1 min read
Galaxy GS-NDG-9422 (NIRCam Image)
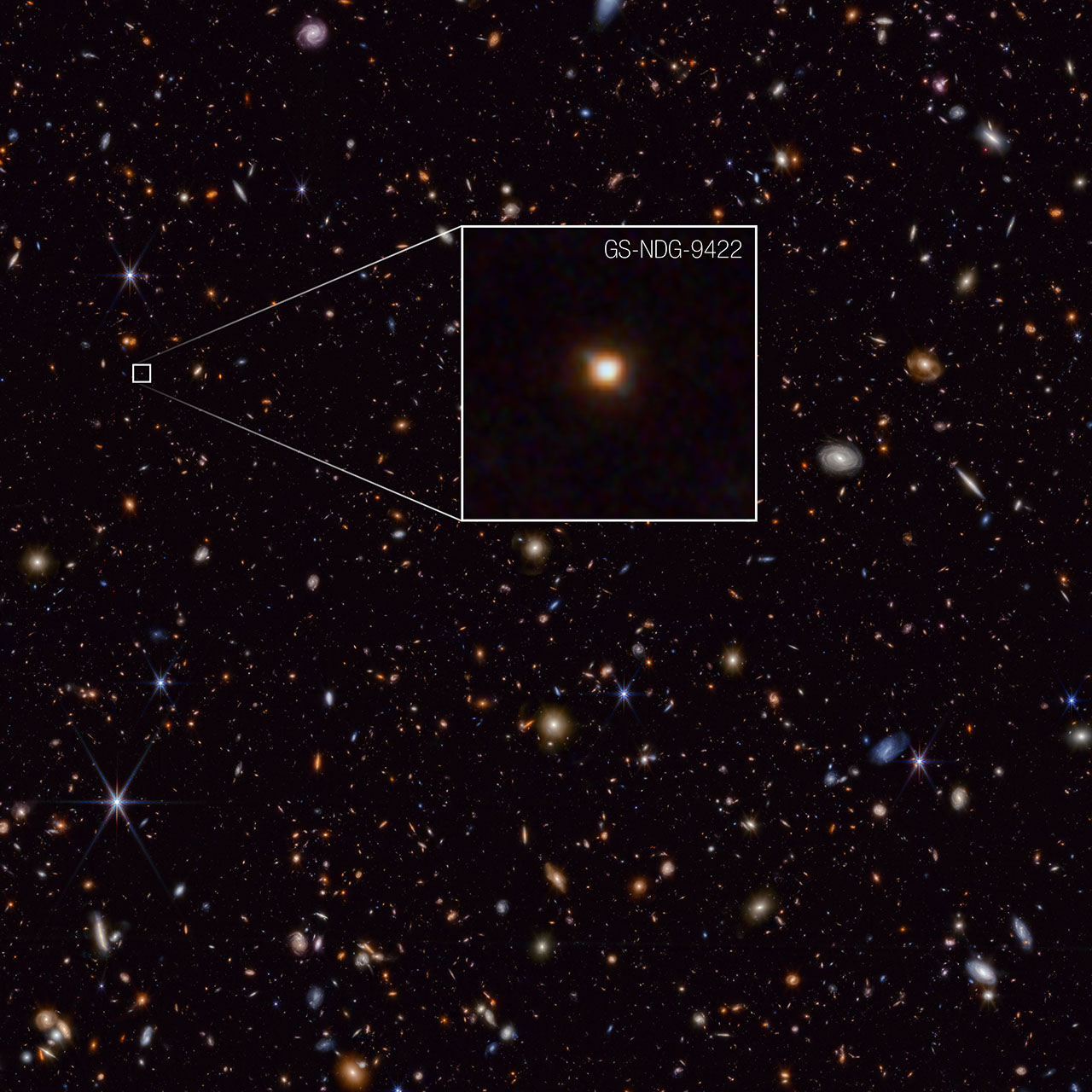

The galaxy GS-NDG-9422 may easily have gone unnoticed. However, what appears as a faint blur in this James Webb Space Telescope NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) image may actually be a groundbreaking discovery that points astronomers on a new path of understanding galaxy evolution in the early universe.
Detailed information on the galaxy’s chemical makeup, captured by Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) instrument, indicates that the light we see in this image is coming from the galaxy’s hot gas, rather than its stars. That is the best explanation astronomers have discovered so far to explain the unexpected features in the light spectrum. They think that the galaxy’s stars are so extremely hot (more than 140,000 degrees Fahrenheit, or 80,000 degrees Celsius) that they are heating up the nebular gas, allowing it to shine even brighter than the stars themselves.
The authors of a new study on Webb’s observations of the galaxy think GS-NDG-9422 may represent a never-before-seen phase of galaxy evolution in the early universe, within the first billion years after the big bang. Their task now is to see if they can find more galaxies displaying the same features.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03:32:36.89
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27:46:49.33
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 3.7 arcminutes across
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 1180 (D. Eisenstein). Image processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.29 Sept. - 10 Oct. 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F090W, F115W, F150W, F200W, F277W, F335M, F356W, F410M, F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GS-NDG-9422, JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, GOODS-S
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Nebular dominated galaxy
- Release DateSeptember 25, 2024
- Science ReleaseIn Odd Galaxy, NASA’s Webb Finds Potential Missing Link to First Stars
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Alex Cameron (Oxford)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F090W + F115W + F150W Green: F200W + F277W + F335M Red: F356W + F410M + F444W

Related Images & Videos
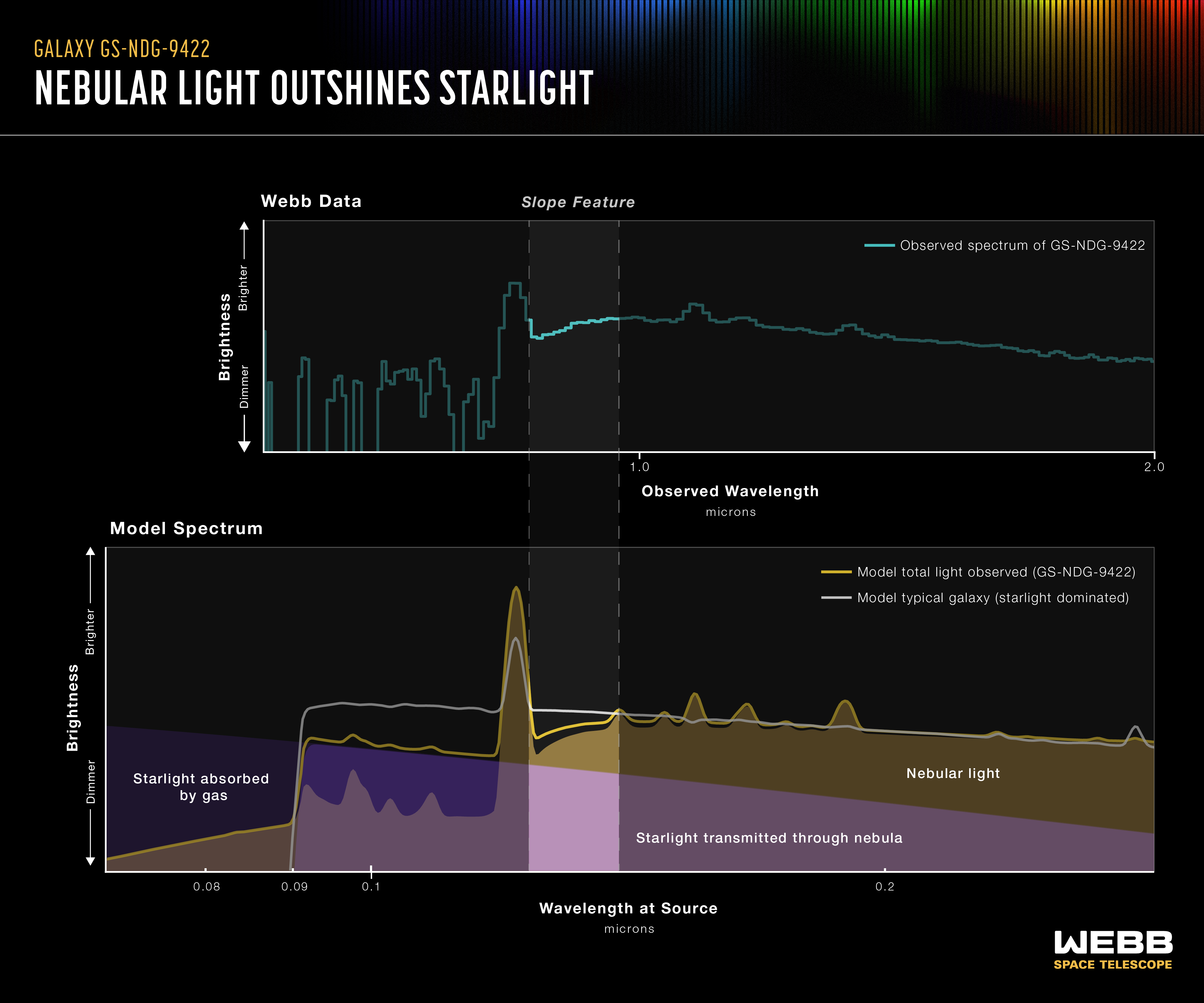
Galaxy GS-NDG-9422 Spectrum (NIRSpec)
This comparison of the data collected by the James Webb Space Telescope with a computer model prediction highlights the same sloping feature that first caught the eye of astronomer Alex Cameron, lead researcher of a new study published in Monthly Notices of the Royal...
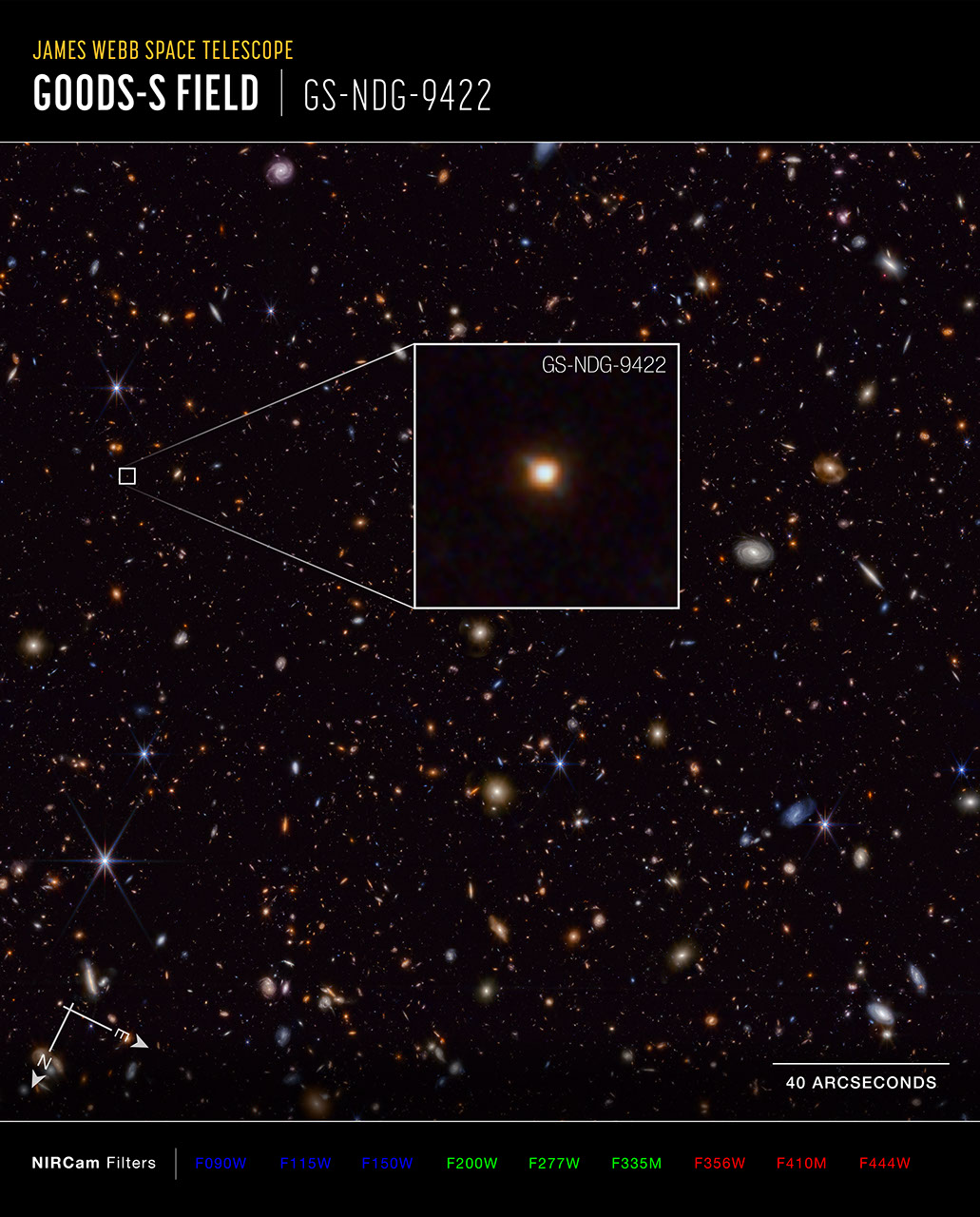
Galaxy GS-NDG-9422 (Compass NIRCam Image)
This image of galaxy GS-NDG-9422, captured by the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instrument, is presented with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. This image shows near-infrared wavelengths of light that have been translated into...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Alex Cameron (Oxford)



























