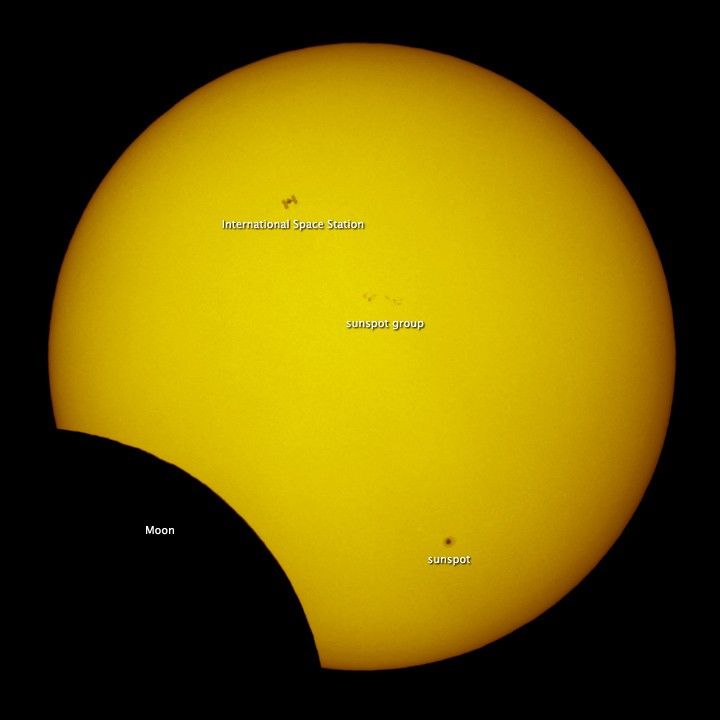
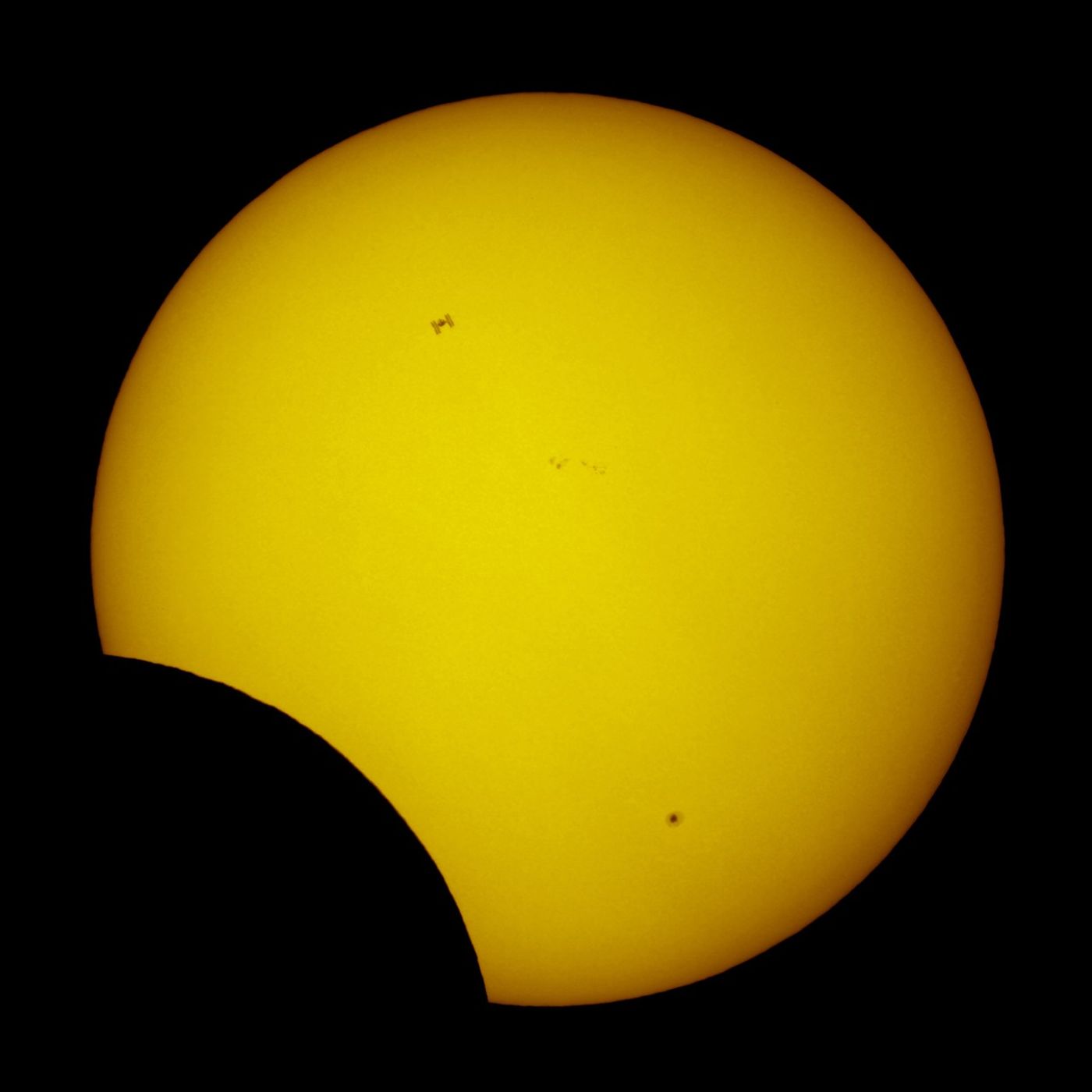
While the Moon was busy passing between the Sun and Earth on January 4 for the first eclipse of 2011, the International Space Station (ISS) made its own pass between them. Powered by the Sun, orbiting the Earth, a satellite like the Moon—the ISS is an expression of how humanity is connected to and keeping an eye on all three bodies.
This photo was taken by astrophotographer Thierry Legault, who set up near Muscat, Oman, to capture this view at 1:09 p.m. local time (9:09 UTC) on January 4, 2011. He had to shoot quickly, as the transit of the space station through the field of view lasted just 0.86 seconds. The ISS was moving at 7.8 kilometers per second (17,000 mph).
The disk of the Sun is partly obscured on the lower left, as the Moon is 20 minutes past the maximum eclipse. The edges of the image are black because the light filters are strong, like a welder's mask, to prevent sunlight from damaging the camera.
The partial solar eclipse was the first of four in 2011, with others coming on June 1, July 1, and November 25. Eclipses occur when the new Moon passes in the line between Sun and Earth. Because the Moon’s orbit is inclined about 5 degrees to Earth’s, the Moon and its shadow often pass above or below the plane of the Earth. Because both orbits are elliptical, the size and shape of eclipses changes slightly with each event.
The image also includes sunspots 1140 (bottom) and 1142 (center), part of solar cycle 24, which should reach maximum in the next two years. Each spot was only producing relatively weak B-class solar flares on the day of the eclipse. Sunspots, flares, and great eruptions known as coronal mass ejections will become much more common in coming months, and each produces its own type of disturbance on Earth, including radio noise, auroras, and satellite and electric power disruptions. The solar cycle also plays a role in Earth's climate.
As for the space station, it is passing overhead regularly, as it makes 15 to 16 circuits around the Earth each day. It can pass through your local skies anywhere from one to three times per day, depending on your latitude and the path of the orbit. You don't have much time to spot it, though, as it crosses the sky in just a few minutes.
“Most people don’t know that, under the right conditions, you can use a telescope to actually see the shuttle and ISS this clearly,” writes astronomer Phil Plait, “and even then it ain’t easy.”
References & Resources
Photograph courtesy of Thierry Legault. Caption by Michael Carlowicz.