1 min read
JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (NIRCam Image)
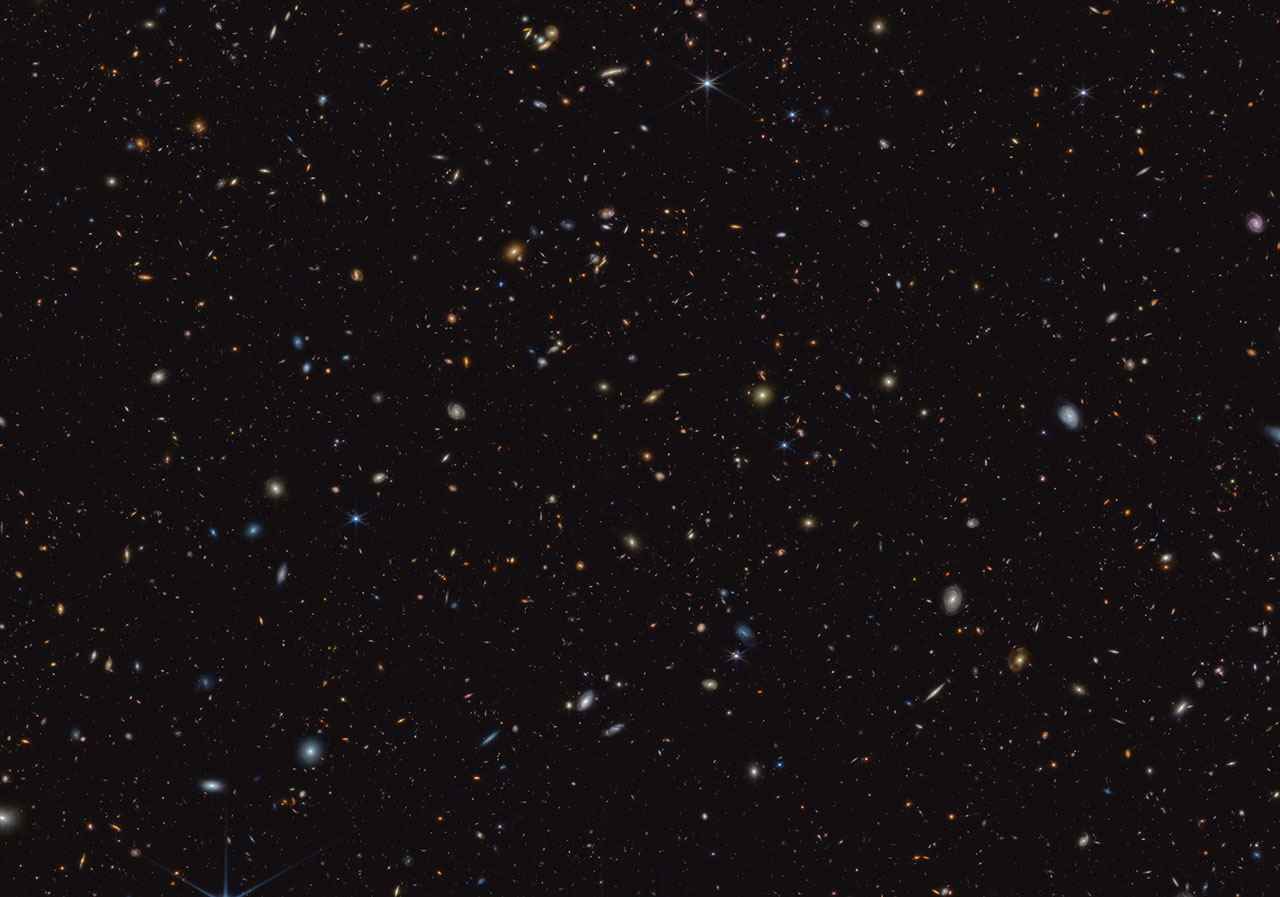

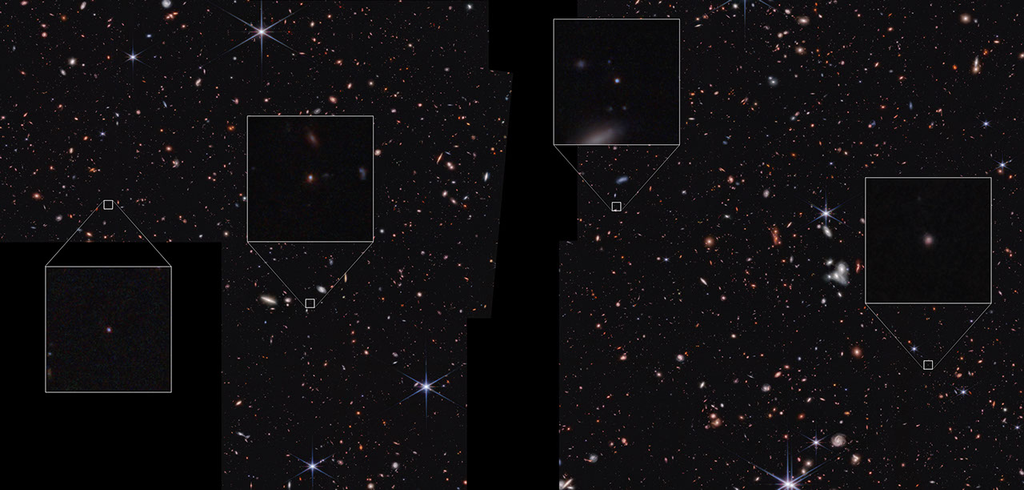
This infrared image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was taken for the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, program. It shows a portion of an area of the sky known as GOODS-South, which has been well studied by the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories. More than 45,000 galaxies are visible here.
Using these and other data, the JADES team has discovered hundreds of galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 600 million years old. The sheer number of these galaxies was far beyond predictions from observations made before Webb’s launch.
The team also has identified galaxies that existed during a time known as the Epoch of Reionization, when the universe underwent a transformation from opaque to transparent. Many of these galaxies shown unusually strong emission line signatures due to the creation of multitudes of hot, massive stars.
In this image, blue, green, and red were assigned to Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) data at 0.9, 1.15, and 1.5 microns; 2.0, 2.77, and 3.35 microns; and 3.56, 4.1, and 4.44 microns (F090W, F115W, and F150W; F200W, F277W, and F335M; and F356W, F410M, and F444W), respectively.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03:32:36.89
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27:46:49.33
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 6 arcminutes across
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 1180 (D. Eisenstein)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.29 Sept. - 10 Oct. 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F090W, F115W, F150W, F200W, F277W, F335M, F356W, F410M, F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, GOODS-S
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Deep Field Survey
- Release DateJune 5, 2023
- Science ReleaseEarly Universe Crackled With Bursts of Star Formation, Webb Shows
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, Brant Robertson (UC Santa Cruz), Ben Johnson (CfA), Sandro Tacchella (Cambridge), Marcia Rieke (University of Arizona), Daniel Eisenstein (CfA); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F090W + F115W + F150W Green: F200W + F277W + F335M Red: F356W + F410M + F444W

Related Images & Videos

JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (NIRCam Compass Image)
This image of the GOODS-South field, captured by Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), shows compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Brant Robertson (UC Santa Cruz), Ben Johnson (CfA), Sandro Tacchella (Cambridge), Marcia Rieke (University of Arizona), Daniel Eisenstein (CfA)
Alyssa Pagan (STScI)