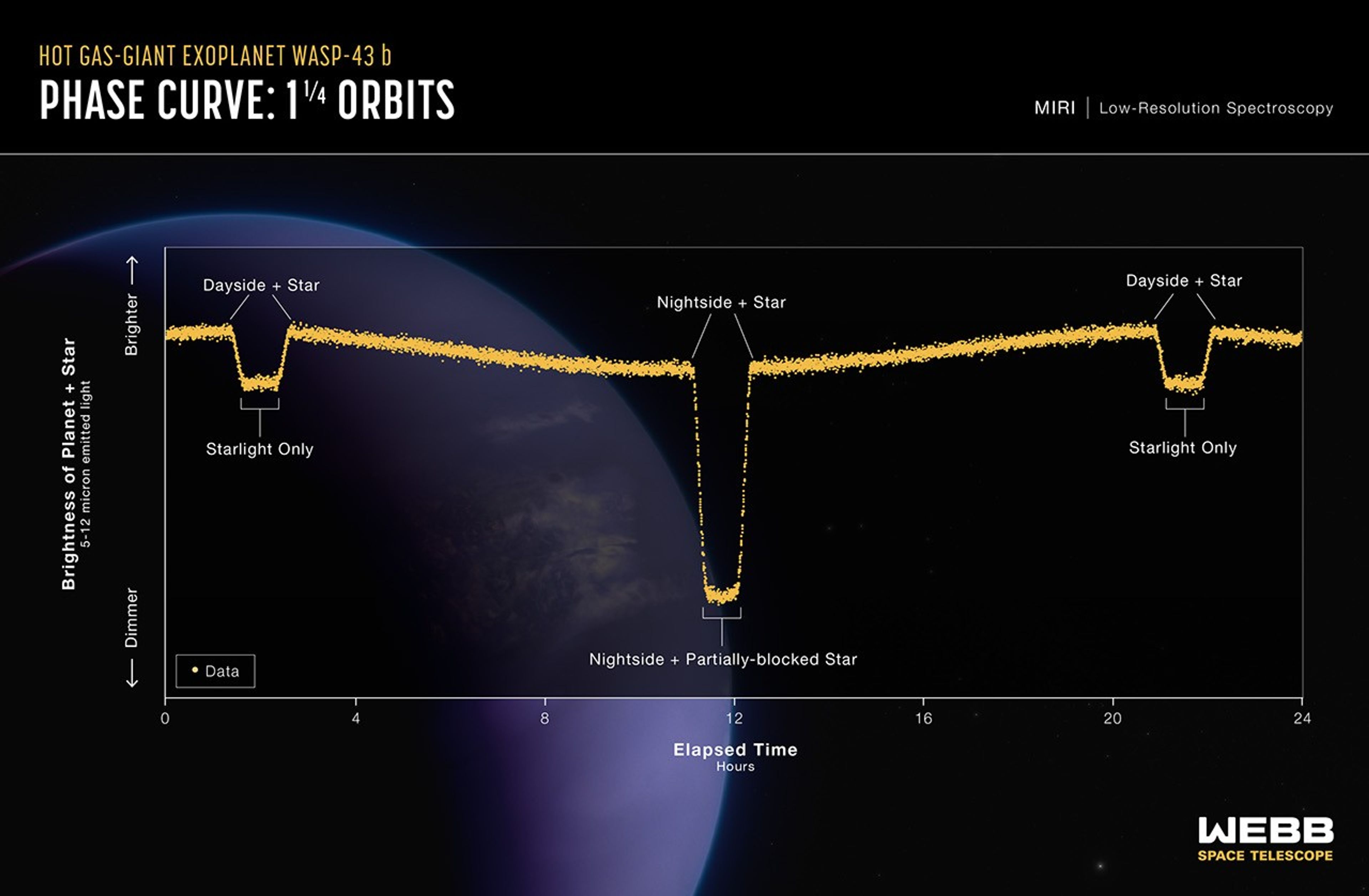
Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (MIRI Phase Curve)
This light curve shows the change in brightness of the WASP-43 system over time as the planet orbits the star. This type of light curve is known as a phase curve because it includes the entire orbit, or all phases of the planet. Because it is tidally locked, different sides of...
