1 min read
Multiwavelength View of Centaurus A (Hubble, Spitzer, Chandra, VLA)

Centaurus A sports a warped central disk of gas and dust, which is evidence of a past collision and merger with another galaxy. It also has an active galactic nucleus that periodically emits jets. It is the fifth brightest galaxy in the sky and only about 13 million light-years away from Earth, making it an ideal target to study an active galactic nucleus – a supermassive black hole emitting jets and winds – with NASA's upcoming James Webb Space Telescope. This image was made using data from the Hubble, Spitzer, and Chandra space telescopes and the Very Large Array.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.13h 25m 28s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-43° 1′ 9″
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Centaurus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.13 million light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is 24 arcmin across. (about 147,000 light years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.CXC>ACIS, HST, SPITZER>IRAC, VLA
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Centaurus A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Elliptical/Active Galaxy
- Release DateMarch 17, 2021
- Science ReleasePeering into a Galaxy’s Dusty Core to Study an Active Supermassive Black Hole
- CreditImage: NASA, CXC, SAO, Astrophotography by Rolf Olsen, NASA-JPL, Caltech, NRAO, AUI, NSF, UOH, M. Hardcastle

X-ray (Purple); Optical (Blue, Red); Infrared (Red), Radio (Red)
Related Images & Videos
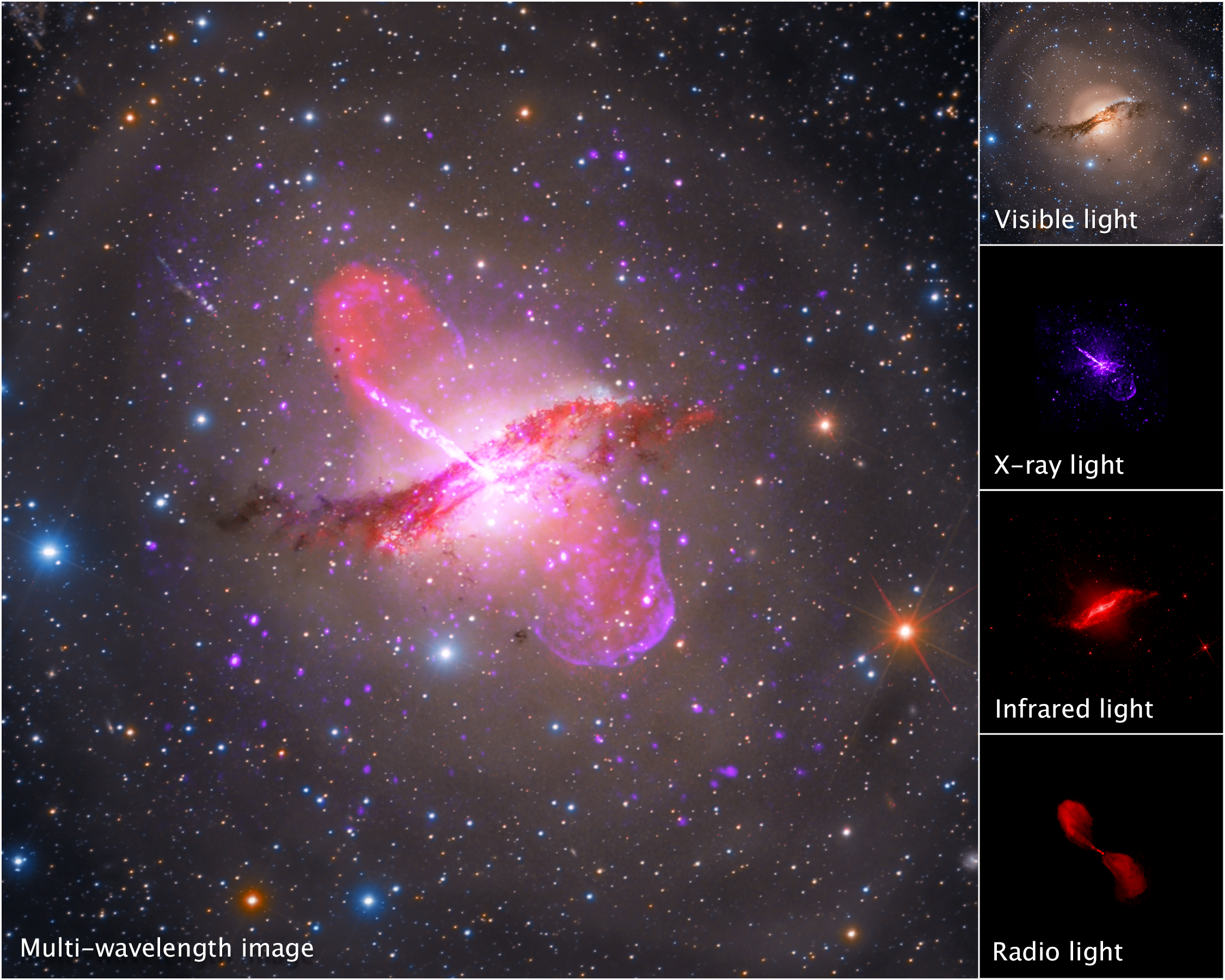
Centaurus A in Different Wavelengths (Hubble, Spitzer, Chandra, VLA)
A breakdown of a multi-wavelength image of galaxy Centaurus A shows light collected by Hubble (visible), Chandra (X-ray), Spitzer (infrared), and the Very Large Array (radio). Centaurus A's dusty core is apparent in visible light, but its jets are best viewed in X-ray and radio...
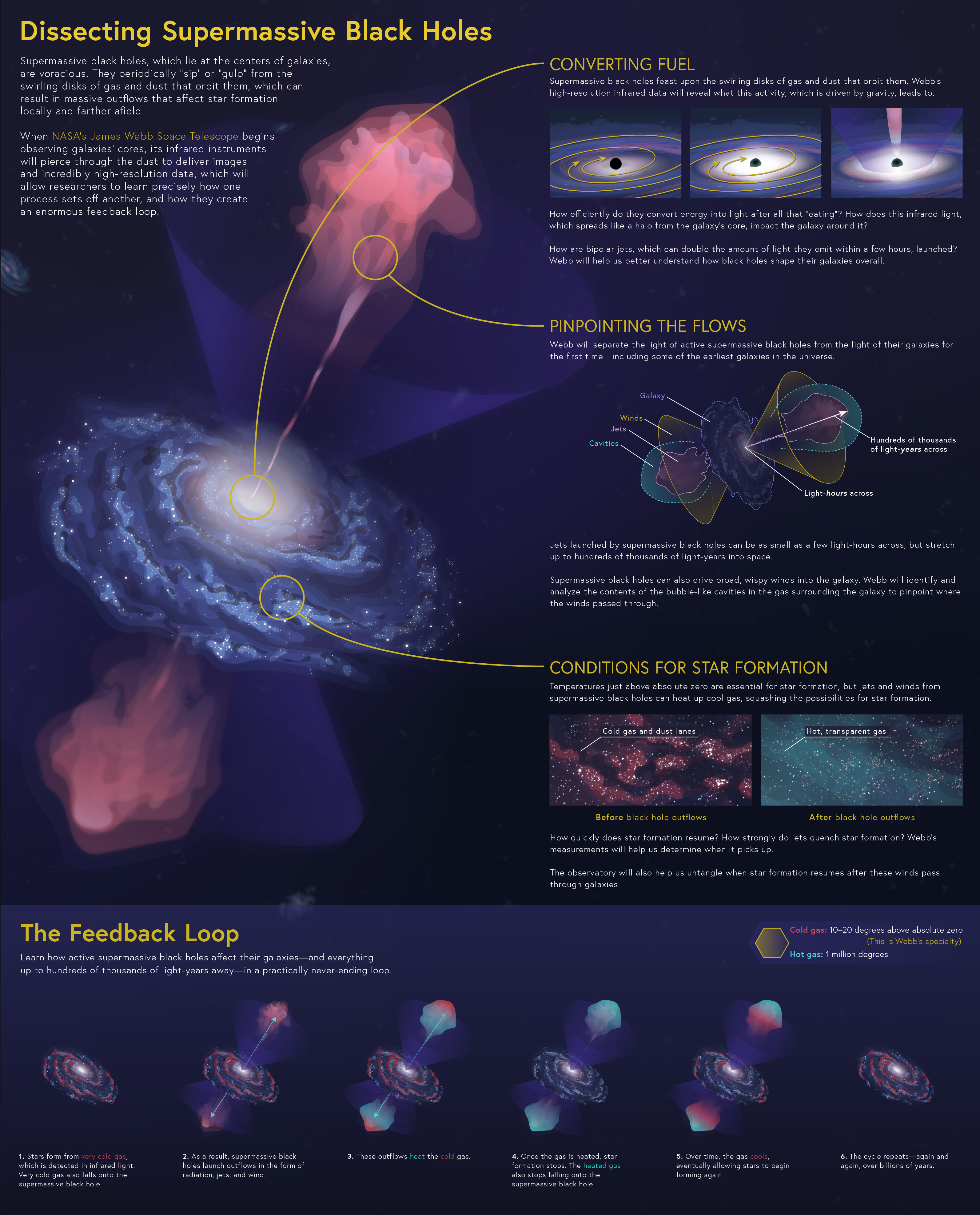
Dissecting Supermassive Black Holes
Supermassive black holes, which lie at the centers of galaxies, are voracious. They periodically “sip” or “gulp” from the swirling disks of gas and dust that orbit them, which can result in massive outflows that affect star formation locally and farther afield. When NASA’s James...

Dissecting Supermassive Black Holes: The Feedback Loop
Watch as the jets and winds from a supermassive black hole affect its host galaxy—and the space hundreds of thousands of light-years away over millions of years. Explore our image and video collections to find more videos in this series, including " Pinpointing the Flows ,” and...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, CXC, SAO, Astrophotography by Rolf Olsen, NASA-JPL, Caltech, NRAO, AUI, NSF, UOH, M. Hardcastle





























