Editor’s Note: Today’s caption is the answer to Earth Observatory’s June 2015 image puzzler.
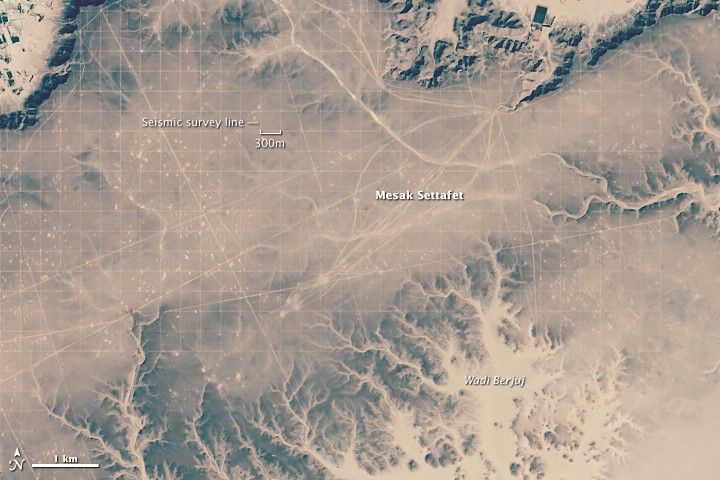
The Messak Settafet plateau rises sharply from the desert in southern Libya. The wedge of dark, erosion-resistant sandstone separates the Ubari sand sea to the north and Murzuq sand sea to the south. In contrast to those sandy areas, the surface of Messak Settafet has been scoured by winds, with just a little sand and a packed layer of gravel and rock known as hamada at the surface. With annual precipitation of little more 20 millimeters (0.8 inches), the plateau is quite hostile to life. Most of the plants and animals that survive on it are found in the dried stream valleys—wadi—that cut the edges of the plateau.
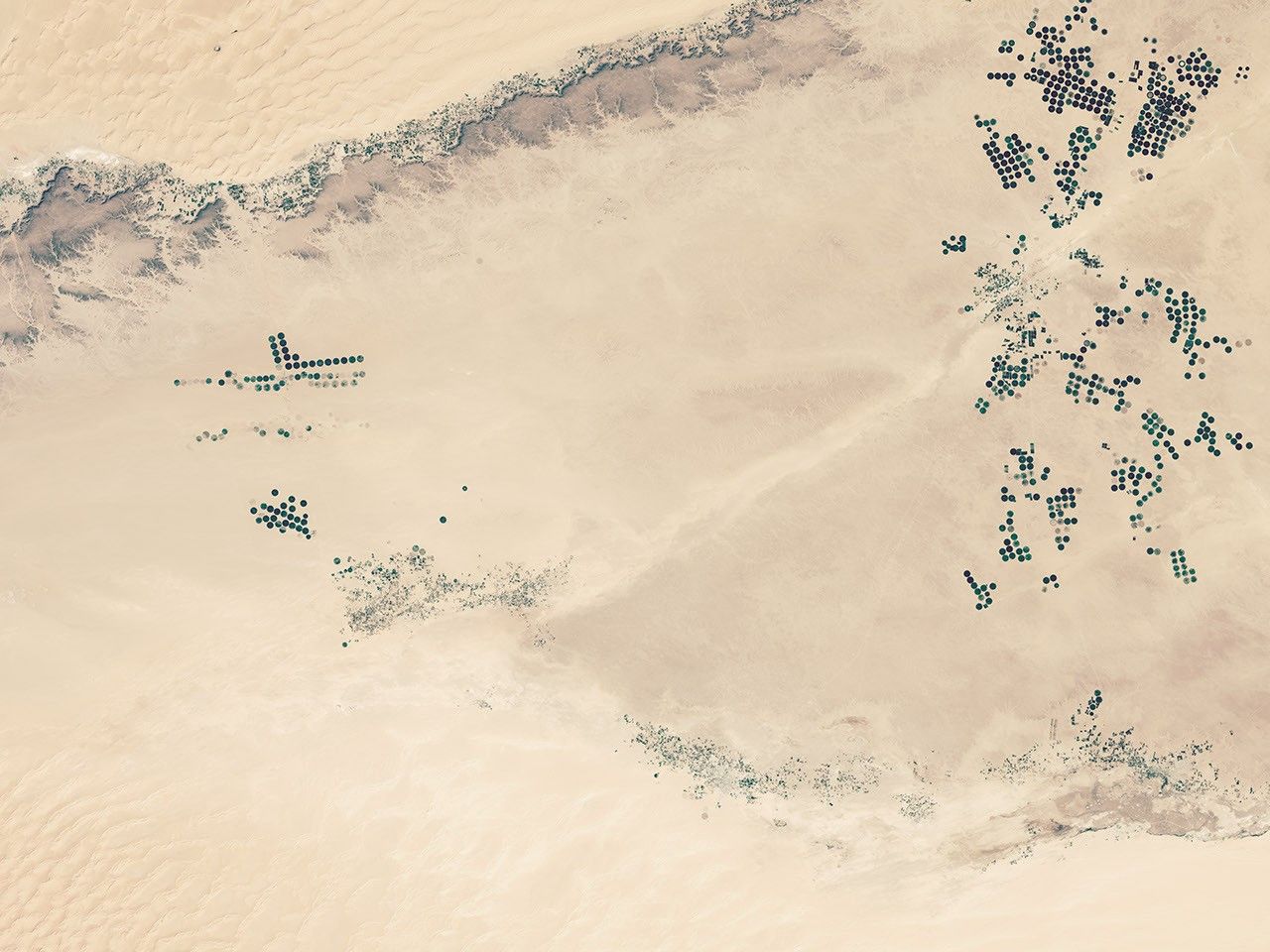
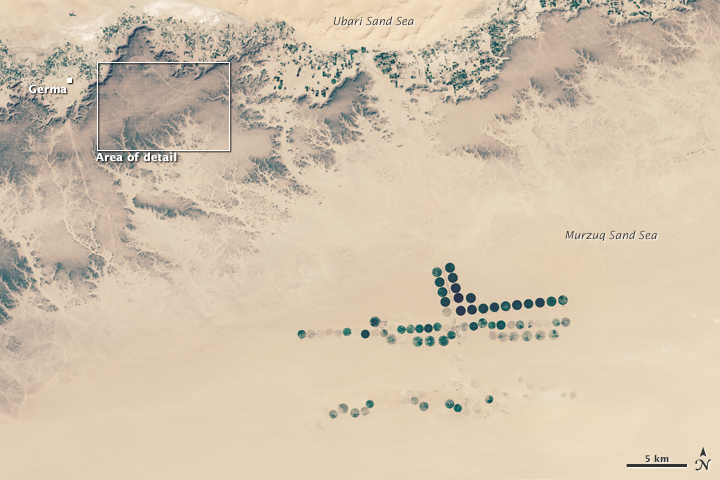
Aside from the occasional adventurous tourist, few people can be found on the plateau. Yet as these satellite images show, humans have left a distinctive mark on it. The grid patterns are truck tracks along seismic survey lines, showing where Occidental Petroleum Corporation explored this patch for oil in 2008. The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired the image on February 11, 2015. The lower image shows a broader view, including parts of the Ubari and Murzug sand seas. The green specks just north of the plateau and the cluster of green circles to the south are irrigated areas.
The seismic survey lines were probably created by several vibroseis or “thumper” trucks. These heavy trucks press vibrating metal plates against the surface to produce seismic waves. By deploying other sensors that detect how underground rock layers reflect these waves, geologists can determine where to drill for oil or gas. Laying the seismic lines down in systematic grid patterns makes it possible for companies to generate three-dimensional seismic images rather than just two-dimensional “slices.”
