1 min read
Effect of Atmosphere on a Planet’s Dayside Temperature
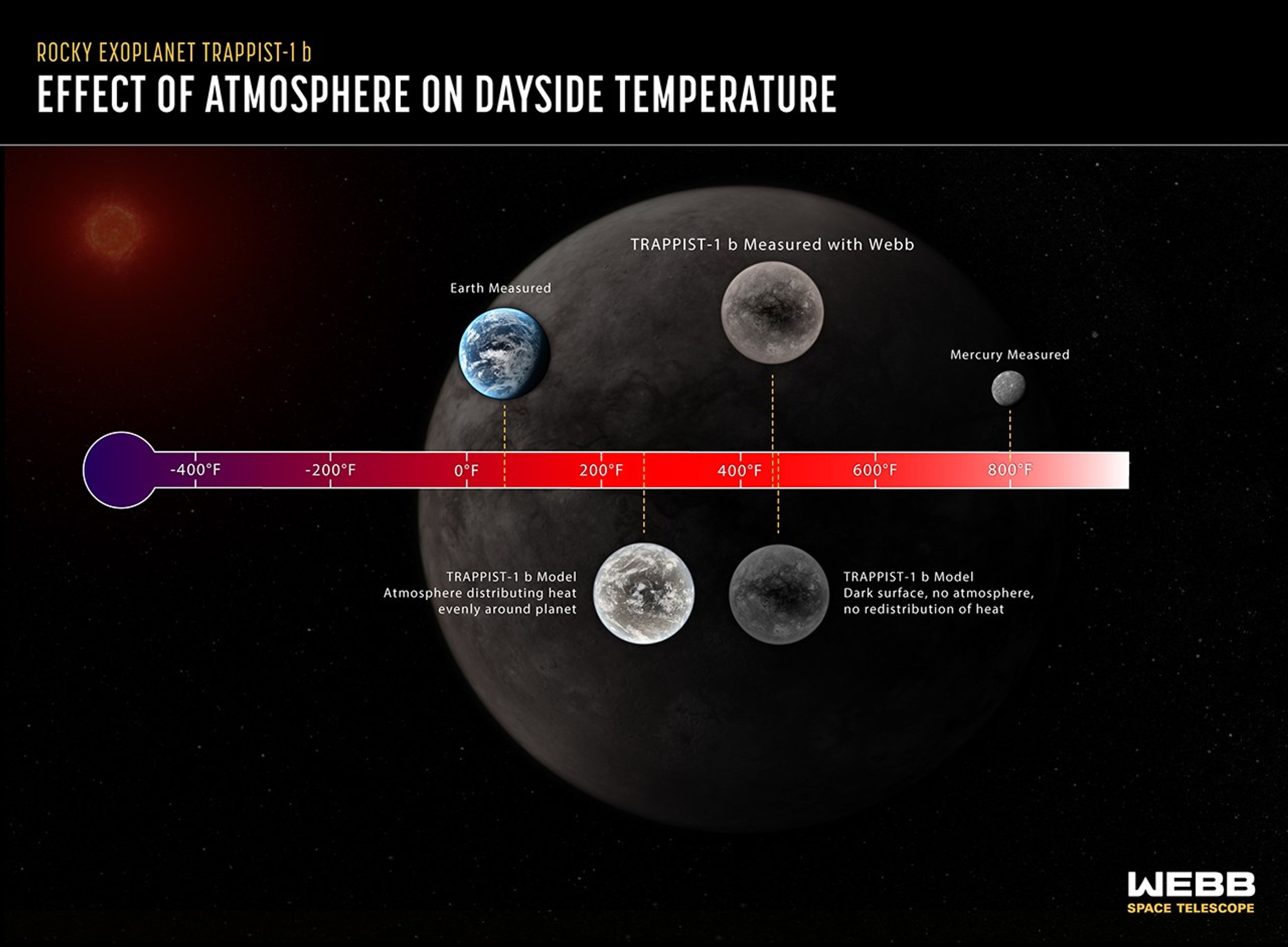
Researchers can determine whether or not a tidally locked rocky planet has an atmosphere by comparing its measured temperature to computer models. In this example, the dayside temperature of the rocky planet TRAPPIST-1 b measured using Webb is very close to the model temperature that assumes the planet has a dark surface and no atmosphere. If the planet did have a substantial atmosphere carrying heat around the planet, the dayside would be significantly cooler, and Webb would have detected less mid-infrared light. TRAPPIST-1 b, which orbits a red dwarf star 40 light-years from Earth, is not part of the Rocky Worlds program.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.23h 06m 30s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-05d 02m 30s
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Aquarius
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.40 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.temperature based on time-series photometry of secondary eclipse
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.2022: November 8, 12, 20, 24, and December 3
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F1500W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.TAPPIST-1 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Rocky exoplanet orbiting red dwarf (M-dwarf) star
- Release DateSeptember 30, 2025
- CreditIllustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI), Andi James (STScI); Science: Thomas Greene (NASA Ames)
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov




























