1 min read
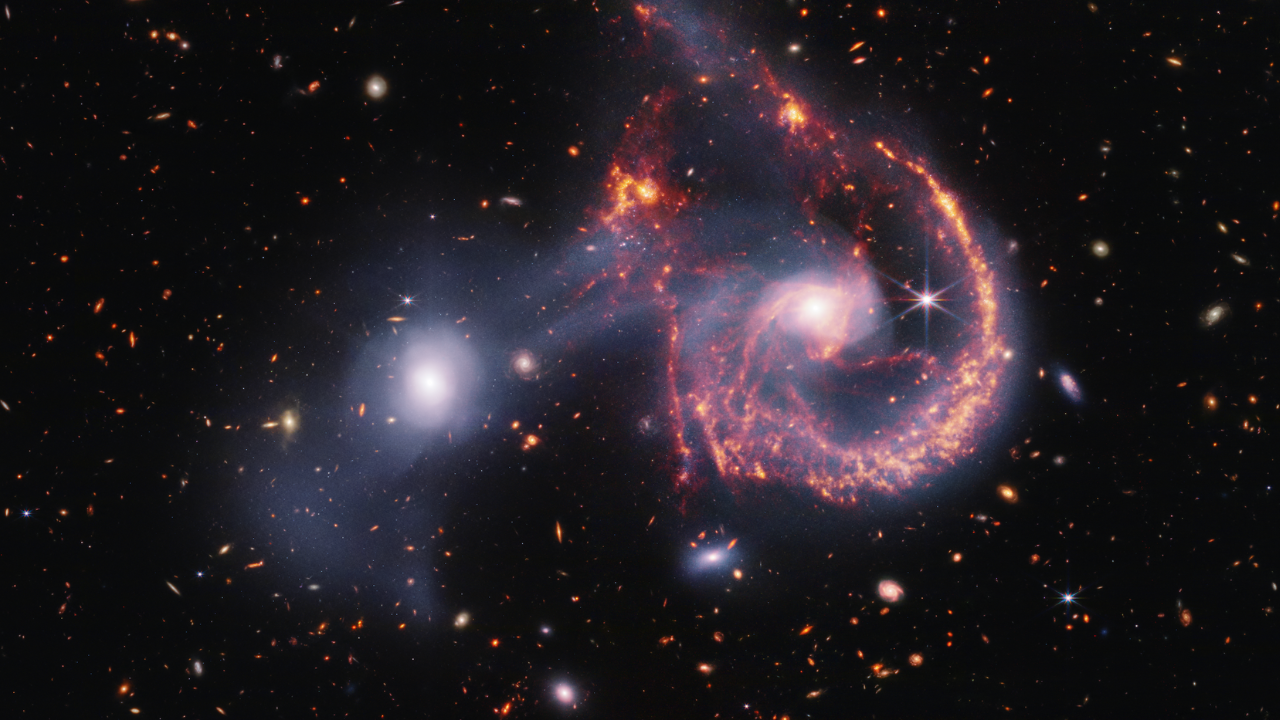
Arp 107 (MIRI Image)

This image of Arp 107, shown by Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), reveals the supermassive black hole that lies in the center of the large spiral galaxy to the right. This black hole, which pulls much of the dust into lanes, also display’s Webb’s characteristic diffraction spikes, caused by the light that it emits interacting with the structure of the telescope itself.
Perhaps the defining feature of the region, which MIRI reveals, are the millions of young stars that are forming, highlighted in blue. These stars are surrounded by dusty silicates and soot-like molecules known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The small elliptical galaxy to the left, which has already gone through much of its star formation, is composed of many of these organic molecules.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10:52:16.82
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+30:04:0.27
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Leo Minor
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 450 million light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 2.4 arcmin across (about 310,000 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 6556 (M. Garcia Marin); Image Processing: M. Garcia Marin, Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.1 May 2024
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F770W, F1000W, F1500W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Arp 107
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Interacting galaxies
- Release DateSeptember 18, 2024
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Provides Another Look Into Galactic Collisions
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the MIRI instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: MIRI> Yellow: F770W, Orange: F1000W, Red: F1500W
Related Images & Videos

Arp 107 (NIRCam and MIRI Image)
This composite image of Arp 107, created with data from the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) reveal a wealth of information about their star-formation history and how these two galaxies collided hundreds of millions of...

Arp 107 (NIRCam and MIRI Compass Image)
The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above). The scale bar is labeled in...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI