1 min read
Exoplanet GJ 1214 b and Its Star (Illustration)

Illustration showing what exoplanet GJ 1214 b could look like based on current information. GJ 1214 b, a warm sub-Neptune-sized exoplanet roughly 48 light-years from Earth, is one of the most studied exoplanets in the galaxy. Previous spectroscopic observations indicate that the planet is shrouded in aerosols (clouds or haze), which have thus far made it impossible to determine the composition of gases that make up its thick atmosphere.
This illustration is based on our knowledge of the planet and its host star, and predictions about the likely properties of the planet’s atmosphere. Spectroscopic data from Webb will help us better understand the gases and aerosols that make up the planet’s atmosphere.
GJ 1214 b is in between Earth and Neptune in terms of size (radius 2.74 times Earth), mass (8.2 times Earth), and density (2.2 times water). It orbits its star at a distance of only 0.015 astronomical unit (1.5% of the distance between Earth and the Sun), completing one orbit in 1.58 Earth-days. The star, GJ 1214, is cool red dwarf star with a radius of just 0.22 times that of the Sun, a mass of just 0.18 times the Sun, and a temperature of just 3,250 kelvins (around 2,975 degrees Celsius), about 2,500 degrees cooler than the Sun.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17:15:19.54
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+04:57:38.45
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ophiuchus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.48 light-years from Earth
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Radius: 2.74 times Earth; Mass: 8.2 times Earth; Density: 2.2 times water; Distance from star: 0.0149 AU; Orbital period: 1.58 Earth-days
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Illustration based on data from several missions.
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GJ 1214 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Warm sub-Neptune exoplanet orbiting an M red dwarf star
- Release DateNovember 17, 2021
- Science ReleaseNASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Primed to Lift the Haze Surrounding Sub-Neptunes
- CreditArtwork: NASA, ESA, CSA, Dani Player (STScI)
Related Images & Videos
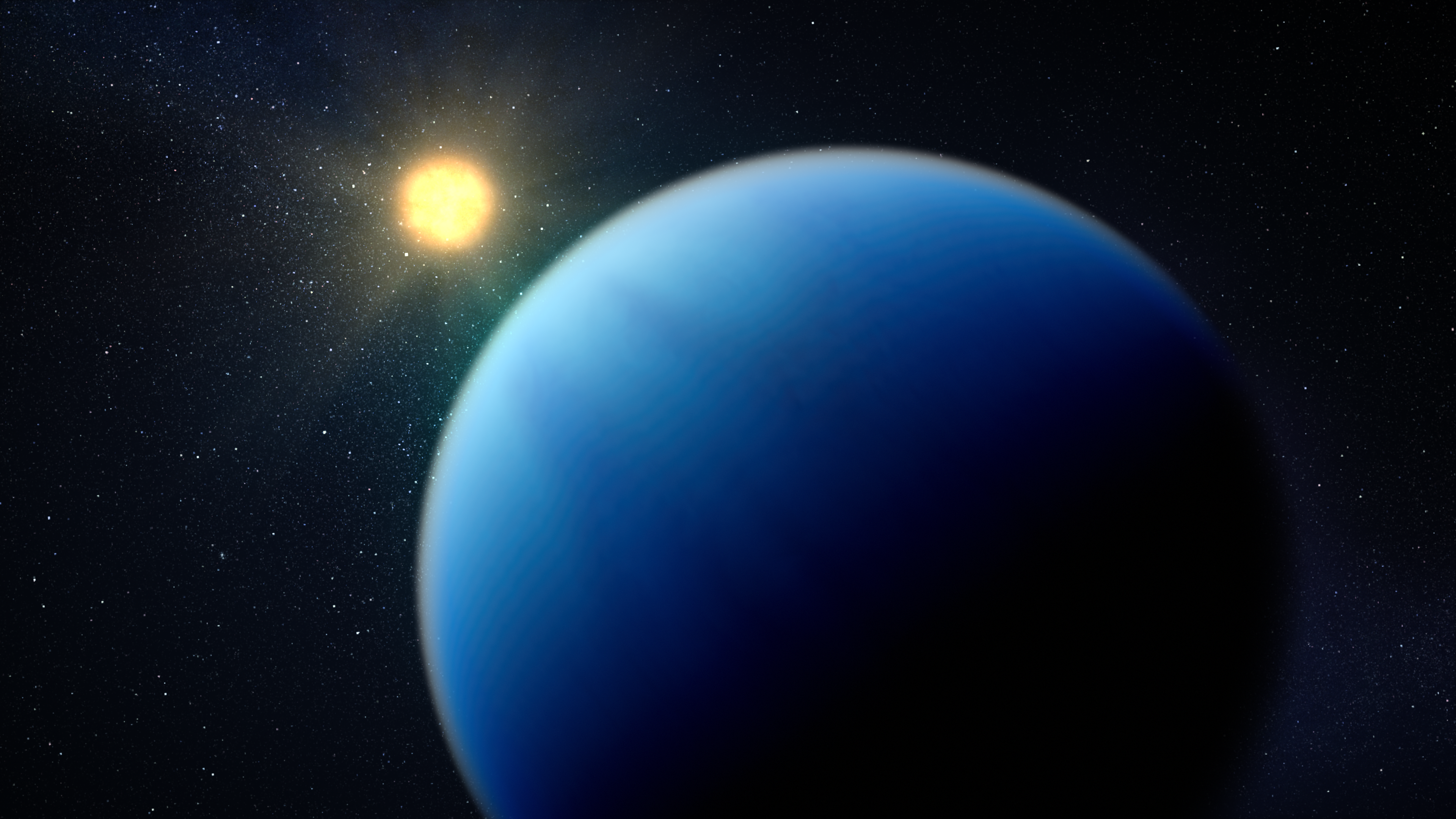
Exoplanet TOI-421 b and Its Star (Illustration)
Illustration of what exoplanet TOI-421 b might look like. TOI-421 b is a hot sub-Neptune-sized exoplanet orbiting a Sun-like star roughly 244 light-years from Earth. TOI-421 b is thought to have a clear atmosphere free of haze and clouds. This illustration is based on our...
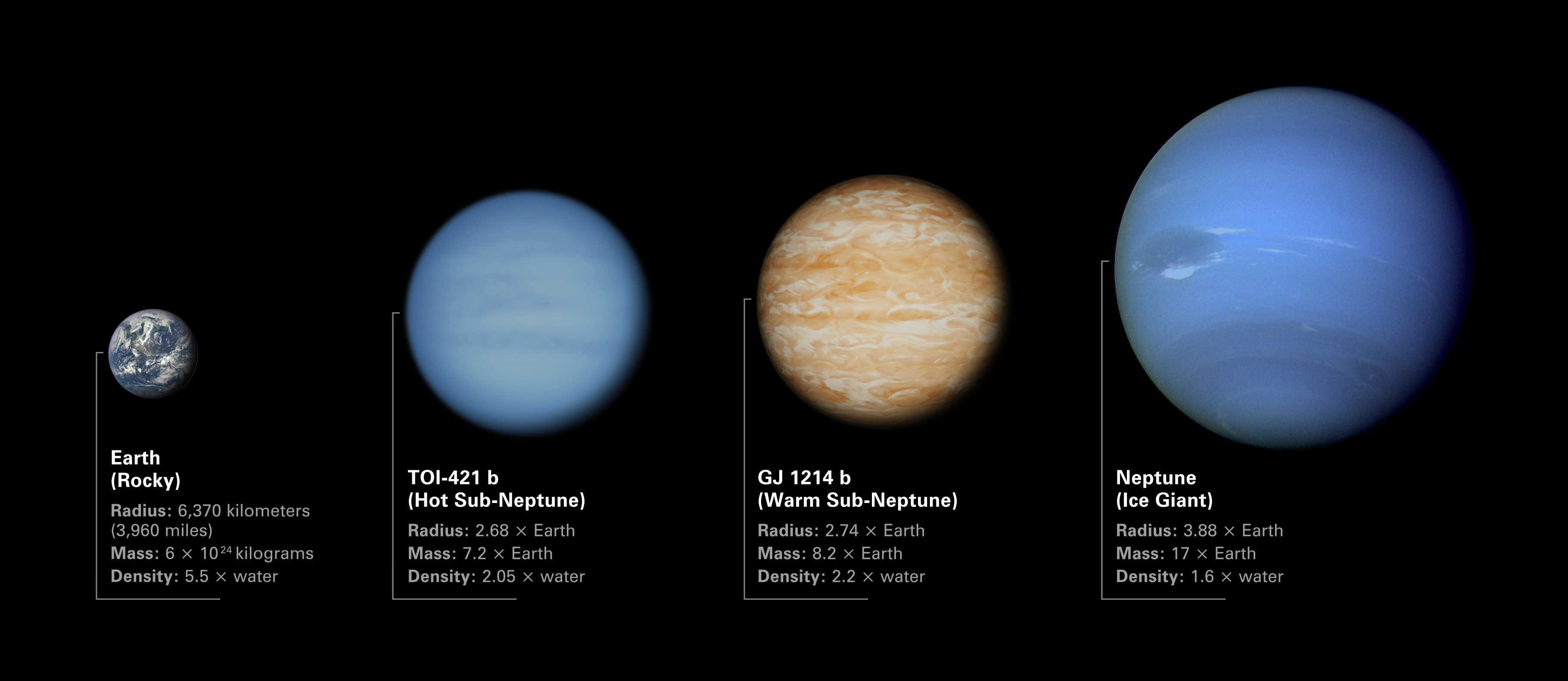

Comparison of TOI-421 b and GJ 1214 b to Earth and Neptune
Illustration comparing the sizes of sub-Neptune exoplanets TOI-421 b and GJ 1214 b to Earth and Neptune. Both TOI-421 b and GJ 1214 b are in between Earth and Neptune in terms of radius, mass, and density. The low densities of the two exoplanets indicates that they must have...
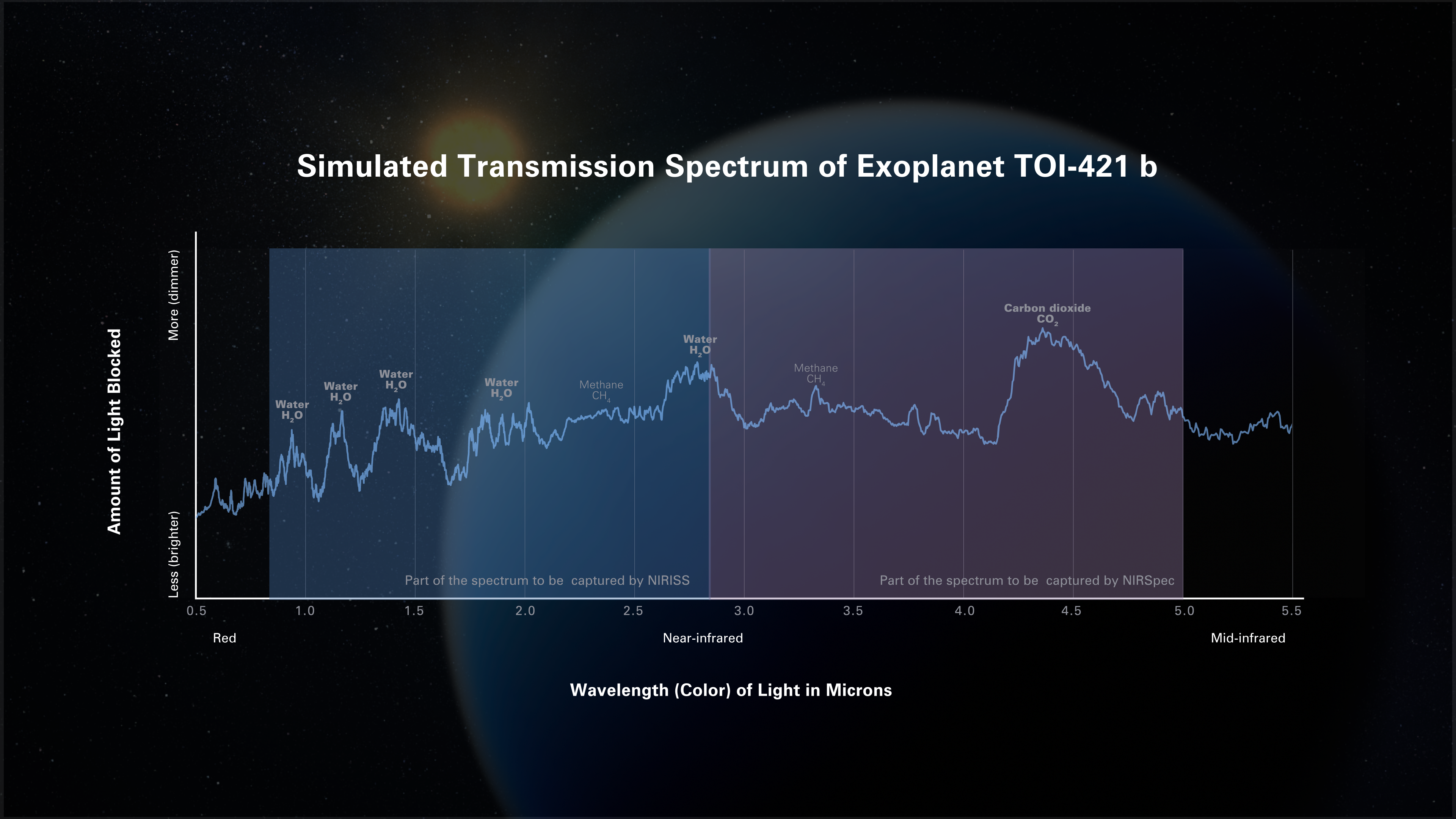
Simulated Transmission Spectrum of Exoplanet TOI-421 b
Possible transmission spectrum of the hot sub-Neptune exoplanet TOI-421 b. A transmission spectrum shows the amount of starlight of different wavelengths (colors) that is blocked by the planet’s atmosphere. Researchers use computer models to predict what spectra will look like...
