1 min read
Diagram of the James Webb Space Telescope’s Main Components
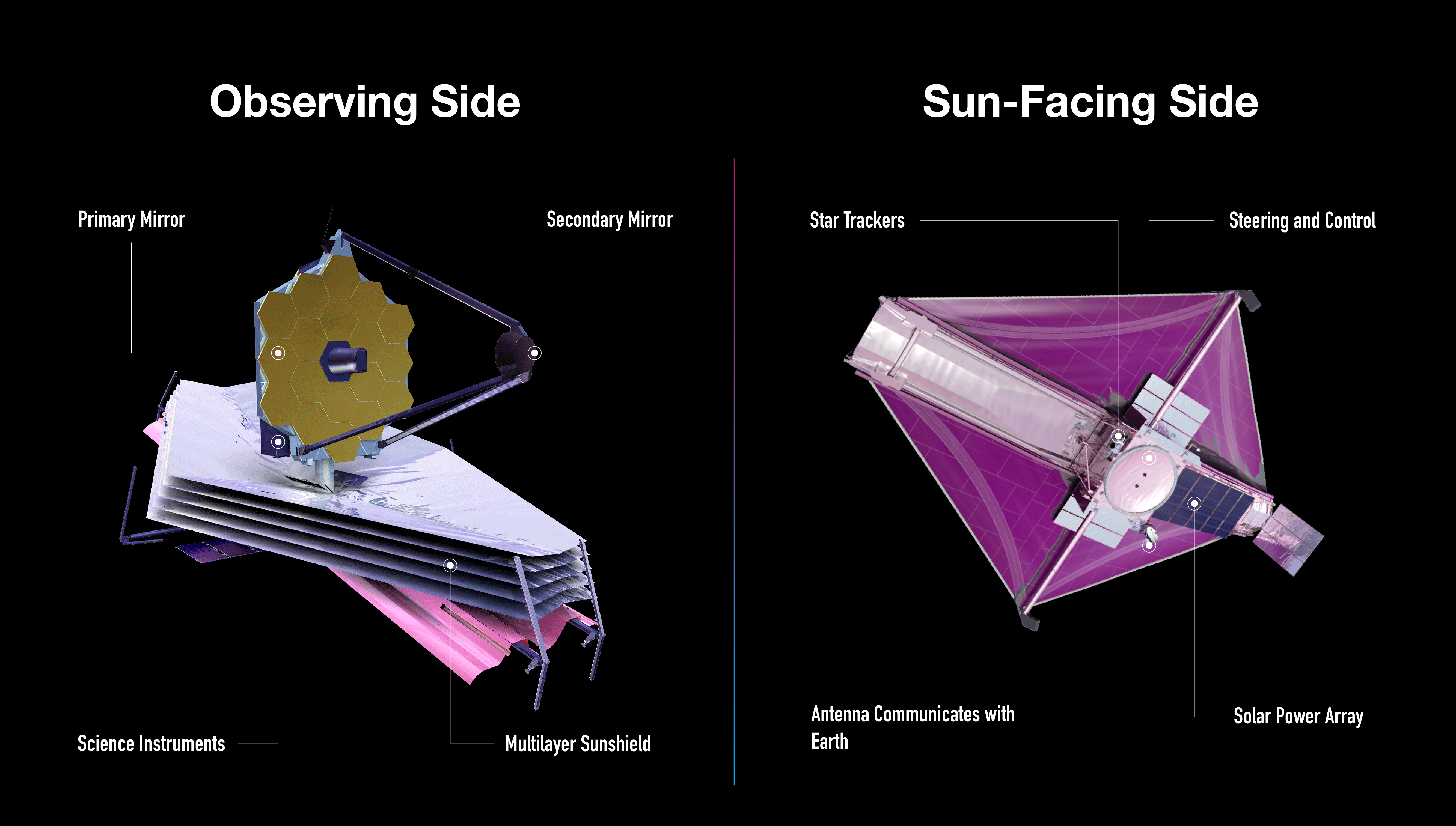
The James Webb Space Telescope has a cool side, which faces away from the Sun, and a hot side, which faces the Sun.
Webb’s tennis court-sized sunshield protects the telescope from external sources of light and heat, which ensures it can detect faint heat signals from very distant objects. It’s very important for its observing side to be very, very cold.
The lower part of Webb, where its five-layered sunshield is, faces the Sun. This is where its equipment that does not need to be cooled, like its solar panel, antennae, computer, gyroscopes, and navigational jets, are.
Webb’s science instruments are housed behind the mirror, separated from the warm communications and control technology by the sunshield.
Find more detail about the telescope’s size, mirrors, sunshield, orbit, and more.
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Joyce Kang (STScI)