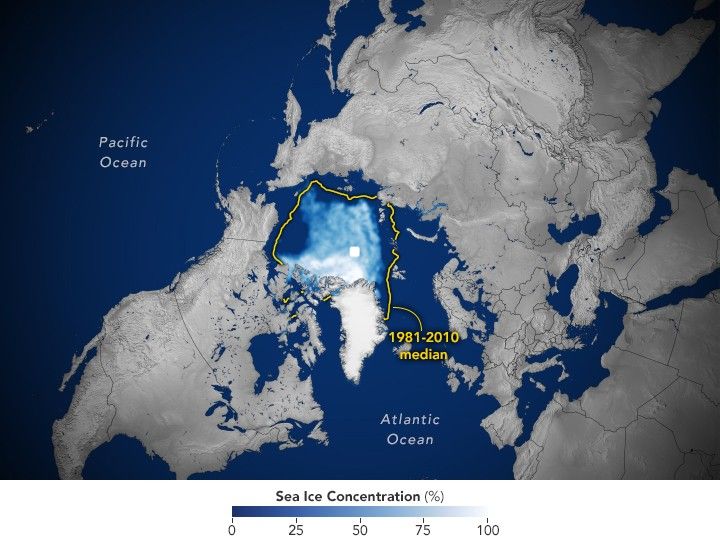
With the end of summer 2025 approaching in the Northern Hemisphere, the extent of sea ice in the Arctic shrank to its annual minimum on September 10, according to NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center. The total sea ice coverage was tied with 2008 for the 10th-lowest on record at 4.60 million square kilometers (1.78 million square miles).
This map shows the sea ice extent (white) on September 10 compared to the 1981-2010 average extent for the same day (yellow line). Scientists calculate sea ice extent by dividing the ocean into a grid of squares and adding up the area of those that meet a concentration threshold; that is, the square is at least 15 percent covered by ice.
The areas of ice covering the oceans at the poles fluctuate through the seasons. Ice accumulates as seawater freezes during colder months and melts away during the warmer months. But the ice never quite disappears entirely at the poles. In the Arctic Ocean, the area the ice covers typically reaches its yearly minimum in September. Since scientists at NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) began tracking sea ice at the poles in 1978, sea ice extent has generally been declining as global temperatures have risen.
“While this year’s Arctic sea ice area did not set a record low, it’s consistent with the downward trend,” said Nathan Kurtz, chief of the Cryospheric Sciences Laboratory at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
Arctic ice reached its lowest recorded extent in 2012. Ice scientist Walt Meier of the National Snow and Ice Data Center at the University of Colorado Boulder, attributes that record low to a combination of a warming atmosphere and unusual weather patterns. This year, the annual decline in ice initially resembled the changes in 2012. Although the melting tapered off in early August, it wasn’t enough to change the year-over-year downward trend.
“For the past 19 years, the minimum ice coverage in the Arctic Ocean has fallen below the levels prior to 2007,” Meier said. “That continues in 2025.”
References & Resources
- NASA Earth (2025, September 17) Arctic Sea Ice Reaches Annual Low. Accessed September 18, 2025.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2016, September 16) Sea Ice. Accessed September 18, 2025.
- National Snow and Ice Data Center (2025, September 17) 2025 Arctic sea ice minimum squeezes into the ten lowest minimums. Accessed September 18, 2025.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Lauren Dauphin, using data from the National Snow and Ice Data Center . Story by James R. Riordon/NASA’s Earth Science News Team, adapted for Earth Observatory.