1 min read
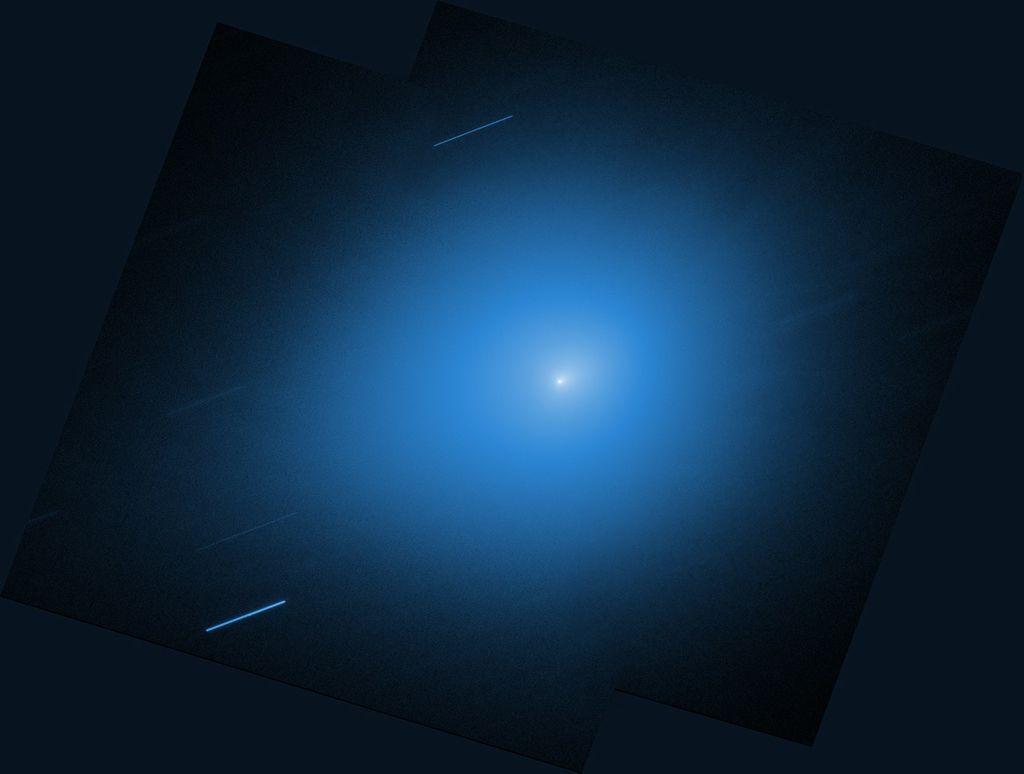
HR 8799 (NIRCam Image)

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has provided the clearest look yet at the iconic multi-planet system HR 8799. The observations detected carbon dioxide in each of the planets, which provides strong evidence that the system’s four giant planets formed much like Jupiter and Saturn, by slowly building solid cores that attract gas from within a protoplanetary disk.
Colors are applied to filters from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), revealing their intrinsic differences. A star symbol marks the location of the host star HR 8799, whose light has been blocked by a coronagraph.
The colors in this image, which represent different wavelengths captured by Webb’s NIRCam, tell researchers about the temperatures and composition of the planets. HR 8799 b, which orbits around 6.3 billion miles from the star, is the coldest of the bunch, and the richest in carbon dioxide. HR 8799 e orbits 1.5 billion miles from its star, and likely formed closer to the host star, where there were stronger variations in the composition of material.
In this image, the color blue is assigned to 4.1 micron light, green to 4.3 micron light, and red to the 4.6 micron light.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.23:07:28.901
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+21:08:02.12
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Pegasus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 127 light-years away
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 1194 (C. A. Beichman). Image processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam Coronagraph
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.27 November 2022, 05 Novemebr 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F410M, F430M, F460M
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.HR 8799
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Star with planets and debris disk
- Release DateMarch 17, 2025
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Images Young, Giant Exoplanets, Detects Carbon Dioxide
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Laurent Pueyo (STScI), William Balmer (JHU), Marshall Perrin (STScI)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample medium wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue= F410M, Green= F430M, Red= F460M
Related Images & Videos

51 Eridani (NIRCam Image)
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) captured this image of Eridani 51 b, a cool, young exoplanet that orbits 890 million miles from its star, similar to Saturn’s orbit in our solar system. The observations detected the planet is rich in carbon...

Young Gas Giant HR 8799 e (NIRCam Spectrum)
This graph shows a spectrum of one of the planets in the HR 8799 system, HR 8799 e, which displays the amounts of near-infrared light detected from the planet by Webb at different wavelengths. The blue and yellow lines are a best-fit model for an atmosphere that would be either...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Laurent Pueyo (STScI), William Balmer (JHU), Marshall Perrin (STScI)