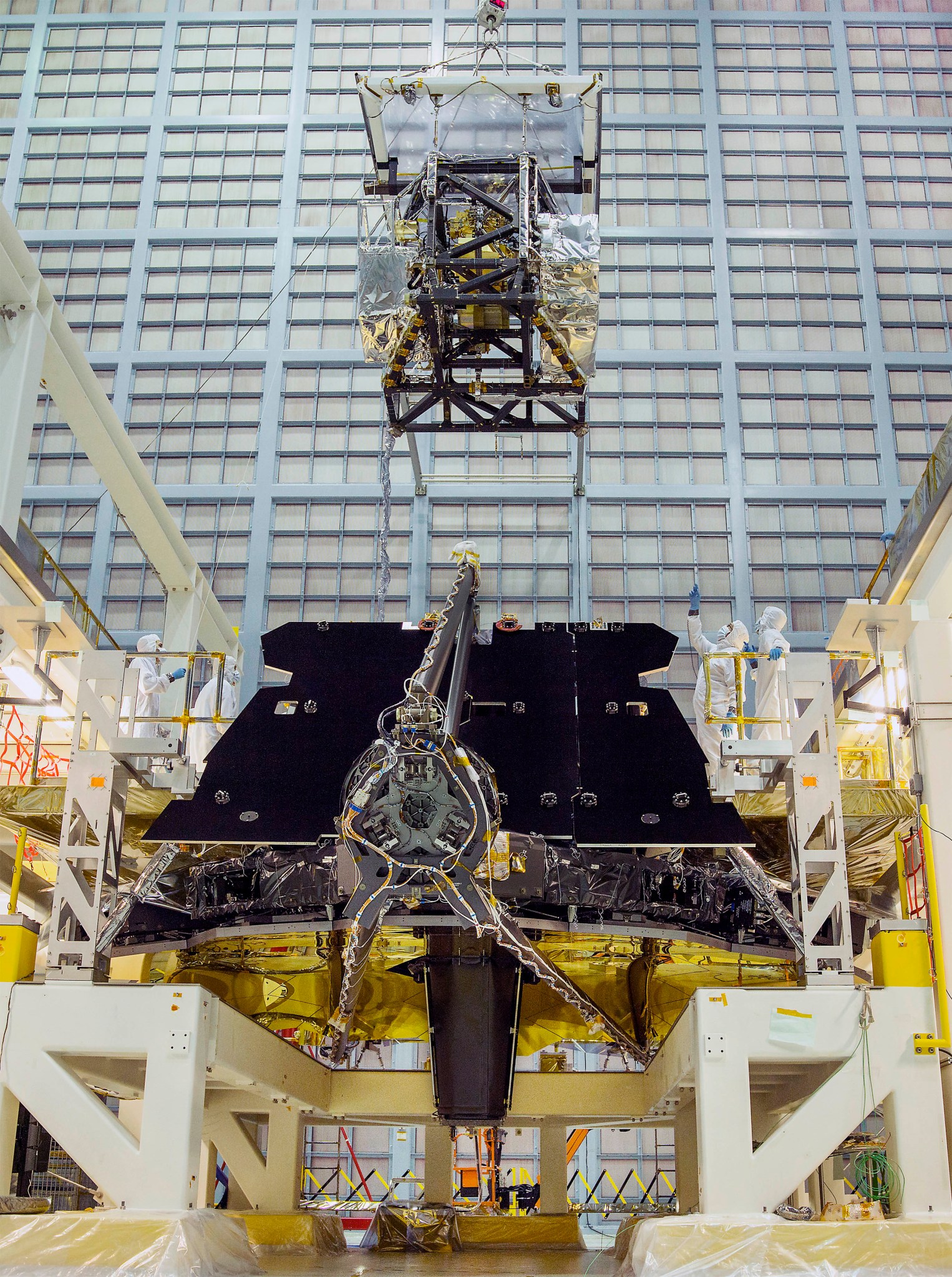
Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM)
ISIM & Webb's Instruments
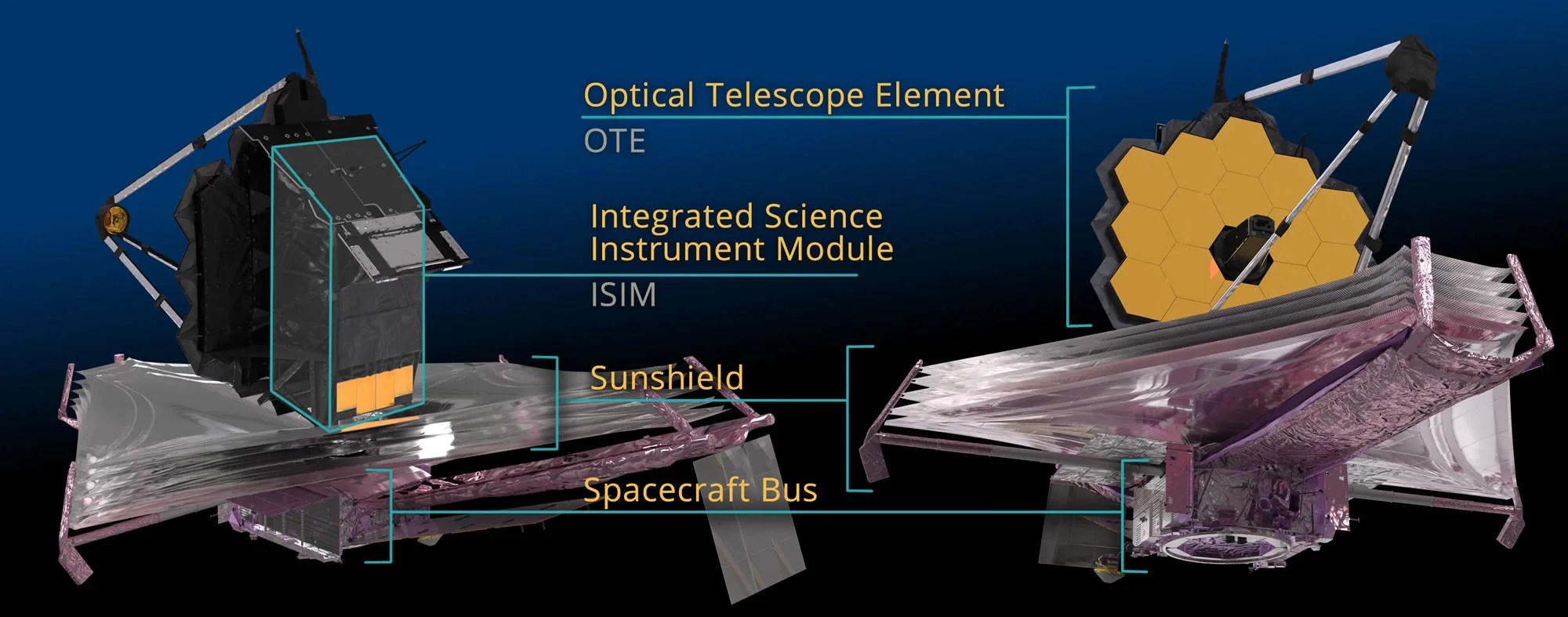
Webb's instruments are contained within the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) which is one of three major elements that comprise the James Webb Space Telescope Observatory flight system. The others are the Optical Telescope Element (OTE) and the Spacecraft Element (Spacecraft Bus and Sunshield).
