1 min read
Giant Star in Dwarf Galaxy Sextans A (Spectrum)
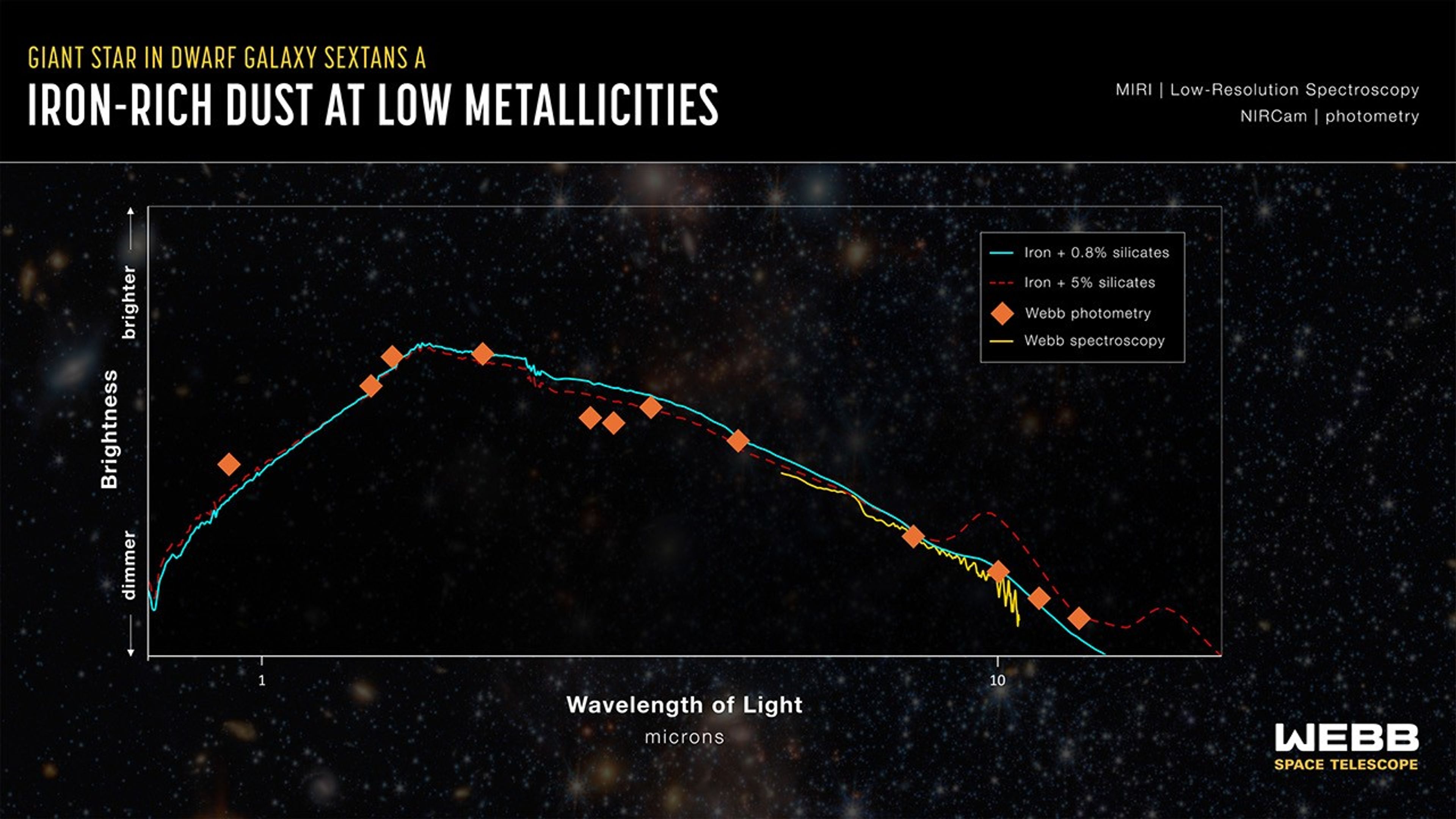
This graph shows a spectrum of a giant star in the Sextans A galaxy at the very end of its evolution, called an Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) star. It displays the amounts of near- and mid-infrared light detected from the star by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope at different wavelengths.
The cyan line and red dashed line are best-fit models for the spectrum that would contain mostly silicate-free dust and dust containing at least 5% silicates, respectively. The Webb data, shown as a yellow line and orange triangles, align most closely with nearly silicate-free dust, most notably in the 10 micron wavelength region of the spectrum.
- Release DateJanuary 6, 2026
- Science ReleaseNASA Webb Finds Early-Universe Analog’s Unexpected Talent for Making Dust
- CreditIllustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Related Images & Videos

Sextans A PAHs Pull-out (NIRCam and MIRI Image)
Images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope of the dwarf galaxy Sextans A reveal polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), large carbon-based molecules that can be a signifier of star formation. The inset at the top right zooms in on those PAHs, which are represented in green.
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov