World of Change: Shrinking Aral Sea
- World of Change: Padma River
- World of Change: Sprawling Shanghai
- World of Change: Ice Loss in Glacier National Park
- World of Change: Snowpack in the Sierra Nevada
- World of Change: Development of Orlando, Florida
- World of Change: Growing Deltas in Atchafalaya Bay
- World of Change: Coastline Change
- World of Change: Managing Fire in Etosha National Park
- World of Change: Green Seasons of Maine
- World of Change: Columbia Glacier, Alaska
- World of Change: Athabasca Oil Sands
- World of Change: Seasons of the Indus River
- World of Change: Global Temperatures
- World of Change: Seasons of Lake Tahoe
- World of Change: Devastation and Recovery at Mt. St. Helens
- World of Change: Collapse of the Larsen-B Ice Shelf
- World of Change: Mountaintop Mining, West Virginia
- World of Change: Yellow River Delta
- World of Change: Drought Cycles in Australia
- World of Change: El Niño, La Niña, and Rainfall
- World of Change: Severe Storms
- World of Change: Burn Recovery in Yellowstone
- World of Change: Global Biosphere
- World of Change: Antarctic Ozone Hole
- World of Change: Amazon Deforestation
- World of Change: Antarctic Sea Ice
- World of Change: Arctic Sea Ice
- World of Change: Water Level in Lake Powell
- World of Change: Mesopotamia Marshes
- World of Change: Solar Activity
- World of Change: Urbanization of Dubai



















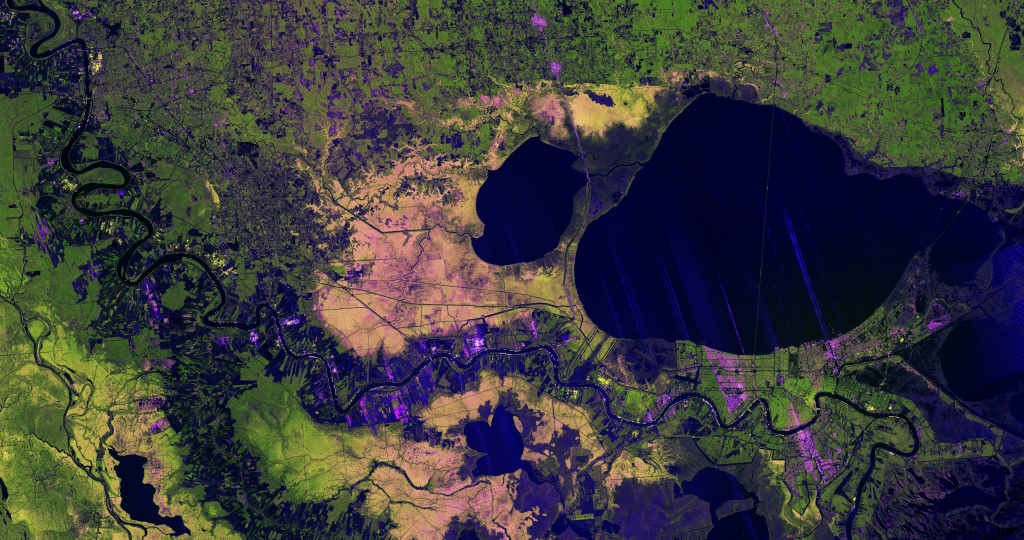
In the 1960s, the Soviet Union undertook a major water diversion project on the arid plains of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. The region’s two major rivers, fed by snowmelt and precipitation in faraway mountains, were used to transform the desert into farms for cotton and other crops. Before the project, the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers flowed down from the mountains, cut northwest through the Kyzylkum Desert, and finally pooled together in the lowest part of the basin. The lake they made, the Aral Sea, was once the fourth largest in the world.
Although irrigation made the desert bloom, it devastated the Aral Sea. This series of images from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite documents the changes. At the start of the series in 2000, the lake was already a fraction of its 1960 extent (yellow line). The North Aral Sea (sometimes called the Small Aral Sea) had separated from the South (Large) Aral Sea.
The South Aral Sea had split into eastern and western lobes that remained tenuously connected at both ends. By 2001, the southern connection had been severed, and the shallower eastern part retreated rapidly over the next several years. Especially large retreats in the eastern lobe of the South Aral Sea appear to have occurred between 2005 and 2009, when drought limited and then cut off the flow of the Amu Darya. Water levels then fluctuated annually between 2009 and 2018 in alternately dry and wet years. In 2014, the eastern lobe of the South Aral Sea completely disappeared. Water levels in summer 2018 were not as low as they might have been, following a round of seasonal snowmelt in the spring.
As the Aral Sea has dried up, fisheries and the communities that depended on them collapsed. The increasingly salty water became polluted with fertilizer and pesticides. The blowing dust from the exposed lakebed, contaminated with agricultural chemicals, became a public health hazard. The salty dust blew off the lakebed and settled onto fields, degrading the soil. Croplands had to be flushed with larger and larger volumes of river water. The loss of the moderating influence of such a large body of water made winters colder and summers hotter and drier.
In a last-ditch effort to save some of the lake, Kazakhstan built a dam between the northern and southern parts of the Aral Sea. The Kok-Aral dike and dam, finished in 2005, separates the two water bodies and prevents flow out of the North Aral into the lower-elevation South Aral. The dam has led fisheries in the North Aral to rebound, even as it has limited flow into the South Aral. Between 2005 and 2006, water levels in the North Aral rebounded significantly and very small increases are visible throughout the rest of the time period. The differences in water color are due to changes in sediments and water depth.