Since their discovery in the late 1700s, astronomers have learned that planetary nebulae, or the expanding shell of glowing gas expelled by a low-intermediate mass star late in its life, can come in all shapes and sizes. Most planetary nebula present as circular, elliptical, or bi-polar, but some stray from the norm, as seen in new high-resolution images of planetary nebulae by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
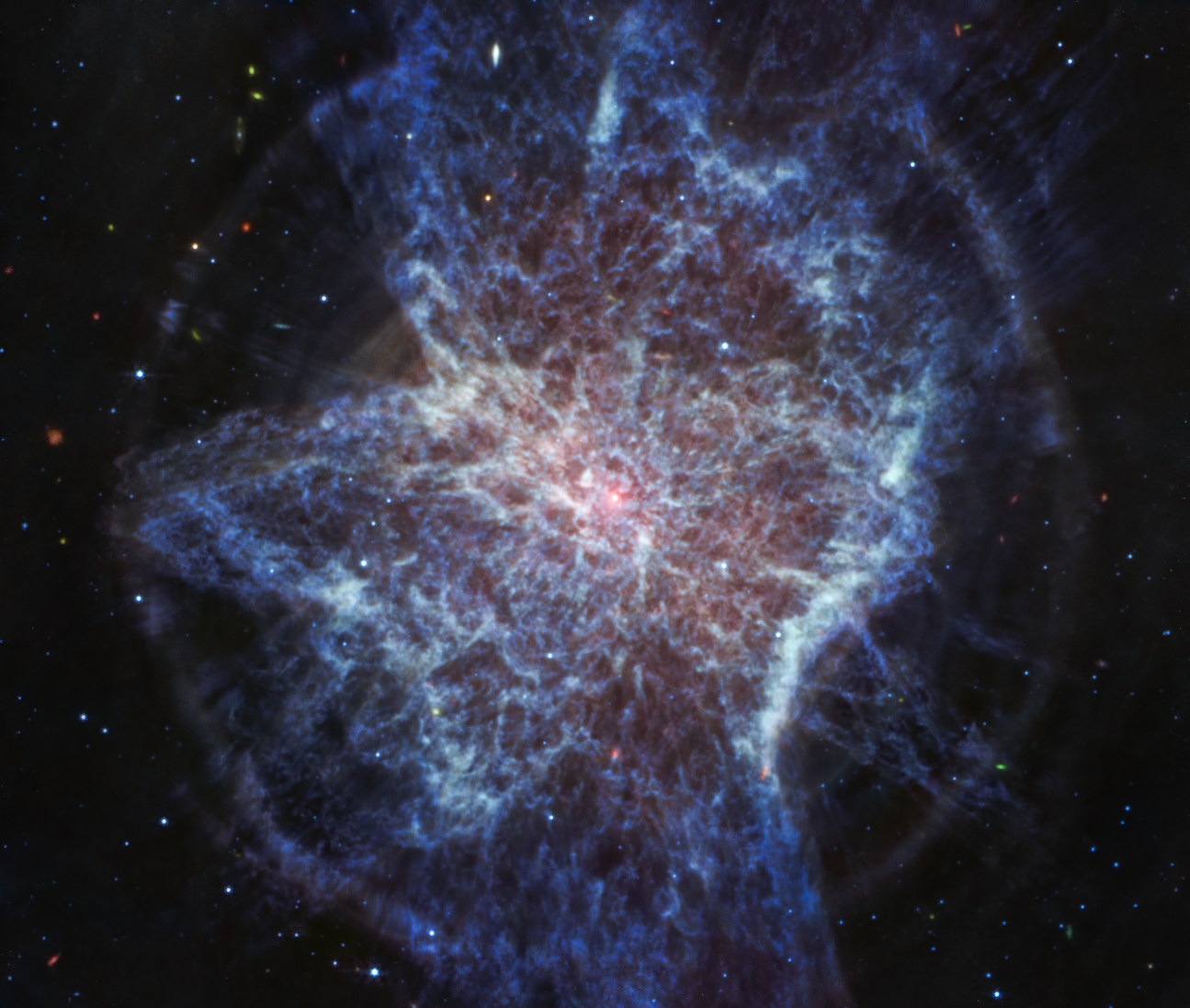
Webb’s newest look at planetary nebula NGC 6072 in the near- and mid-infrared shows what may appear as a very messy scene resembling splattered paint. However, the unusual, asymmetrical appearance hints at more complicated mechanisms underway, as the star central to the scene approaches the very final stages of its life and expels shells of material, losing up to 80 percent of its mass. Astronomers are using Webb to study planetary nebulae to learn more about the full life cycle of stars and how they impact their surrounding environments.
Image: NGC 6072 (NIRCam Image)
First, taking a look at the image from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), it’s readily apparent that this nebula is multi-polar. This means there are several different elliptical outflows jetting out either way from the center, one from 11 o’clock to 5 o’clock, another from 1 o’clock to 7 o’clock, and possibly a third from 12 o’clock to 6 o’clock. The outflows may compress material as they go, resulting in a disk seen perpendicular to it.
Astronomers say this is evidence that there are likely at least two stars at the center of this scene. Specifically, a companion star is interacting with an aging star that had already begun to shed some of its outer layers of gas and dust.
The central region of the planetary nebula glows from the hot stellar core, seen as a light blue hue in near-infrared light. The dark orange material, which is made up of gas and dust, follows pockets or open areas that appear dark blue. This clumpiness could be created when dense molecular clouds formed while being shielded from hot radiation from the central star. There could also be a time element at play. Over thousands of years, inner fast winds could be ploughing through the halo cast off from the main star when it first started to lose mass.
Image: NGC 6072 (MIRI Image)
The longer wavelengths captured by Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) are highlighting dust, revealing the star researchers suspect could be central to this scene. It appears as a small pinkish-whitish dot in this image.
Webb’s look in the mid-infrared wavelengths also reveals concentric rings expanding from the central region, the most obvious circling just past the edges of the lobes.
This may be additional evidence of a secondary star at the center of the scene hidden from our view. The secondary star, as it circles repeatedly around the original star, could have carved out rings of material in a bullseye pattern as the main star was expelling mass during an earlier stage of its life.
The rings may also hint at some kind of pulsation that resulted in gas or dust being expelled uniformly in all directions separated by say, thousands of years.
The red areas in NIRCam and blue areas in MIRI both trace cool molecular gas (likely molecular hydrogen) while central regions trace hot ionized gas.
As the star at the center of a planetary nebula cools and fades, the nebula will gradually dissipate into the interstellar medium — contributing enriched material that helps form new stars and planetary systems, now containing those heavier elements.
Webb’s imaging of NGC 6072 opens the door to studying how the planetary nebulae with more complex shapes contribute to this process.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
Downloads & Related Information
The following sections contain links to download this article's images and videos in all available resolutions followed by related information links, media contacts, and if available, research paper and Spanish translation links.