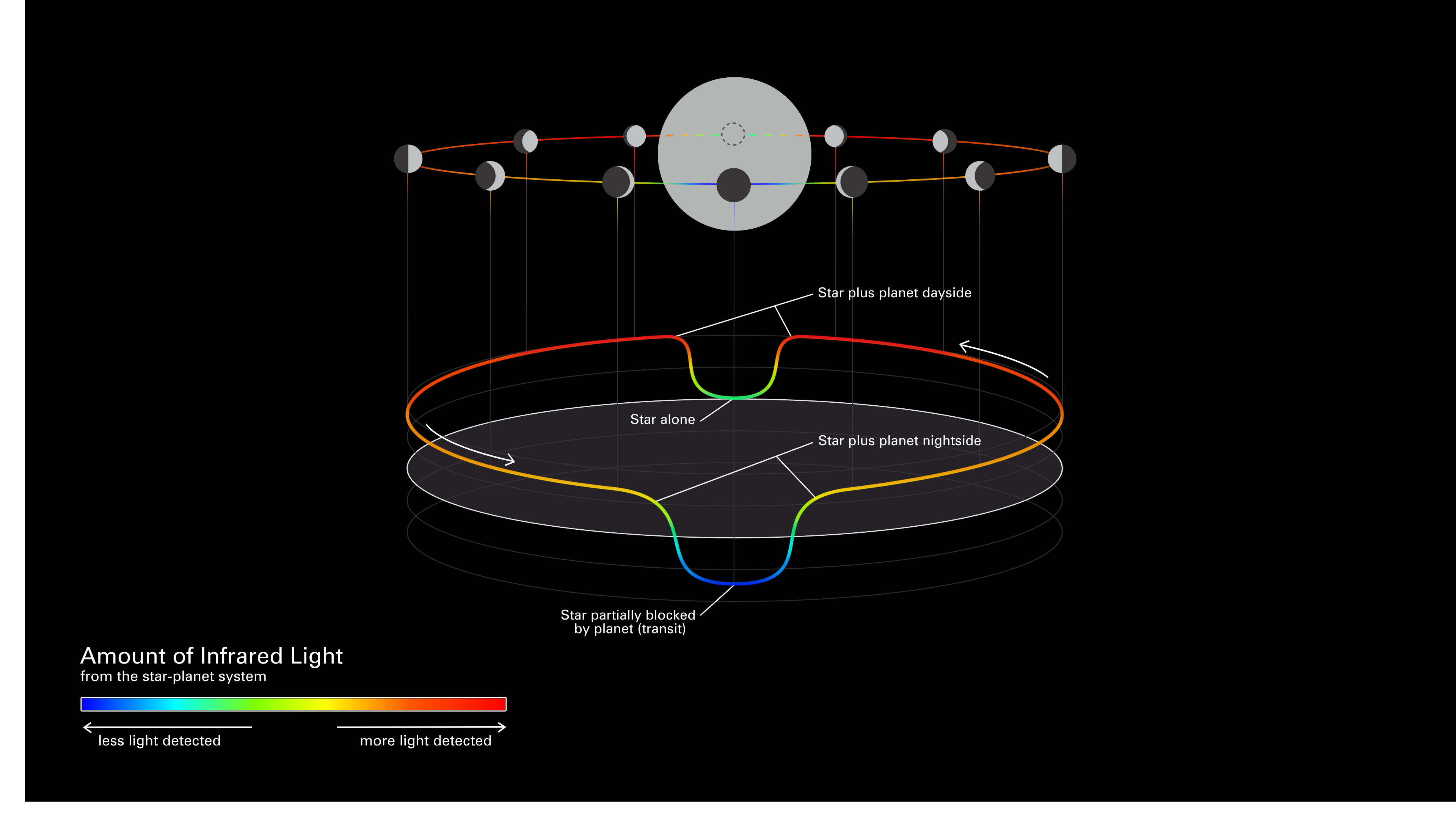
Diagram of an Exoplanet Phase Curve
This simplified diagram of an exoplanet phase curve shows the change in total brightness of a star–planet system as the planet orbits the star. The system looks brighter when more of the lit side of the planet is facing the telescope (full phase), and dimmer when more of the...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Dani Player (STScI)




























