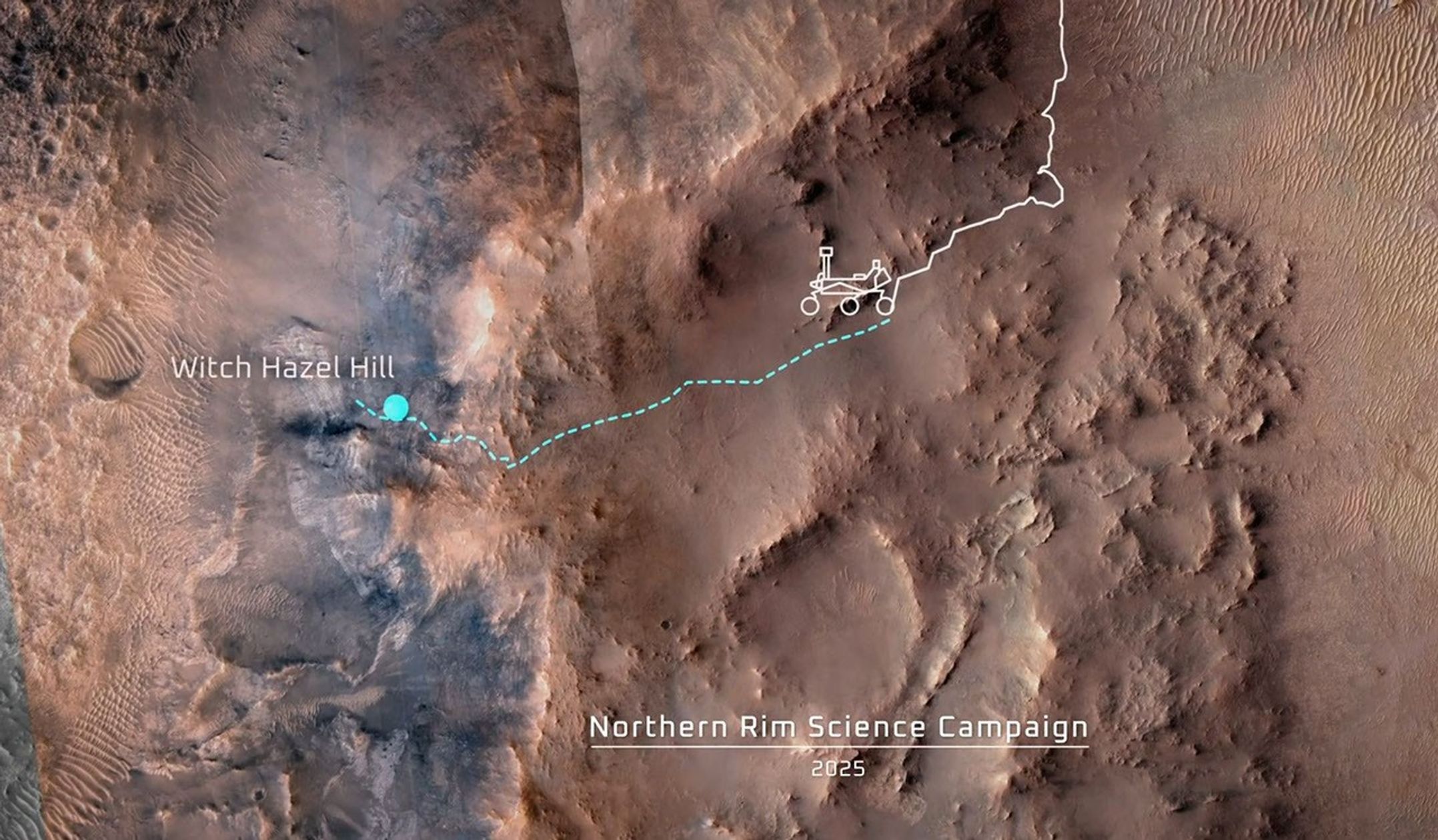
Proposed Route of Perseverance’s Northern Rim Science Campaign
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/University of Arizona |
|---|---|
| Historical Date | December 4, 2024 |
| PIA Number | PIA26480 |
| Language |
|
Dec. 12, 2024
Click here for animation (.mp4, 302 MB)
This animation shows the position of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover as of Dec. 4, 2024, the 1,347th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, along with the proposed route of the mission's fifth science campaign, dubbed Northern Rim, over the next several years.
This map was made using data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera as well as the European Space Agency's (ESA) High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
JPL built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For more about Perseverance: science.nasa.gov/mission/mars-2020-perseverance/