“Although the surface of the Messak is all rocks, the sub-surface is dust. As the seismic trucks and heavy vehicles drove, the rocks got buried in the dust and the process created the network of roads you see in the satellite imagery,” explained Marta Lahr, an archaeologist at the University of Cambridge. Lahr was part of a team that surveyed the area for evidence of prehistoric stone tools—which are quite common on the plateau—before the oil exploration occurred and potentially damaged the artifacts. “I imagine that, with time, the tracks will disappear as the dust blows away and the now buried rocks are exposed again, but I do not know how long it will take.”
The photograph below, taken by Lahr while conducting field work on the plateau, offers a view of the tracks from the ground.
References & Resources
- EarthSky (2013, June 12) Bob Hardage: Using seismic technologies in oil and gas exploration. Accessed June 26, 2015.
- Foley, R. & Lahr, M. (2015, March 11) Lithic Landscapes: Early Human Impact from Stone Tool Production on the Central Saharan Environment. PLoS ONE, 10 (3).
- Kröpelin, S. (2002) Damage to Natural and Cultural Heritage by Petroleum Exploration and Desert Tourism in the Messak Settafet (Central Sahara, Southwest Libya). Geo-Sciences in Northern Africa.
- Maurin Media (2012, September 7) Vibroseis Trucks For Geophysical Prospectin. Accessed June 26, 2015.
- Oil and Gas Lawyer How do seismic surveys work? Accessed June 26, 2015.
- Rig Zone How Does Land Seismic Work? Accessed June 26, 2015.
- University of Cambridge (2015, March 11) Saharan ‘carpet of tools’ is the earliest known man-made landscape. Accessed June 26, 2015.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey . Caption by Adam Voiland, with assistance from Marta Lahr (University of Cambridge) and David Mattingly (University of Leiceister). Congratulations to Stefano for being the first to answer the puzzler correctly.