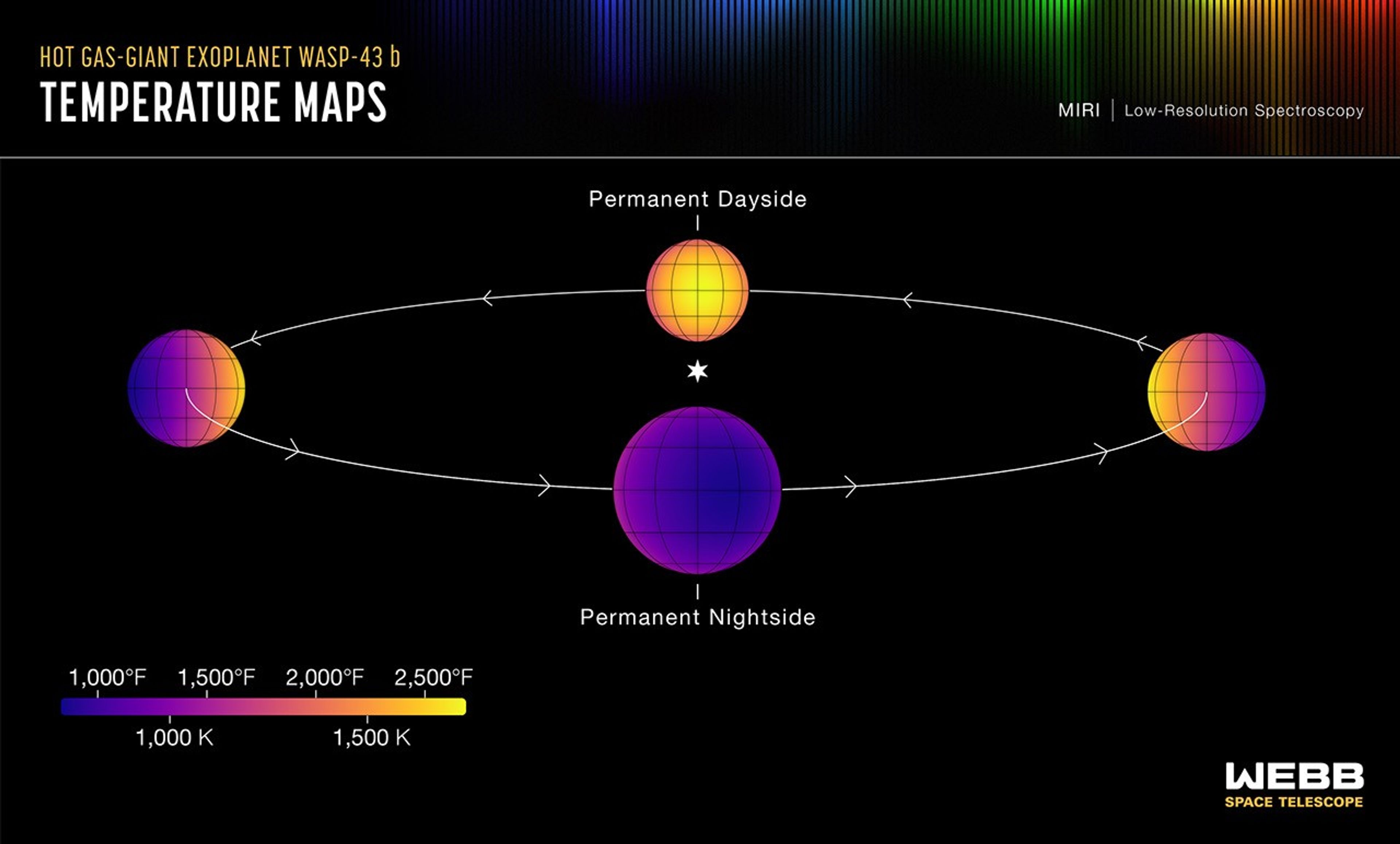
Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Temperature Maps)
This set of maps shows the temperature of the visible side of the hot gas-giant exoplanet WASP-43 b, as the planet orbits its star. The temperatures were calculated based on more than 8,000 brightness measurements of 5- to 12-micron mid-infrared light detected from the...