Webb's Instruments
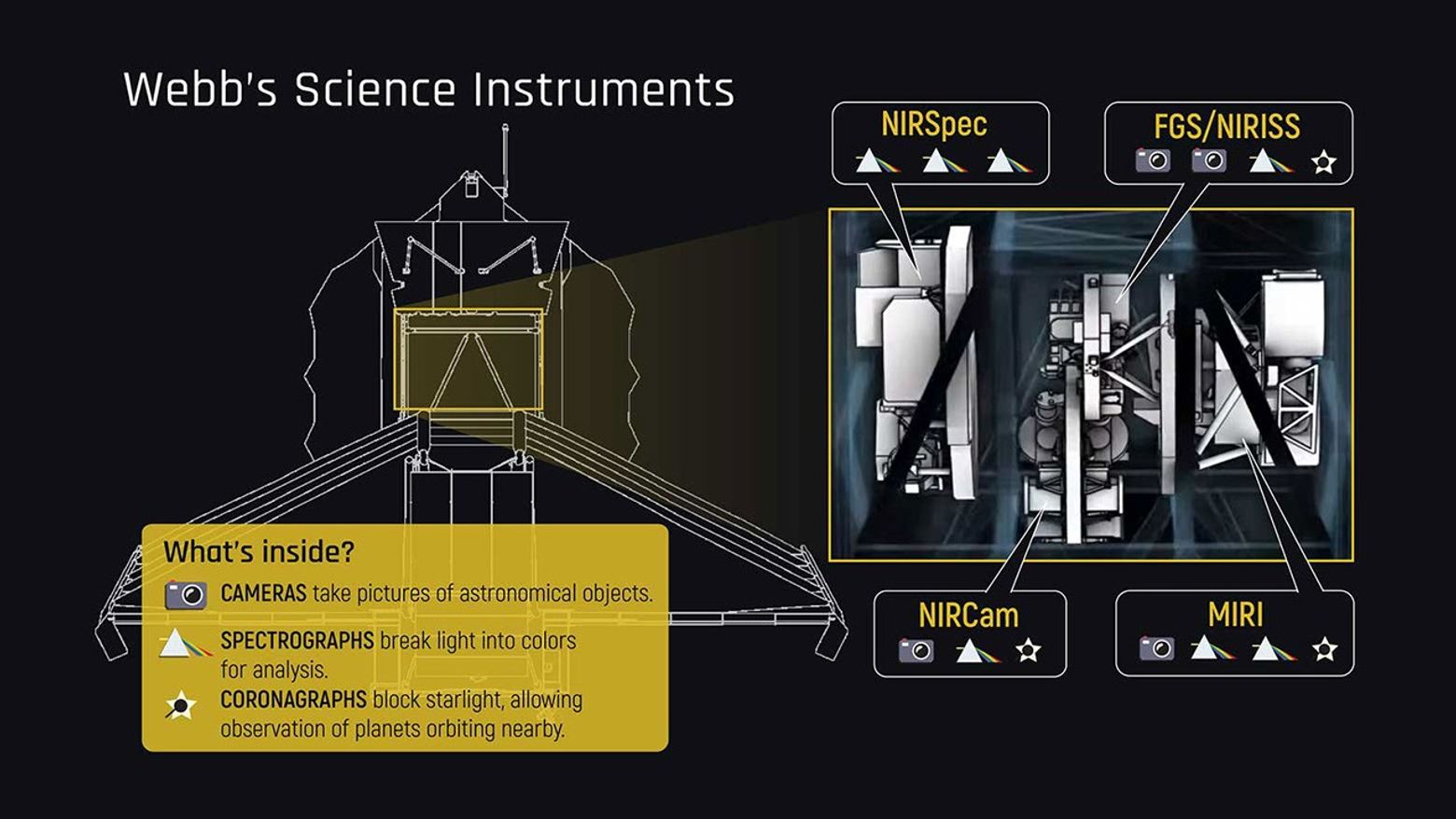
The James Webb Space Telescope’s four scientific instruments are capable of examining the universe across a range of light called infrared, which is beyond the red end of the visible light rainbow (Webb also captures a little visible red as well). Infrared wavelengths are broken down into near-, mid-, and far-infrared ranges. Each instrument has unique features that allow astronomers to study a variety of astronomical objects in different ways.
Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam)
As Webb’s primary camera, NIRCam looks at near-infrared wavelengths (known as near-infrared because these wavelengths are near to the red end of the visible spectrum). It can detect light from the earliest galaxies in the process of formation, stars in nearby galaxies, young stars in the Milky Way, and objects from a distant region of our solar system called the Kuiper Belt. The instrument is also important to exoplanet research; its coronagraph and time-series imaging capability allow it to track the motion of exoplanets as they orbit their star.
Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec)
NIRSpec is a multi-object, near-infrared spectrograph. A spectrograph is a device that breaks light up into its component colors for detailed analysis. NIRSpec detects near-infrared wavelengths and is capable of observing more than 100 objects simultaneously thanks to its innovative microshutter assembly. It is designed to study, among other things, star formation and the chemical composition of young, distant galaxies.
Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)
MIRI has a sensitive camera and a spectrograph to study distant stellar populations, the physics of newly forming stars, and the sizes of faintly-visible comets and Kuiper Belt objects. MIRI is also equipped with a coronagraph, which blocks the glare of a bright object to allow clear observations of faint objects close to it, like exoplanets orbiting a star.
Fine Guidance Sensors/Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS)
FGS is Webb’s guide camera, which helps point the telescope. NIRISS gathers spectra (like NIRSpec), and capture images of the universe at near-infrared wavelengths (like NIRCam), observing both extremely bright and faint objects. NIRISS will be particularly useful for studying the composition of exoplanet atmospheres, among other research. FGS and NIRISS have different purposes but are packaged in one unit.
Wavelength Coverage

ISIM In Depth:
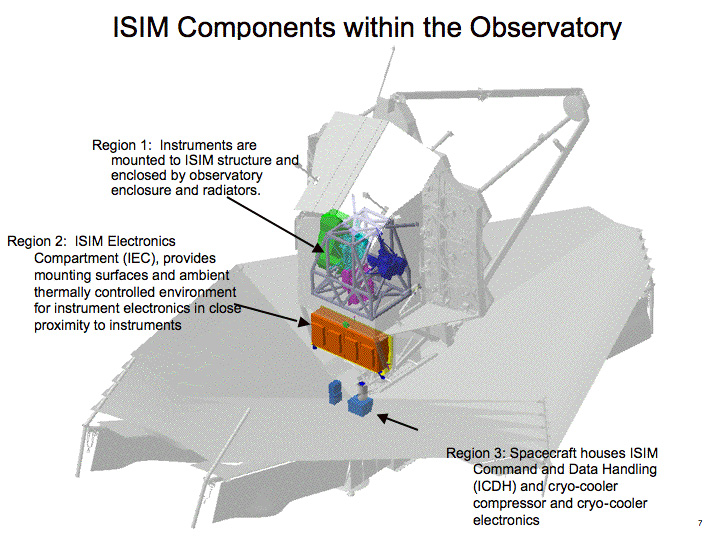
Integrating four major instruments and numerous subsystems into one payload, the ISIM, was a daunting endeavor. To simplify integration, engineers divided the ISIM into three regions.
The "region 1" component is the cryogenic instrument module. This chills the detectors down to 39 K, a necessary first-stage cooling effort so that the spacecraft's own heat doesn't interfere with the infrared light (a form of heat) detected from distant cosmic sources. The ISIM/OTE Thermal Management Subsystem provides passive cooling. Other devices get the detectors even colder.
The "region 2" component is the ISIM Electronics Compartment, which provides the mounting surfaces and ambient thermally controlled environment for the instrument control electronics.
The "region 3" component, located within the Spacecraft Bus, is the ISIM Command and Data Handling subsystem, with integral ISIM flight Software, and the MIRI cryocooler compressor and control electronics.
ISIM Image Gallery
The image below is a SLIDESHOW. Hover over the image to see the image title and controls. Click the image to go to a detail page with more info and the ability to download the image at various resolutions (click downward arrow in lower right corner).