Land

Play

Read
NASA Missions Studying Land

GEDI
GEDI is the first laser to create 3-D maps of Earth's forests and geographic features, such as how tall the forest is, how dense its branches are, and how its leaves are spaced throughout the canopy.

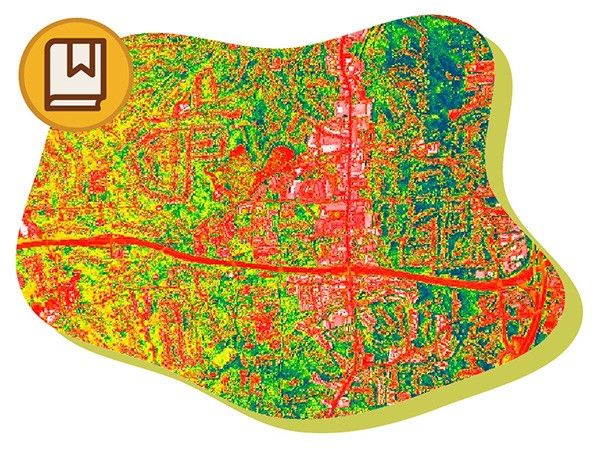
Landsat Satellites
Landsat satellites provide essential information about land surfaces to help scientists detect and monitor melting glaciers, urban growth, natural disasters such as floods and droughts, as well as changes in farms and forests.

NISAR
NISAR will use radar to see through the clouds to learn about the planet. It will measure all of the world’s land and ice twice every 12 days.
PACE
This mission studies phytoplankton (a type of tiny algae), ocean color and measures atmospheric particles and clouds.

SMAP
SMAP improves our ability to predict and monitor floods and droughts. It also helps to improve regular weather forecasts. It can also help predict how much food farm crops will produce.

Suomi-NPP
Suomi-NPP is a satellite with five instruments that watch Earth's environment and climate.