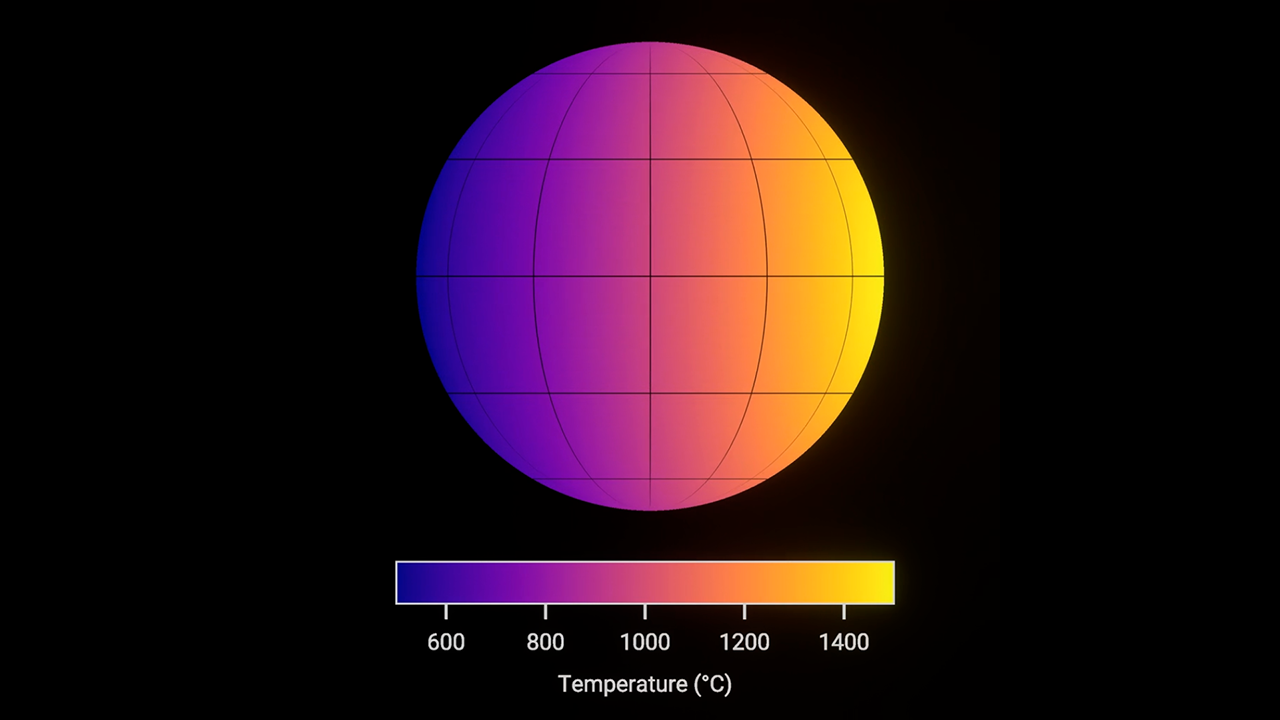
Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Rotating Global Temperature Map)
Global temperature map of the hot gas giant exoplanet WASP-43 b. This map was made based on the brightness of 5- to 12-micron mid-infrared light detected from the planet by MIRI (the Mid-Infrared Instrument) on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. In general, the hotter an object...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)





























